PRINCIPLES OF ACCOUNTING ACCOUNTING EQUATION DEBITS
advertisement

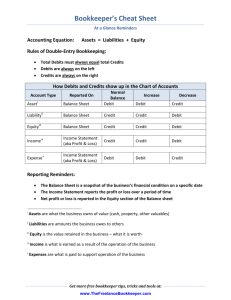
PRINCIPLES OF ACCOUNTING Preparing Journal Entries Created 2005 by Michael Worthington Elizabeth City State University ACCOUNTING EQUATION Assets = Liabilities + Capital ­ Drawing + Revenues ­ Expenses (add “Drawing” & “Expenses” to both sides) Assets + Expenses + Drawing = Liabilities + Capital + Revenues Assets, __________ and Expenses are all on the debit (left) side of the equals sign Liabilities, Capital and Revenues are all on the credit (right) side of the equals sign DEBITS (Dr) AND CREDITS (Cr) Assets + Drawing + Expenses = Liabilities + Capital + Revenue Assets, Drawing and Expenses are on the debit (left) side of the equals sign, so the normal __________ of these accounts is DEBIT = Liabilities, Capital and Revenue are all on the credit (right) side of the equals sign, so their normal balance is CREDIT Post to the normal balance side to increase an account Post to the opposite side to ____________ an account 1 Balancing the Books Whatever is done to one side of the accounting equation must also be done to the other side to keep the equation in ______________. So if one account is debited, then the other account must be credited Or if one account is credited, then the other account must be debited DOUBLE­ENTRY BOOKKEEPING Whatever is done to the debit (left) side of the accounting equation must also be done to the credit (_________) side of the equation. So all journal entries must include at least two accounts (one debited and one credited), but there may be three or more accounts. Every journal entry must include at least one debit and one _______ The total of the debited amounts must equal the total of the credited amounts Then the entry is “in balance” Look for Key Words Transactions always affect at least two accounts Key words point to those accounts Identifying key _________ unlocks the solution “Cash”, “Paid”, “Payment”, “Deposit” or “Check” are key words that identify cash If no key words point to cash, then cash is NOT involved 2 CA$H Debit CASH when a payment is received to increase cash which has a __________ normal balance Credit CASH when a payment is made to reduce the balance of cash Debit _______ for deposits “Debit” and “Deposit” both begin with the letter “D” Credit CASH when a check is issued to pay bill “Credit” and “Check” both begin with the letter “C” On Open Account But most businesses do offer credit to customers In fact, transactions between businesses are almost always on __________ The words “on account” means that the transaction is charged to a revolving credit account, which is similar to a credit card Key words “on account”, “billed” or “invoice” point to either Accounts Receivable (AR) or ____________ Payable (AP) AP or AR If the firm will eventually have to PAY for the purchase, use _____________ Payable (AP) But if the firm will eventually RECEIVE a payment from a customer, use Accounts Receivable (AR) 3 DATE ACCOUNT TITLE DEBIT CREDIT DATE ACCOUNT TITLE DEBIT CREDIT “Dread” Accounting D R “Debit” is abbreviated “DR” E xpenses A ssets D rawing or ___________ Expenses, Assets and Drawing or Dividends accounts have debit normal balances – all other accounts have normal credit balances Summary Every journal entry must include at least one debit account and one credit account Total Debits = Total Credits Key terms indicate names of the accounts 4