Module 3 – Unit 2: Reading & Vocabulary
advertisement

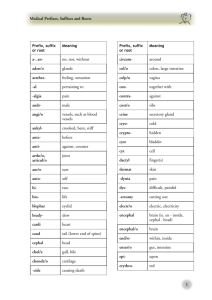
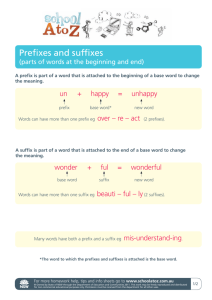
Module 3 – Unit 2: Reading & Vocabulary Building Medical Vocabulary Think About It What does “epigastric” mean? Can you divide it into three parts: prefix, root, and suffix? Do you know what each part means? Read the following statements and decide if each is True (T) or False (F), based on your knowledge of medical terminology. If possible, think of an example to support your answer. 1. Medical terms can be made up of as many as four parts. T F 2. T F 3. The main part of a medical word is called the “root. ” Linking vowels help make words easier to pronounce. T F 4. A medical term can have only one root. T F 5. The most common vowel used for linking is “i.” T F Read the following passage about medical terminology. After you finish reading, check your answers above. How Does Medical Terminology Work? Most medical terms can be broken down into one or more word parts. For simplicity in explanation, we will say that there are four possible word parts, and any given medical term may contain one, some, or all of these parts. We will classify these word parts as (1) roots, (2) prefixes, (3) suffixes, and (4) linking or combining vowels. An example of a word with three of the above parts is the medical term "pericarditis", which means "inflammation of the outer layer of the heart". Pericarditis can be divided into three parts: peri - card – itis Once divided into its essential parts, pericarditis can be translated: the prefix "peri" translates to "surrounding", the root "card" translates to "heart", and the suffix "itis" translates to "inflammation". Hence, pericarditis is an inflammation of the area English Health Train: Module 3 – Unit 2 Copyright 2006 San Francisco Welcome Back Center surrounding the heart, or an inflammation of the outer layer of the heart, anatomically known as the pericardium. Medical terms always consist of at least one "root", although they may contain more. The root of a word is that part which contains the essential meaning of the word. An example of this was seen above in the term "pericarditis". The root of the word – “card” - refers to the heart, so any prefix or suffix added to the root (card) will only function to add to the specificity of that word. An example of this would be the prefix "brady", which means "slow". If "brady" is added to the root "card", the term "bradycard" - which roughly means "slow heart" - is created. Then, if the suffix "ia" - which means "abnormal state" – is added to "bradycard", the medical term "bradycardia" is formed. The translation of bradycardia (brady - card - ia) is slow - heart - abnormal state, or the abnormal state of a slow heart rate. As was discussed above, a medical term must have at least one root, but does not have to have a prefix and/or a suffix. An example of this is the term "sternocleidomastoid", which is a muscle that has attachments at the sternum, the clavicle, and the mastoid. The term sternocleidomastoid can be divided into three parts (three roots, in this case): stern - o - cleid - o - mastoid. Notice that there are vowels between the three roots. These are "linking or combining vowels", which serve to make a term easier to pronounce. The vowel used most of the time is "o", but other vowels such as "i" and "a" are also used. Combining vowels are often used between roots and suffixes or roots and other roots, but they are not used between prefixes and roots. Adapted from: University of Minnesota. http://www.gen.umn.edu/faculty_staff/jensen/1135/medterms/mterm2.html. Retrieved 11/02/04. Scanning Medical Texts: Roots, Prefixes, and Suffixes 1. Scan the short passage and underline the six words below in the passage. 2. Divide the words into roots, prefixes, suffixes, and linking vowels. 3. Decide on the meaning of each word by checking the meanings of the root, prefix, and suffix in the charts that follow the passage. asymptomatic lymphadenopathy neurological conjunctivitis myaligias myocarditis English Health Train: Module 3 – Unit 2 Copyright 2006 San Francisco Welcome Back Center Clinical Manifestations of West Nile Virus Infection Most persons with West Nile virus infection are asymptomatic. Approximately one in five infected persons develops a mild, febrile illness, and approximately one in 150 infected persons manifests neurological symptoms. Symptomatic illness generally follows an incubation period of two to 15 days. The majority of symptomatic patients have a self-limited, febrile illness, occasionally with headache, nausea, and vomiting. Chills, myalgias, and overwhelming fatigue are common complaints. Some patients may have lymphadenopathy and conjunctivitis. Occasionally, patients develop a brief myocarditis associated with West Nile virus infection. Adapted from: The Journal of the American Medical Association. http:// jama.ama-assn.org/. Retrieved 11/03/04. ROOT card, cardi coron cyt ceph gastr cerebr myo, myco neur neph oste lymph vaso derm arthr, articul gengiv conjunctiv adeno MEANING heart heart cell head stomach brain muscle nerve kidney bone lymph vessel skin joint gum conjunctiva gland English Health Train: Module 3 – Unit 2 Copyright 2006 San Francisco Welcome Back Center PREFIX aepiendoperiprecontrabihypoabambihemibradyhydro mono SUFFIX -ac -al -ar -ary -eal -ial -ic -ical -ous -ectomy -otomy -itis -oma -oscopy, -scopic -plegia -emia -opathy -algia MEANING without on, upon, over within surrounding before against double under, too little away from both sides half slow water one MEANING Pertaining to (adjective) surgical removal, excision cutting, incision inflammation tumor, swelling visual examination paralysis related to blood disease pain English Health Train: Module 3 – Unit 2 Copyright 2006 San Francisco Welcome Back Center