U7 review aca key
advertisement

/
Name ,/
Date
/ ?
.......
Period
/"
Physics i Unit 7 Test Review
By the time we finish this unit and all related activities you shouRd be
abme to:
1. Make the distinction between energy storage and transfer.
2. Be able to recognize and identify energy storage mechanisms: gravitational, kinetic, elastic,
internal, etc.
3. Recognize the universal, fundamental nature of energy as opposed to different forms of energy.
4. View friction or deformation as a mechanism for dissipating energy. (Eint)
5. Recognize and identify modes of energy transfer: worldng, heating, radiating.
6. Use representational tools (pie charts, bar graphs & energy flow diagrams) to analyze a system in
terms of energy storage and transfer.
7. Analyze a system of energy interactions appropriately, according to any system designation.
8. Determine the quantity of energy transferred between the various accounts (kinetic, elastic
potential, gravitational potential, and internal energy) during an interaction.
9. Explain working as:
energy transfer to/from system via external force
W = FAx (both parallel to motion)
10. Define power as rate of energy usage; calculate power in watts.
11. Remember how to convert weight to mass and vice versa. Also, know how to convert units.
AE=W+Q+R
Eel = ½ RAx2
Ek = ½ mY2
Eg = mgAy
W - FIIAX
r, = AE / At = W / at
(746 W = 1 hp)
*** The following review is not all inclusNe, just a sampling of problems to practice.
Study your notes, worksheets, etc. as well as this review.***
Review Questions
Describe the energy changes as you lift a book atconstant speed:
/
.
....
/_
/
j
;
A 3 kg mass is held 4 m above the ground. What is the approximate gravitational energy of the
mass with respect to the ground?
?-
.
......
..,
/
It takes 10000 J to push a car 20 m across a road. Assuming that the push is in the same
direction as the displacement, what is the size of the force on the car?
/
J ., _
, .
.............
.
.... .
....... ._
,J
.....
,''J ,,, ,.
/ ........................................
Which requires more energy: lifting a 50 kg sack vertically 2 meters or lifting a 25 kg sack
vertically 4 meters?
,
A spring-loaded dart gun fires a sharp dart straight up which then sticks in the ceiling. (The
ceiling now has a hole in it. = deformation)
In it iai
System Circle
Ek Eg Eel
..........
I
ÿ---4
?.'
#
....
Fin al
ÿ. Ek Eg Eel Eÿt
•
12
t
!
ÿ -
i- ....
2
6. A swing is observed to rise to a maximum height of 1.5 m above its lowest point. How fast is it
going at its lowest point? (Ignore friction and air resistance)
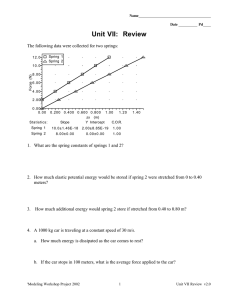
7. How much elastic potential energy would be stored if a spring, with a spring constant of .20,
were stretched from 0 to 0.40 meters?
J
,
........
/
....
/
/':,/.
A 1000 kg car is traveling at a constant speed of 30 m/s.
a. How much energy is dissipated as the car comes to rest?
b. If the car stops in 100 meters, what is the average force applied to the car?
/
,
"
.;!!, '/ h
:'),, :.;
,,'"
" ,
................................
i
i
I
9. A 1.5 kg kitten jumps down from a 2.0 meter high fence.
a. What is the kitten's AEg?
/
+ ] ,/1
.! '
I
/
,.
S
b. What will be the kitten's speed when it reaches the ground?
10. A 50g dart rests up against a spring that has been compressed 0.050 meters.
a. If 1.25 J of work were required to compress the spring, what is its spring constant?
,
.; /..! x
;
li
b. What is the maximum velocity of the dart after the spring has transferred its energy to it?
i
,
/"
...........
[. // {, ,"
/ ;??' +
,/
;
7
,; ............................. ;, ...... {
c. Fill in the energy bar graphs for the above situation when the dart reaches a height of 1 m.
•
I n I ial
System Circle
? Ek Eg
i
4. Ik II lel lÿt
"ÿ" ÿi-
.........
i
)
i
F i n al
;,!, !i;i'.: ,.,
i
,,,"
t
+