Drivers for Gas Compression
advertisement

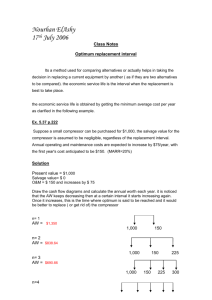
Drivers for Gas Compression A comparison between reciprocating engines, turbines, and electric motors Presented by Wayne Longer Courtesy of Compressor station design 73,000 horse-power 42” pipeline Courtesy of Courtesy of Exhaust-Catalyst-Air intake-Engine coolers-Gas coolers-Separators rte Courtesy of How does the air flow ? Courtesy of Working space – overhead bridge crane - ventalation Courtesy of Note the insulation on the exhaust systems Courtesy of How Does an Engineer Decide? Factors and Examples Company ABC Project Factors for Deciding Driver & Compressor Site information – environmental issues – operating conditions • pressure ratios • volume of gas • variability of operation Owning and operating costs – initial capital expenditure – fuel/electricity costs – maintenance What driver is familiar – like to go with what you know Risk assessment – driver reliability - storm outage? – redundancy of units – crank failure? – mix of driver types Driver Options Driver Options Reciprocating Engines Major players – Caterpillar – Waukesha – Wärtsilä CAT G16CM34 Typical engine power 1200 - 8000 bhp Operate at 750 - 1000 rpm CAT G3612 Waukesha ATGL16V Driver Options Turbines Major players Solar Mars 90 – Solar – Siemens – Elliot GE10-2 – GE – Rolls-Royce – MAN Turbo Typical power 1500 - 30,000 bhp Operate at 11,000 - 23,000 rpm GE10-1 Driver Options Electric Motors Major players – Toshiba – Siemens – Rockwell (formerly Reliance) – Ideal – GE – ABB Typical power 1300 - 20,000 bhp Operate typically at 300 - 3600 rpm Siemens H-Compact Siemens H-Compact PLUS – high speed motors at 12,000 - 23,000 rpm Direct Drive Systems Frame 2 (high speed motor) Compressor Options Compressor Options Reciprocating Major players – – – – Ariel Dresser-Rand Cameron Compression GE Ariel JGV/6 300 - 1800 rpm input speed Wide operating range 1 to 10,000 PSI – Advantage at higher pressure ratios, > 3:1 Dresser-Rand HOS Cameron Axis Compressor Options Centrifugal Solar C16 Dresser-Rand Datum Major players – Solar – Dresser-Rand – Siemens – Rolls Royce Operates with higher speed drivers (motors and turbines) Sweet spot at low pressure ratios and high volumes – < 1.4 pressure ratio is ideal Operate best at lower discharge pressures – < 2000 psi Siemens STC-SV Package Combinations Package Combinations Reciprocating Compressor Recip Engine Electric Motor Package Combinations Centrifugal Compressor Turbine Electric Motor Emerging Technology Dual Drive Engine or Electric motor driver Flexibility – lowest cost by the hour Reduced emissions Performance Characteristics Fuel and Power* Compression Efficiency (Turndown – Flexible operation) De-ration Emissions Noise * For the following comparison tables, cost of electricity is based solely on cents/kWhr price; demand charges not included and could substantially increase yearly energy cost Electricity Source: Energy Information Administration Engine Fuel and Power 4700 - 5500 bhp* ($4.00/MMBtu and 6.5 cents/kWhr at 8000 hours/year) Btu/bhp-hr $/year Efficiency or kW rpm bhp ($/hp-hr) G3616 4735 1000 39% 6736 $1,020,638 (.0269) Turbines Gas Turbine Motors 4700 15,000 27.9% 9125 $1,372,400 (.0366) 501 KC-5 5500 13,600 29.6% 8495 $1,495,120 (.0339) DDS Frame 8 5360 7000 97.5% 4101 Toshiba/ Siemens 5500 1800 96.5% 4252 $2,132,565 (.0497) $2,211,040 (.0502) * Ratings based on companies’ published ISO conditions Demand charges not included and could substantially increase yearly electric costs Fuel and Power 7700 - 10,400 bhp* ($4.00/MMBtu and 6.5 cents/kWhr at 8000 hours/year) Btu/bhp-hr Efficiency or kW bhp rpm Engines G16CM34 8180 750 42.7% 5959 Wärtsilä 16V34SG Turbines Gas Turbine 9360 750 44.3% 5793 7700 15,000 32% 7960 Gas Turbine 10,310 15,200 34% 7484 Toshiba/ Siemens 10,000 1800 96.5% 7730kwk Motor $/year ($/hp-hr) $1,559,827 (.0238) $1,735,119 (.0232) $1,961,344 (.0318) $2,469,121 (.02993) $4,019,896 (.0502) •Ratings based on companies’ published ISO conditions @ 70F – Turbines de-rate as temp increases • Demand charges not included and could substantially increase yearly electric costs. Combined cycle True Carbon foot print ??? Additional Electric Power Costs Demand charges – based on total at site power – no charge if electricity is not used • even 1 kW of usage triggers total kW demand charge – can be firm or interruptible • firm is more expensive – usually between $5 - $8 per kW in one month – some companies charge per kW-hr • $.009/kW-hr is common Electric Motor Power 5000 bhp = 3731 kW Demand Charge ($/kW-Mo) $6.50 Yearly Demand Charge $291,000 Compression Efficiency Reciprocating compressor – typically run at 70% - 85% efficiency – suited for higher pressure ratios >1.4:1 ratios Centrifugal – typically run at 70% - 85% efficiency – highest efficiencies at lower pressure ratios 1.2:1 •high pressure ratios favor reciprocating compressors •low pressure ratios favor centrifugal compressors Horsepower De-rate Ambient Temperature Altitude Fuel gas Site specific ??? Turbine60 G16CM34 and Taurus Available Power 9000 8500 Power, bhp 8000 7500 G16CM34 G16CM34 Turbine - 60 Sea(ISO) level Taurus Taurus Turbine - 60 500(500 ft ft) 7000 Taurus ft) Turbine - 60 1500(1500 ft 6500 6000 5500 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 Temp, degF 70 80 90 100 Fuel Consumption (btu/bhp-hr) Fuel Consumption at Sea Level 10000 9500 9000 8500 8000 7500 7000 6500 6000 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 Ambient Temp (deg F) G3616 Recip Centaur Turbine 50 80 90 100 De-rate - Electric Motor Ambient Temperature Insulation usually enough to avoid de-ration Altitude Typical motor will not de-rate until 3500 ft. Above 3500 ft. requires special insulation - cooler – possible derating (though not as severe as engines and turbines) Load change Turndown does not affect motor efficiency much . Emissions (g/bhp-hr) w/o after treatment (Oxidation Catalyst 90% reduction) NOx CO THC G3600 0.5 - 0.7 2.5 6.0 GCM34 0.5 – 0.7 2.0 6.0 - 7.0 0.9 2.0 6.0 0.2 - 0.6 0.6 0.2 Wärtsilä 16V34SG Turbine Electric Motor At site only from packaging leaks (valves, vents…) Transfers emissions to power plant - Carbon foot print?? Noise Comparison Reciprocating Engine 128 dBA noise dampening required in some areas Turbine 82 dBA high frequency noise – dissipates quickly with distance Electric Motor 70 dBA considered noiseless if inside building – Exception - air flow for cooling and gas flow in pipe Packaging and Installation Comparison Packaging and Installation G3600 Air inlet system Exhaust system Cooling system Package controls/electronics Recip compressor Scrubbers Pulsation bottles Gas cooler Packaging and Installation G3616 Package approx weight: 95,000 lbs – G3616: 65,900 lbs – Compressor: 28,600 lbs Package approx length: 29 feet 116” 223” Package approx width: Package approx height: 137 inches 178 inches Note: does not include auxiliary modules, additional piping Packaging and Installation - GCM34 Air inlet system Exhaust system Fuel Module Combined Module Unit Control Panel Recip compressor Scrubbers Pulsation bottles Gas cooler Packaging and Installation - G16CM34 Package approx weight: 300,000 lbs – G16CM34: 179,080 lbs – Compressor: 120,000 lbs Package approx length: 42 feet Package approx width: 220 inches Package approx height: 137 inches Note: does not include auxiliary modules, building/infrastructure or additional piping 319” 185” Packaging and Installation Turbine Air inlet system Exhaust system Cooling system Package controls Rotating compressor Scrubbers Gas cooler Packaging and Installation Turbine (6000 hp) CENTRIFUGAL COMPRESSOR COOLING SYSTEM (off skid) Packaging and Installation Electric Motor with Reciprocating Compressor Air ducting Cooling System Package controls Recip compressor Scrubbers Pulsation bottles Gas cooler Typical motor weight: 20,000 lbs +/- 5000 Typical motor length: 75” +/- 25” 4 throw compressor 116” Packaging and Installation Electric Motor with Centrifugal Compressor Air ducting Cooling System Package controls/electronics Couplings Gear box or transmission Centrifugal compressor Packaging and Installation Electric Motor with Centrifugal Compressor Typical motor weight: 20,000 lbs +/- 5000 Typical motor length: 75” +/- 25” Other package dimensions similar to turbine – addition of gear box or transmission could greatly increase length Packaging and Installation Additional Requirements Reciprocating Engines and Turbines Usually need enclosure Possible noise suppression and exhaust after treatment Similar installation for both drivers Packaging and Installation Additional Requirements Electric Motor Building / enclosure needed Sub-station – includes switchgear, breaker, transformers, drives Need VFD or transmission for variable speed Need transmission lines – Could take a years or more to get power to compression station (Eagleford shale) – Right-away procurement Lifetime Maintenance Compared (includes labor at $100/hour and oil at $7.40/gallon) Gas turbines Average ~ $0.0035/bhp-hr Downtime over 15 years 280 hours Reciprocating engines G3600 avg. ~ $0.0036/bhp-hr GCM ~ $0.0037/bhp-hr Downtime over 15 years Electric motors Less than $10,000/year or $.0004/bhp-hr Downtime over 15 years 240 hours G3600 800 hours CM 730 hours How Does an Engineer Decide? Factors and Examples Company ABC Project Factors for Deciding Driver & Compressor Site information – environmental issues – operating conditions • pressure ratios • volume of gas • variability of operation Owning and operating costs – initial capital expenditure – fuel/electricity costs – maintenance What power is familiar – like to go with what know Risk assessment – power reliability storm outage? – redundancy of units – mix of driver types Example 1 Project Specifics 4,500 bhp required Not in non-attainment area – emissions not a major issue Site rated at sea level and 100 degrees (F) ambient temperature Average operating pressure ratio of 1.3 and discharge pressure of 1100 psi – centrifugal and reciprocating compressors both options No horsepower in place – no customer preference 2 miles from electricity power source Example 1 Compression Options G3616 (4735 bhp, 6736 Btu/bhp-hr) Gas Turbine (4700 bhp, 9050 Btu/bhp-hr) 5000 bhp electric motor with reciprocating compressor 5000 bhp electric motor with centrifugal compressor Example 1 Initial Capital Expenditures Driver Driver Cost Package Cost Other Install Costs $4,000,000* Total ($MM) $7.20 Total ($/bhp) $1521 G3616 $1,360,000 $3,200,000 Gas Turbine $1,950,000 $3,750,000 $4,000,000* $7.75 $1550 Electric Motor (5000 bhp w/ reciprocating) Electric Motor (5000 bhp w/ centrifugal) $225,000 $900,000 $6,505,000 $7.51 $1501 $225,000 $1,000,000 $6,605,000 $7.61 $1521 * Includes facility and additional piping and controls Example 1 Electric Motor Installation Breakdown Package $900,000 (reciprocating compressor) $1,000,000 (centrifugal compressor) Total VFD Substation with Transmission ($150/bhp) everything Lines included ($1 mill/mi) Facility, controls and piping $750,000 $855,000 $2,000,000 $3,000,000 $6,505,000 $750,000 $855,000 $2,000,000 $3,000,000 $6,605,000 Example 1 Driver and Compressor Owning and Operating Costs* 15 year outlook (15 years covers one major overhaul) Driver Maintenance Lifecycle Cost 15 Year Fuel/Electricity 15 Year Fuel Maintenance bhp-hr Cost Cost G3616 (4735) Gas Turbine (4700 hp) Electric Motor (5000 bhp) $.0044/bhp-hr =$2,471,700 $.0269/bhp-hr =$15,284,580 $.0038/bhp-hr =$2,250,000 $.0366/bhp-hr =$20,642,400 $.0012/bhp-hr =$690,000 8000 hours/year, $4.00/MMBtu, 6.5 cents/kWhr $.048/bhp-hr =$29,820,000 Example 1 Driver and Compressor Owning and Operating total Costs* 15 year outlook Driver Initial Capital Expenditures Maintenance Fuel/ Electricity Total (in millions) Total ($/bhp) G3616 $7,200,000 $2,471,700 $15,284,580 $24,956,280 $5270 Gas Turbine $7,750,000 $2,250,000 $20,642,000 $30,642,000 $6519 Electric Motor $7,605,000 $690,000 $29,820,000 $38,115,000 $7623 * 8000 hours/year, $4.00/MMBtu, 6.5 cents/kWhr Advantages/Disadvantages Reciprocating Engine Advantages Fuel efficiency Operation under variable loads and pressure ratios Well known technology Disadvantages Emissions High maintenance intervals and costs Complex package Lower compressor efficiency at lower pressure ratios Advantages/Disadvantages Turbine Advantages Long maintenance intervals Low emissions Lower first cost for high horsepower applications due to larger horsepower blocks Higher efficiencies at lower pressure ratios 1.2 Disadvantages Fuel consumption High maintenance costs Minimal turndown / load reduction Starting and stopping takes hours off life cycle Altitude and ambient temperature quickly affect power and heat rate Advantages/Disadvantages Electric Motor Advantages Low maintenance costs and intervals No emissions at site Turndown does not affect motor efficiency much Can be used with centrifugal or reciprocating compressor Disadvantages Dependency on power company (interruptions in service) If high power source not within 2 - 3 miles, installation cost are high (14.7 KV) Complex controls required (VFD or variable speed gear box) Sources Manufacturers Ariel Corporation Caterpillar Solar Turbines Pipeline Companies Kinder Morgan El Paso Pipeline Spectra Energy Others Alliance Engineering Miratech Emissions Solutions Shermco Industries Packagers Compressor Systems Inc. Exterran References Ariel Corporation Ariel Performance Software Arielcorp.com Caterpillar Gas Engines Gas Engine Rating Pro software catoilandgas.cat.com CAT, CATERPILLAR, their respective logos, "Caterpillar Yellow," the "Power Edge" trade dress as well as corporate and product identity used herein, are trademarks of Caterpillar and may not be used without permission.