right to self-determination
advertisement

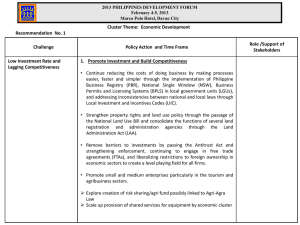
RIGHT TO SELF-DETERMINATION • International customary law, as • A nation is a • The term peoples defined in the UN Charter, the historically should include International Covenant on constituted, stable Economic, Social and Cultural nations/nationalities, national minorities, community of people, Rights, and the International Covenant on Civil and Political ethnic minorities, formed on the basis of Rights, affirms the right of all and indigenous a common language, peoples to self determination, peoples, all of whom territory, economic by virtue of which they freely have the inalienable life, and psychological determine their political right to self make-up manifested status and freely pursue their determination. in a common culture. economic, social and cultural development. Sultanate of Sulu Sultanate of Maguindanao Pat a Pangampong ku Ranaw HISTORY OF RESISTANCE The 1896 Revolution helped in stopping Spanish expansionism to Mindanao. HISTORY OF COLONIALISM Kiram-Bates Treaty (1899) “FRIENDLY RELATIONS” Treaty of Paris 1898 •Respect Religion and Tradition •Recognition of Religious and Political Authority Monthly Allowance: •$250 for the sultan •$60-$75 for each datu In exhange ----- x Moro weapons x Piracy & Slavery COLONIAL INJUSTICE SYSTEMATIC LAND GRABBING •Land Registration Act of 1902 (Torrens Titling vs Adat – no ownership) •Philippine Bill of 1902 (16 has vs 1,634 has) •Public Land Act of 1903 – unregistered become Public Lands BUD DAJO MASSACRE (1906) - More than 1,000 Moro men, women and children dead BUD BAGSAK MASSACRE (SULU, 1913) Americanization of Bangsamoro June 1903 – MORO PROVINCE (Zamboanga, Lanao, Cotabato, Davao & Sulu) • Kategorya ng mga probinsya -“sibilisado” at “di-sibilisado.” 1912 – Pensionado: 200 Moro youth schooled in America •Undermined authority of Imam and Shariah •Imposed Cedula vs. drakat (zakat) of agama. •Prohibition of Madrasah-- Arabic & Qur’an •1911- prohibition of weapons •Agricultural Corporations – more than 1,634 hectares •1913 to 1917 - Seven Agricultural Colonies: Pikit, Silik, Paidu Pulangi, Pagalungam, Glan (Cotabato Province) & Momungan Lanao FOREIGN-OWNED PLANTATIONS AND RESETTLEMENTS YEAR NAME OF COMPANY HECTARES 1906 Davao P lanters Association (Abaca, Coconut, Rubber) 1910 159 European and American Plantations 1926 Del Monte Corp (Bukidnon) (Pineapple) 1,024 sa simula-- 7,922 expansion 1914 Weyerhauser (Maguindanao) - Logging concession 72,000 has 1929 Goodyear Tire and Rubber Co (Zamboanga) –rubber plantation 1937 Dole (Cotabato)- Pineapple Findlay Miller (Lanao) logging Lianga Bay Logging (Surigao) 1,000,000 (?) 39,489 7,750 6,818 • 1st Cotabato Valley – Christians 16 has vs. 8 has Moro families • 1930 – 17 agricultural settlements in Cotabato, Davao, Zamboanga del Sur, Agusan & Lanao • Plantations for Export , mining and logging. Coconut and sugar mills • Cooper Act of 1902 • Act 2254 & Act 2280 1913 • Public Land Act No. 2874 of 1919 • Commonwealth Act No. 141 of 1936 • Act No. 141 ACT No. 141 (American Administration) • 4 has for Moros • 24 for Christians • 1,024 has for corporations In 1935, a group of Maranaw datus petitioned for a separate state from President Roosevelt. Even earlier, some prominent Sulu sultans also made a "declaration of rights and purposes" asking for some independence for Sulu. 1946 – Republic of the Philippines 1948-1960 roughly 1.2 million Filipinos migrated to Mindanao NATIONAL OPPRESSION JABIDDAH MASSACRE • • • • MAR Settlements Five-Year Plan State-Directed Settlement Policy (1975-1980) 1960-1970, estimated 362,000 people migrated to Mindanao • Tawi-Tawi Balimbing-Bongao 1975 – another 106,912 • Sulu Panamao-Talipao-Patikul hectares for public resettlement • Basilan Lamitan-Sumisip-Maluso in Mindanao 1977 Philippine Ministry of • ZdlNorte Liloy-Salug-Sindangan Agrarian Reform (MAR) - 44 settlement w/ area 734,825 ha • Lanao del Norte and Sur and 49,898 settler families • Cotabato Province March 18, 1968 28-64 Moro youth were killed in Corregidor Island due to OPLAN MERDEKA 1969 – 1972 : Creation of MNLF December 23, 1976 – TRIPOLI AGREEMENT, essentially giving up independence and settling for autonomy in Maguindanao and Sulu (MINSUPALA) July 1977- 1986: AFP’s “search and destroy" but Moro defended territories 1971 to 1976 of military operations, 50,000 to 80,000 died and 300,000 displaced 1983 – MNLF split between Misuari and Hashim Salamat Post Martial Law: 1986-1991 1987 Constitution --Creation of the ARMM; integration of some Sharia laws in the fields of customary and marriage laws; GRP formula for peace negotiation is US and Japan’s recipe for intervention: Demobilization Disarmament Reintegration/Rehabilitation 1996 GRP-MNLF FINAL PEACE AGREEMENT, Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao and Southern Philippines Council for Peace and Development; SZOPAD RA 9094 Expanded ARMM March 1984 - Ustadz Hashim Salamat publicly announced the split from Misauri-led MNLF and established the Moro Islamic Liberation Front (MILF) Four Point Program: •Islamization •Strengthen organization •Military Strength •Self Reliance 1999: GRP-MILF Peace Negotiations Ceasefire – GRP violations 33 Major Camps and Satellite Camps: Abubakre and Bushra CPP-NPA-NDFP in Mindanao 1964 – KABATAAN MAKABAYAN (Moro Recruits) CP P ARMAS 1970’s Guerilla Zones and Basees in Mindanao, including Moro and Lumad areas 1982 – Moro Revolutionary Organization (MRO) and Moro Revolutionary Army (MRA) CNL MAKIBAKA Kabataang Makabayan 1989 Rectification Movement 1999 NDF-MILF Tactical Alliance RCTU 2005 – Moro Resistance and Liberation Organization VICTIMS OF NATIONAL OPPRESSION Christian Settlers - 13 Million Moro Population - 3.7 Million Lumad Population - 2.1 Million ARMM – 2.4 Million inhabitants Mindanao Tri-People Muslim Christian Settlers 72% 20% 8% IPs Lumad 18 Ethnolinguistic Groups Moro 13 tribes BANGSAMORO: Thirteen Ethnolinguistic groups Palawanis & Molbog Kalbogan Jama Mapun Badjao Yakan Maranao Iranon Maguindanao Tausug Samal/Sama Bangingi Kalagan Sangir LUMAD: Eighteen Ethnolinguistic groups MAMANWA 7,1800 MANOBO 250,000 HIGAONON 265,000 SUBANEN 858,970 TIGWAHANON 36,128 BANWAON 5,000 DIBABAWON 81,997 LUMAD are the 18 ethnolinguistic tribes found in Mindanao TALAANDIG 10,000 TEDURAY 354,625 MANSAKA 115,248 15,000 MATIGSALOG TEDURAY T’BOLI 374,212 B’LAAN 256,106 MANDAYA 268,913 MANSAKA 115,248 Christian Visayan Settlers SURIGAONON Cebuano CHAVACANO Cebuano ILOCANO ILONGGO Continuing Challenge: High incidence of poverty, poor quality of life – Mindanao has continually lagged behind in social services. • Though urban poverty has decreased by 31 percent since 1991, rural poverty has also increased by 31 percent since 1991. • Poverty incidence in Mindanao reached 38.8 percent, an increase of 1.1 percent from 2003 figures • 6 of the 10 poorest provinces are from Mindanao • 19.2 % of families in Mindanao are food poor. • Mindanao has 4 of the bottom 5 provinces in the Human Development Index • 4.67 million families that earned less than what they needed for basic food and non-food needs LANDED ELITES AMPATUAN Lobregat Family Cassava and Coconut Plantation, Balabagan, Lanao del Sur Landed and Political elite in the ARMM Pinol – Arakan Valley Complex; PALMA Complex; Plough Now, Pay Later; African Palm Plantation QuebranzaDimaporo coconut plantations BF Goodrich and Sime Darby Tires; One Town One Product (rubber) Paglas Banana Nestle investments Plantation on Coffee Growers Mangudadatu plantations AlcantaraDominguez mining POST- 2010 ELECTIONS IN MINDANAO Noynoy’s Mindanao Agenda? Can he change Mindanao Politics? PLUNDER OF RESOURCES TVI OPERATION IN SIOCON, ZAMBOANGA del NORTE LIGUASAN MARSH • • • Comprehensive Dev’t Plan for the Liguasan Marsh 1999 – 2025 Known to have extensive oil and natural gas deposits, which oil companies and the Phil. Gov’t are keen to exploit Project-SEED-Pikit or Social, Economic Enhancement Program (SEED) POLITICAL REPRESSION ALL-OUT WAR to WAR ON TERROR MILITARY OPERATIONS IN MINDANAO: •April 2000 – All-Out War •November 2001 – Pursuit Ops vs. Misuari •January-July 2002: Balikatan in Basilan •August 2002: Foreign Terrorist Organization •February 2003 – Buliok War •September 2003 – Lanao Offensives February 2005 – Maimbong Sulu Between 400,000 and 1M displaced; 160,000 dead ALL-OUT WAR to WAR ON TERROR March 24, 2001 “Agreement on the General Framework for the Resumption of Peace Talks” GRP-MILF Tripoli Agreement on Peace of 2001 •The Security and Rehabilitation Aspects are in the nature of confidence-building. •Ancestral Domain is political in nature and as such it is the door to all other political issues in the negotiations. August 7, 2001 Guidelines for the Ceasefire September 11, 2001 Twin Towers Bombing US War on Terror (2001) and the US-RP Balikatan (2002) under the VFA (1999) Balikatan US-RP Joint Military Exercises in Moro Areas JOINT OPERATIONS TASK FORCE – MEDCAPS 2005 PHILIPPINES (since 2002), Camp SIOCON (TVI) Sirawai Navarro, Zamboanga City Canatuan Gold Camp Malagutay, MEDCAPS 2005 Brgy. Malagutay, Edwin Andrews Air Sirawai Zamboanga City Base in Sta. Maria, Zamboanga City 3rd Marine Brigade, Camp Teodolfo Bautista, Busbus, Jolo Sulu) TAWI-TAWI USNS MERCY NAVAL BOAT; Philippine Naval Station, Batu-Batu, Panglima Sugala, MEDCAPS CAMP Mt. Butig RANAO 6th Infantry 05 BAYANIHAN Division, Talayan;Camp Siongco, MEDCAPS in Maguindanao Parang 64th IB, Datu Piang, Maguindanao US BOMB EXPERTS, FBI, CIA AND AUSTRALIAN SPIES BALANCE PISTON 06-02 BALANCE PISTON 06-02 MEDCAPS MEDCAPS 2005 Carmen, North Cotabato US TROOPS 2005 Lamitan Carmen, North Cotabato; LEBAK, SK Lamitan; 2007 MEDCAP MIDSAYAP SEABEES, Tipo-Tipo US TROOPS IN SARANGGANI Disregard of Civil and Political Rights Disregard of Civil and Political Rights Bu Bizma: Victim of US-RP Balikatan POLITICAL REPRESSION IN MINDANAO 1.The Human Security Act (Republic Act 9372) & War on Terror 2. AFP’s Oplan Bantay Laya (20022006) Oplan Bantay Laya II (2006-2010) 3. National Internal Security Plan – Indigenous People 3. Extra-Judicial Killings & Abductions 4. 2006– Executive Order 546 – establishing paramilitary troops or CVO’s 5.US Counter Insurgency Guide and Oplan Bayanihan 6. Investment Defense Forces for plantations and mining Highlighted EJK Case under 10th Infantry Division Aquino’s Mindanao: JUSTICE TO THE VICTIMS OF WAR Year 2008-2010 600,000 to 750,000 displaced US Counter Insurgency Guide Oplan Bayanihan PROSECUTE ARROYO PRESENCE OF US TROOPS PROSECUTE THE AMPATUANS PRIVATE ARMIES No. Of Active Area 8 PAGs Ilocos 3 PAGs Cagayan Valley 6 PAGs Central Luzon 6 PAGs Calabarzon 4 PAGs Mimaropa 7 PAGs Bicol 6 PAGs Western Visayas 2 PAGs Central Visayas 1 PAGs Eastern Visayas 2 PAGs Zamboanga Peninsula 7 PAGs Northern Mindanao 1 PAG Caraga 19 PAGs ARMM Malacañang-formed Independent Commission Against Private Armies, said that of the 112 identified private armed groups (PAGs), a total of 72 remain active GPH-MILF PEACE TALKS 2011 • • • •February 9, 2010 •January 4 GPH letter •International Monitoring Team •International Coordinating Group MILF calls for the release of 25 MILF members including Engr. Eduard Guerra( a.k.a. Abraham Yap Alonto), arrested on September 22 at the Davao International Airport en route to Geneva, Switzerland, to attend a meeting of the United Nations Human Rights Council • • • 2008 Memorandum on Ancestral Domain Terms of Reference Concepts and Principles Territory Resources Governance GPH-MNLF PEACE TALKS 2011 Amendatory bill for Republic Act (RA) 9054-ARMM expansion Will present RA9054 to the OIC Fourth Tripartite Meeting: Out of the 32 issues, 3 items in common: •area of autonomy •sharing of revenues between central government and regional government in strategic minerals transitional mechanism X. Rights of Indigenous Peoples, National Minorities and Nationalities for SelfDetermination And Decolonization Against Discrimination, Racism, and National Oppression by Imperialism andSAGUNA Local Reaction SU BANGSA, SU MORO, MANININDEG! TAKBEER! ALLAHU AKBAR!