Template for Electronic Submission of Organic Letters
advertisement
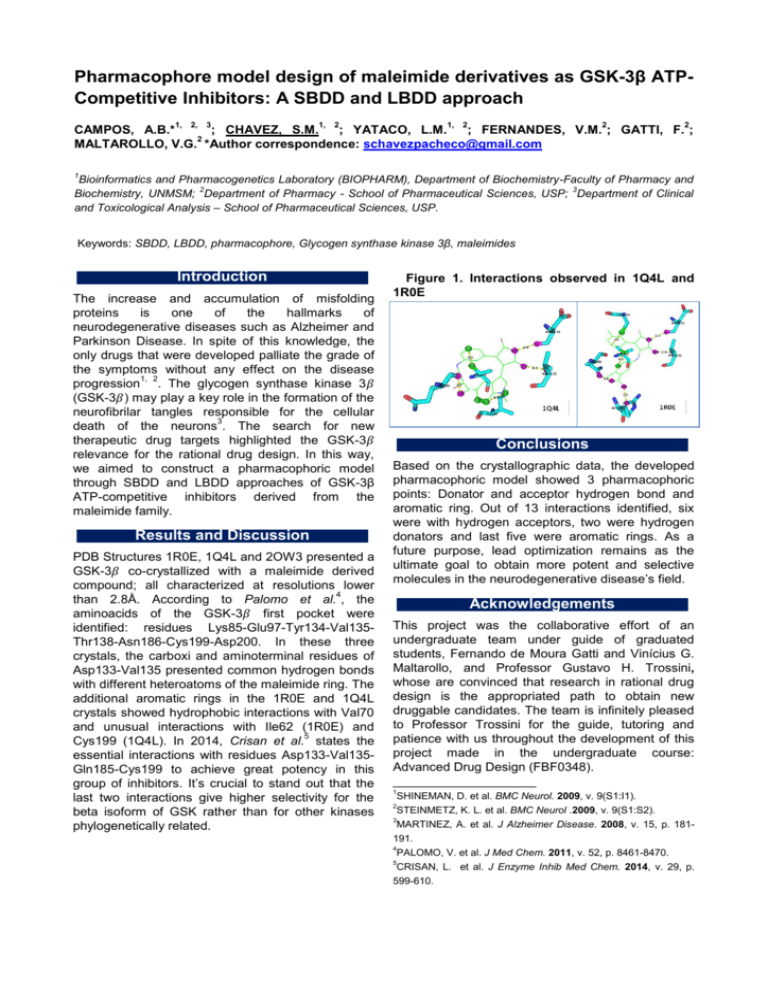
Pharmacophore model design of maleimide derivatives as GSK-3β ATPCompetitive Inhibitors: A SBDD and LBDD approach 1, 2, 3 1, 2 1, 2 2 2 CAMPOS, A.B.* ; CHAVEZ, S.M. ; YATACO, L.M. ; FERNANDES, V.M. ; GATTI, F. ; 2 MALTAROLLO, V.G. *Author correspondence: schavezpacheco@gmail.com 1 Bioinformatics and Pharmacogenetics Laboratory (BIOPHARM), Department of Biochemistry-Faculty of Pharmacy and 2 3 Biochemistry, UNMSM; Department of Pharmacy - School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, USP; Department of Clinical and Toxicological Analysis – School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, USP. Keywords: SBDD, LBDD, pharmacophore, Glycogen synthase kinase 3β, maleimides Introduction The increase and accumulation of misfolding proteins is one of the hallmarks of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer and Parkinson Disease. In spite of this knowledge, the only drugs that were developed palliate the grade of the symptoms without any effect on the disease 1, 2 progression . The glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK-3 ) may play a key role in the formation of the neurofibrilar tangles responsible for the cellular 3 death of the neurons . The search for new therapeutic drug targets highlighted the GSK-3 relevance for the rational drug design. In this way, we aimed to construct a pharmacophoric model through SBDD and LBDD approaches of GSK-3β ATP-competitive inhibitors derived from the maleimide family. Results and Discussion PDB Structures 1R0E, 1Q4L and 2OW3 presented a GSK-3 co-crystallized with a maleimide derived compound; all characterized at resolutions lower 4 than 2.8Å. According to Palomo et al. , the aminoacids of the GSK-3 first pocket were identified: residues Lys85-Glu97-Tyr134-Val135Thr138-Asn186-Cys199-Asp200. In these three crystals, the carboxi and aminoterminal residues of Asp133-Val135 presented common hydrogen bonds with different heteroatoms of the maleimide ring. The additional aromatic rings in the 1R0E and 1Q4L crystals showed hydrophobic interactions with Val70 and unusual interactions with Ile62 (1R0E) and 5 Cys199 (1Q4L). In 2014, Crisan et al. states the essential interactions with residues Asp133-Val135Gln185-Cys199 to achieve great potency in this group of inhibitors. It’s crucial to stand out that the last two interactions give higher selectivity for the beta isoform of GSK rather than for other kinases phylogenetically related. Figure 1. Interactions observed in 1Q4L and 1R0E Conclusions Based on the crystallographic data, the developed pharmacophoric model showed 3 pharmacophoric points: Donator and acceptor hydrogen bond and aromatic ring. Out of 13 interactions identified, six were with hydrogen acceptors, two were hydrogen donators and last five were aromatic rings. As a future purpose, lead optimization remains as the ultimate goal to obtain more potent and selective molecules in the neurodegenerative disease’s field. Acknowledgements This project was the collaborative effort of an undergraduate team under guide of graduated students, Fernando de Moura Gatti and Vinícius G. Maltarollo, and Professor Gustavo H. Trossini, whose are convinced that research in rational drug design is the appropriated path to obtain new druggable candidates. The team is infinitely pleased to Professor Trossini for the guide, tutoring and patience with us throughout the development of this project made in the undergraduate course: Advanced Drug Design (FBF0348). ____________________ 1 SHINEMAN, D. et al. BMC Neurol. 2009, v. 9(S1:I1). STEINMETZ, K. L. et al. BMC Neurol .2009, v. 9(S1:S2). 3 MARTINEZ, A. et al. J Alzheimer Disease. 2008, v. 15, p. 181191. 4 PALOMO, V. et al. J Med Chem. 2011, v. 52, p. 8461-8470. 5 CRISAN, L. et al. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2014, v. 29, p. 599-610. 2