Anatomy of Human Muscles
advertisement

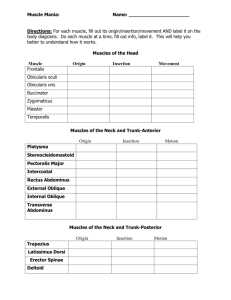
Anatomy of Human Muscles PURPOSE: To develop skill in identifying muscle names and locations relative to other regional structures. To determine origin, insertion and principle action of muscles through analysis of muscle location, shape and arrangement. PROCEDURE Skeletal muscles, mainly under voluntary control are the muscles of most interest in gross anatomy for many reasons (muscle building, body contouring, sports training to name a few). They are attached at each end – either to bone or connective tissue – mostly via tendons (cordlike dense regular connective tissue) and aponeuroses (wide thin tendons). The origin is the attachment to the stationary bone which serves as the stronghold. The insertion is the attachment to the movable bone where the force applied by muscle contraction causes a specific movement. Each muscle attachment is relative with respect to body movements. In two different muscles, these attachments may be reversed. Muscle names are generally descriptive using one or more of seven criteria: 1. the location of the muscle 2. the relative size of the muscle 3. the shape of the muscle 4. the muscle origin and insertion 5. the direction of the muscle fascicles (bundles of muscle fibers), i.e. rectus (along a longitudinal axis), transverse (perpendicular to a longitudinal axis), oblique (across a longitudinal axis at an angle different than perpendicular) 6. the arrangement of fascicles within the muscle (pennate, orbicularis) 7. the principle action of the muscle The action of a muscle is the movement caused by that muscles contraction. Generally the movements possible are the following (16 mostly paired opposites): flexion or extension adduction or abduction medial rotation or lateral rotation supination or pronation inversion or eversion elevation or depression protrusion (protraction) or retrusion (retraction) opposition 1 circumduction Review these actions from your Anatomy 35 text and notes. Using Gilroy’s Atlas of Anatomy and Clemente’s Anatomy Dissector as your 1st references, and your Anatomy 35 Human Anatomy text as your 2nd reference, you will describe the position of each muscle listed in the following tables relative to other regional structures. Other references will be available in the cadaver lab to assist you in this research. Each student will fill in the following characteristics found in the heading of each table: origin, insertion, (Principle) Action, and Primary Nerve. By following each muscle to its attachments on a prosected cadaver, you will also see the origin and insertion. The principle action of the muscle can be determined by looking at the position, shape, angle, and attachments. Verify all of your findings with your references. Students will also be expected to determine the major blood vessels supplying the muscles listed. Prompts for this information can be found following the data tables. I. MUSCLES OF THE HEAD AND NECK 1. Muscles of Facial Expression Muscle Occipitofrontalis (frontal belly) Origin Insertion Action Primary Nerve Occipitofrontalis (occipital belly) Orbicularis oculi Levator labii superioris Zygomaticus major/minor Buccinator Orbicularis oris Levator anguli oris Depressor anguli oris Depressor labii inferioris Mentalis Platysma Risorius 2 Describe the major blood vessels that both supply and drain the muscles described above. Details should at least include secondary branches from the aorta and major tributaries to the internal and/or external jugular vein. 2. Muscles of Mastication Muscle Temporalis Masseter Origin Insertion Action Primary Nerve 3. Muscles of the Submandibular Region Muscle Digastric – anterior belly Digastric – posterior belly Stylohyoid Mylohyoid Geniohyoid Origin Insertion Action Primary Nerve Describe the major blood vessels that both supply and drain the muscles described above. Details should at least include secondary branches from the aorta and major tributaries to the internal and/or external jugular vein. 3 4. Muscles of the Anterior Neck Muscle Sternocleidomastoid Omohyoid (superior belly) Omohyoid (inferior belly) Sternohyoid Origin Insertion Action Primary Nerve Sternothyroid Thyrohyoid NOTE: 1. The anterior triangle of the neck has several subdivisions. What are these subdivisions? Identify the muscles from the previous tables that are found in each of these subdivisions. What other important structures are found in these subdivisions? Describe the major blood vessels that both supply and drain the muscles described above. Details should at least include secondary branches from the aorta and major tributaries to the internal and/or external jugular vein. 4 II. Muscles of the Trunk 1. Muscles of the Thoracic Wall Muscle Anterior Scalene Posterior Scalene Middle Scalene External intercostal Internal intercostal Origin Insertion Action Primary Nerve Describe the major blood vessels that both supply and drain the muscles described above. Details should at least include secondary branches from the aorta and major tributaries to the azygous vein and/or superior vena cava. 2. Intrinsic Back Muscles Muscle Splenius capitus Erector Spinae: a. Iliocostalis b. Longissimus c. Spinalis Origin Insertion Action Primary Nerve NOTE: What are the 3 portions of the semispinalis muscle? Describe the major blood vessels that both supply and drain the muscles described above. Details should at least include secondary branches from the aorta and major tributaries to the azygous vein. 5 3. Muscles of the Posterior Abdominal Wall Muscle Diaphragm Origin Insertion Action Primary Nerve Quadratus lumborum Psoas major Iliacus Describe the major blood vessels that both supply and drain the muscles described above. Details should at least include secondary branches from the aorta and major tributaries to the azygous and/or inferior vena cava. 4. Muscles of Anterolateral Abdominal Wall Muscle External oblique Internal oblique Transversus abdominis Rectus abdominis Origin Insertion Action Primary Nerve Describe the major blood vessels that both supply and drain the muscles described above. Details should at least include secondary branches from the aorta and major tributaries to the azygous and/or inferior vena cava. 6 II. Muscles of the Upper Limb 1. Anterior Muscles of the Shoulder and Arm Muscle Pectoralis major Pectoralis minor Subclavius Serratus anterior Subscapularis Biceps brachii Coracobrachialis Brachialis Triceps brachii Origin Insertion Action Primary Nerve Describe the major blood vessels that both supply and drain the muscles described above. Details should at least include secondary branches from the aorta and major tributaries to the superior vena cava. 7 2. Posterior Muscles of the Shoulder and Arm Muscle Trapezius Latissimus dorsi Levator scapulae Rhomboid minor Rhomboid major Deltoid Supraspinatus Infraspinatus Teres minor Teres major Origin Insertion Action Primary Nerve NOTE: What is the rotator cuff? Which of these muscles compose the rotator cuff? Describe the major blood vessels that both supply and drain the muscles described above. Details should at least include secondary branches from the aorta and major tributaries to the azygous and/or vena cavae. 8 3. Anterior Forearm Muscles Muscle Pronator teres Flexor carpi radialis Palmaris longus Flexor carpi ulnaris Flexor digitorum superficialis Flexor digitorum profundus Flexor pollicus longus Pronator quadratus Origin Insertion Action Primary Nerve Describe the major blood vessels that both supply and drain the muscles described above. Details should at least include secondary branches from the aorta and major tributaries to the superior vena cava. 9 4. Posterior Forearm Muscles Muscle Brachioradialis Extensor carpi radialis longus Extensor carpi radialis brevis Extensor digitorum Extensor digiti minimi Extensor carpi ulnaris Anconeus Supinator Abductor pollicis longus Extensor pollicis longus Extensor pollicis brevis Origin Insertion Action Primary Nerve Describe the major blood vessels that both supply and drain the muscles described above. Details should at least include secondary branches from the aorta and major tributaries to the superior vena cava. 10 5. Intrinsic Hand Muscles Muscle Abductor pollicis brevis Flexor pollicis brevis Opponens pollicis Palmaris brevis Abductor digiti minimi Flexor digiti minimi Opponens digiti minimi Origin Insertion Action Primary Nerve Describe the major blood vessels that both supply and drain the muscles described above. Details should at least include secondary branches from the aorta and major tributaries to the superior vena cava. 11 IV. Muscles of the Lower Limb 1. Anterior Thigh Muscles Muscle Psoas major Iliacus Tensor fascia latae Sartorius Origin Insertion Action Primary Nerve Rectus femoris Vastus lateralis Vastus medialis Vastus intermedius Describe the major blood vessels that both supply and drain the muscles described above. Details should at least include secondary branches from the aorta and major tributaries to the azygous vein and/or the inferior vena cava. 12 2. Medial Thigh Muscles Muscle Pectineus Origin Insertion Action Primary Nerve Adductor longus Adductor magnus Gracilis Describe the major blood vessels that both supply and drain the muscles described above. Details should at least include secondary branches from the aorta and major tributaries to the inferior vena cava. 13 3. Muscles of the Gluteal Region Muscle Gluteus maximus Gluteus medius Gluteus minimus Piriformis Origin Insertion Action Primary Nerve Gemellus superior Gemellus inferior Quadratus femoris Describe the major blood vessels that both supply and drain the muscles described above. Details should at least include secondary branches from the aorta and major tributaries to the inferior vena cava. 14 4. Posterior Thigh Muscles Muscle Semitendinosus Semimembranosus Biceps femoris Origin Insertion Action Primary Nerve Describe the major blood vessels that both supply and drain the muscles described above. Details should at least include secondary branches from the aorta and major tributaries to the inferior vena cava. 15 5. Muscles of the Anterolateral Leg Muscle Tibialis anterior Extensor hallucis longus Extensor digitorum longus Fibularis longus Fibularis brevis Origin Insertion Action Primary Nerve Describe the major blood vessels that both supply and drain the muscles described above. Details should at least include secondary branches from the aorta and major tributaries to the inferior vena cava. 16 6. Muscles of the Posterior Leg Muscle Gastrocnemius Soleus Plantaris Popliteus Flexor hallicus longus Flexor digitorum longus Tibialis posterior Origin Insertion Action Primary Nerve Describe the major blood vessels that both supply and drain the muscles described above. Details should at least include secondary branches from the aorta and major tributaries to the inferior vena cava. 17 7. Muscles in Sole of Foot Muscle Abductor hallucis Flexor digitorum brevis Flexor digitorum longus Origin Insertion Action Primary Nerve Abductor digiti minimi Quadratus plantae Flexor hallucis brevis Adductor hallucis Flexor digiti minimi brevis Extensor digitorum brevis 18