ATP & ADP Cycle Notes
advertisement

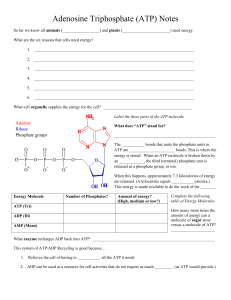
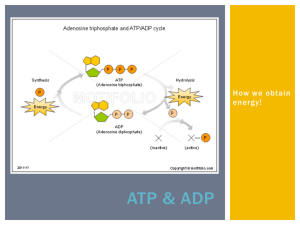
ATP & ADP Cycle Notes What is ATP? • ____________________________________________________ (ATP). • Supplies __________________________________________________. • One molecule of ATP is composed of 3 parts: 1. Nitrogenous base (_________________________). 2. Sugar (____________________). 3. ________________________________________groups. § These three groups are bonded together by _______________________________ ______________________________. Breaking Bonds in ATP: • Cells ___________________________________ between the ______________________________________ to supply energy for most cellular functions. • When the bond breaks holding the phosphate, ___________________________________________ ______________________________. o With a __________________________________________________for reuse. Use and Release of Energy: • When any of the phosphate bonds are broken or formed, ______________________________. o Energy is _________________________________________________________________________ from ATP. o Energy is ___________________________________________________________________________ to the molecule. • To constantly supply the cell with energy, the ________________________________________ ________________________________________, which carries much more energy than ADP. ATP – ADP Cycle: • To supply cells with energy, a ______________________________________________________________. o ADP is formed and a phosphate is released back into the cytoplasm. o ________________________________________________________________________________. • ADP becomes ATP when a __________________________________________________________________ molecule. o The energy required to attach the phosphate to ADP is much less than the energy produced when the phosphate bond is broken. o ________________________________________________________________________________. The Energy Storage Process: • The ADP molecule is ______________________________________________________________________. o Lipid, carbohydrate, or protein. • When the food molecule is _________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________, which can then be used as energy in the cell. • When ____________________________________________________________and stripped, the ____________________________________________________________ to be used for the creation of macromolecules (large molecules) like proteins. • Every time you eat food, or take in energy, you are essentially “re-­‐charging” your ADP by adding extra Phosphates in order to form ATP. Food / Fuel Molecules: • Carbohydrates: o Molecules most commonly broken down to produce ATP. o Remember “immediate energy”??? o From one glucose molecule you _____________________________________________! • Lipids: o Store the MOST energy. o These are fats! o 80% of energy in the body is from lipids. o From one triglyceride molecule you _____________________________________________! • Proteins: o Least likely molecule to be broken down to make ATP. o Amino acids are not usually needed for energy. o If used, they produce the same amount of energy as a carbohydrate.