Answer
advertisement
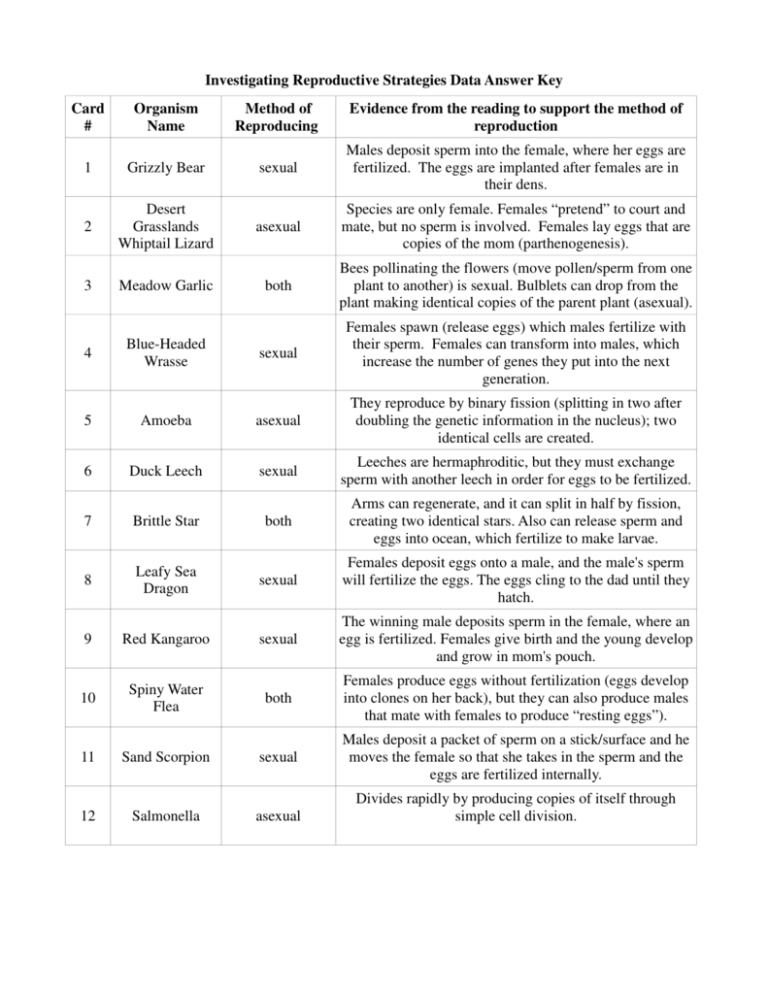
Investigating Reproductive Strategies Data Answer Key Card # Organism Name Method of Reproducing Evidence from the reading to support the method of reproduction sexual Males deposit sperm into the female, where her eggs are fertilized. The eggs are implanted after females are in their dens. 1 Grizzly Bear 2 Desert Grasslands Whiptail Lizard asexual Species are only female. Females “pretend” to court and mate, but no sperm is involved. Females lay eggs that are copies of the mom (parthenogenesis). 3 Meadow Garlic both Bees pollinating the flowers (move pollen/sperm from one plant to another) is sexual. Bulblets can drop from the plant making identical copies of the parent plant (asexual). 4 Blue-Headed Wrasse sexual Females spawn (release eggs) which males fertilize with their sperm. Females can transform into males, which increase the number of genes they put into the next generation. 5 Amoeba asexual They reproduce by binary fission (splitting in two after doubling the genetic information in the nucleus); two identical cells are created. 6 Duck Leech sexual Leeches are hermaphroditic, but they must exchange sperm with another leech in order for eggs to be fertilized. 7 Brittle Star both Arms can regenerate, and it can split in half by fission, creating two identical stars. Also can release sperm and eggs into ocean, which fertilize to make larvae. 8 Leafy Sea Dragon sexual Females deposit eggs onto a male, and the male's sperm will fertilize the eggs. The eggs cling to the dad until they hatch. sexual The winning male deposits sperm in the female, where an egg is fertilized. Females give birth and the young develop and grow in mom's pouch. 9 Red Kangaroo 10 Spiny Water Flea both Females produce eggs without fertilization (eggs develop into clones on her back), but they can also produce males that mate with females to produce “resting eggs”). 11 Sand Scorpion sexual Males deposit a packet of sperm on a stick/surface and he moves the female so that she takes in the sperm and the eggs are fertilized internally. 12 Salmonella asexual Divides rapidly by producing copies of itself through simple cell division.