ATP & ADP - GarzScience!
advertisement
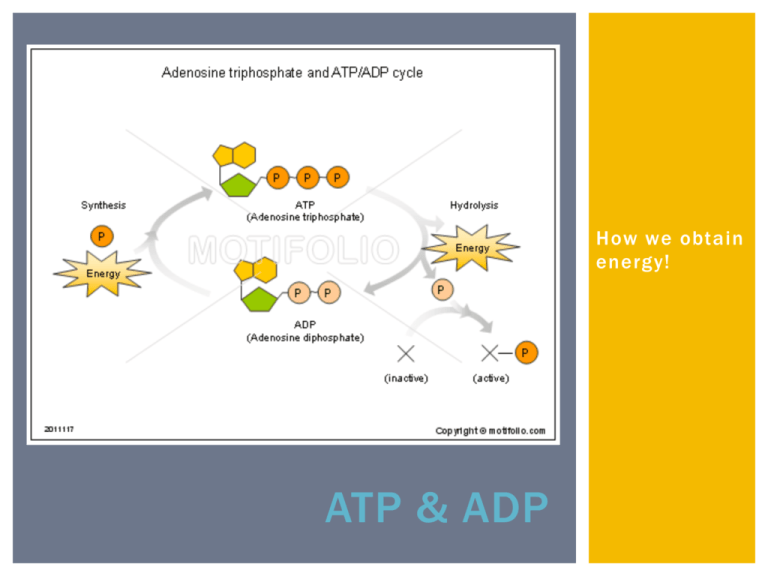
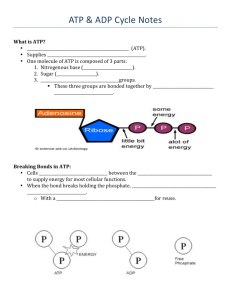
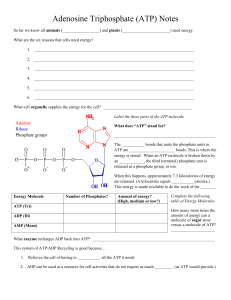
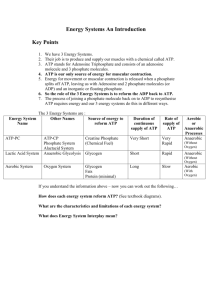
How we obtain energy! ATP & ADP WHAT IS ATP? ¡ Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) ¡ Supplies energy to ALL cells ¡ One molecule of ATP is composed of 3 parts: 1. Nitrogenous base (Adenosine) 2. Sugar (Ribose) 3. Three phosphate groups § These three groups are bonded together by HIGH ENERGY BONDS BREAKING BONDS IN ATP ¡ Cells break the bonds between the 3 phosphates to supply energy for most cellular functions ¡ When the bond breaks holding the phosphate, ATP is turned into ADP § With a phosphate available for reuse USE AND RELEASE OF ENERGY ¡ When any of the phosphate bonds are broken or formed, energy is involved § Energy is released when a phosphate is removed from ATP § Energy is used when phosphate is attached to the molecule ¡ To constantly supply the cell with energy, the ADP is recycled creating more ATP, which carries much more energy than ADP ATP – ADP CYCLE ¡ To supply cells with energy, a “high energy” bond in ATP is broken. § ADP is formed and a phosphate is released back into the cytoplasm § ATP à ADP + phosphate + energy ¡ ADP becomes ATP when a free phosphate attaches to the ADP molecule § The energy required to attach the phosphate to ADP is much less than the energy produced when the phosphate bond is broken. § ADP + phosphate + energy à ATP ANIMATIONS ¡ ATP/ADP Cycle Animation THE ENERGY STORAGE PROCESS 1. The ADP molecule is waiting for a “food molecule” § Lipid, carbohydrate, or protein 2. When the food molecule is broken down an extra phosphate attaches to the ADP to form ATP, which can then be used as energy in the cell. 3. When ATP is broken down and stripped, the energy is then transferred to be used for the creation of macromolecules (large molecules) like proteins. ¡ Ever y time you eat food, or take in energy, you are essentially “recharging” your ADP by adding extra Phosphates in order to form ATP FOOD / FUEL MOLECULES ¡ Carbohydrates: § Molecules most commonly broken down to produce ATP § Remember “immediate energy”??? § From one glucose molecule you can form up to 36 ATP! ¡ Lipids: § Store the MOST energy § These are fats! § 80% of energy in the body is from lipids § From one triglyceride molecule you can form up to 146 ATP! ¡ Proteins: § Least likely molecule to be broken down to make ATP § Amino acids are not usually needed for energy § If used, they produce the same amount of energy as a carbohydrate.