Williamson Ether Synthesis Synthesis of 2
advertisement
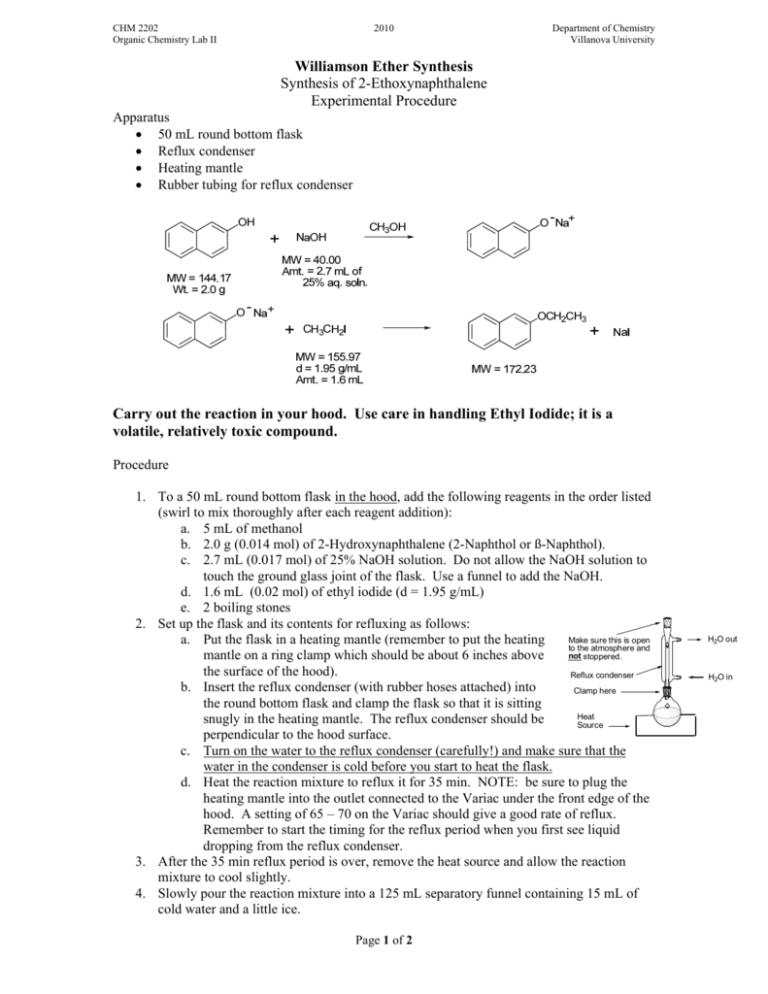
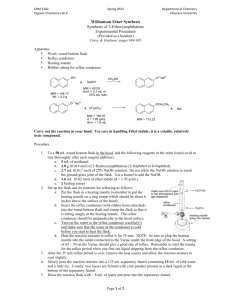
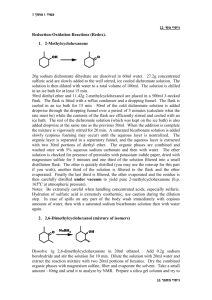
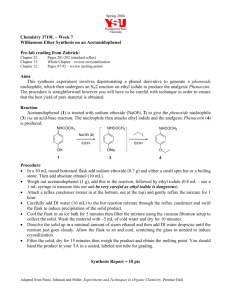
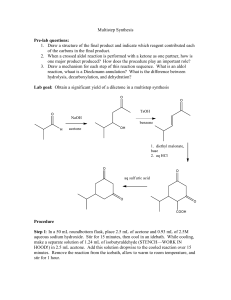
CHM 2202 Organic Chemistry Lab II 2010 Department of Chemistry Villanova University Williamson Ether Synthesis Synthesis of 2-Ethoxynaphthalene Experimental Procedure Apparatus ! 50 mL round bottom flask ! Reflux condenser ! Heating mantle ! Rubber tubing for reflux condenser Carry out the reaction in your hood. Use care in handling Ethyl Iodide; it is a volatile, relatively toxic compound. Procedure 1. To a 50 mL round bottom flask in the hood, add the following reagents in the order listed (swirl to mix thoroughly after each reagent addition): a. 5 mL of methanol b. 2.0 g (0.014 mol) of 2-Hydroxynaphthalene (2-Naphthol or ß-Naphthol). c. 2.7 mL (0.017 mol) of 25% NaOH solution. Do not allow the NaOH solution to touch the ground glass joint of the flask. Use a funnel to add the NaOH. d. 1.6 mL (0.02 mol) of ethyl iodide (d = 1.95 g/mL) e. 2 boiling stones 2. Set up the flask and its contents for refluxing as follows: Make sure this is open a. Put the flask in a heating mantle (remember to put the heating to the atmosphere and not stoppered. mantle on a ring clamp which should be about 6 inches above the surface of the hood). Reflux condenser b. Insert the reflux condenser (with rubber hoses attached) into Clamp here the round bottom flask and clamp the flask so that it is sitting Heat snugly in the heating mantle. The reflux condenser should be Source perpendicular to the hood surface. c. Turn on the water to the reflux condenser (carefully!) and make sure that the water in the condenser is cold before you start to heat the flask. d. Heat the reaction mixture to reflux it for 35 min. NOTE: be sure to plug the heating mantle into the outlet connected to the Variac under the front edge of the hood. A setting of 65 – 70 on the Variac should give a good rate of reflux. Remember to start the timing for the reflux period when you first see liquid dropping from the reflux condenser. 3. After the 35 min reflux period is over, remove the heat source and allow the reaction mixture to cool slightly. 4. Slowly pour the reaction mixture into a 125 mL separatory funnel containing 15 mL of cold water and a little ice. Page 1 of 2 H2O out H2O in CHM 2202 Organic Chemistry Lab II 2010 Department of Chemistry Villanova University 5. Rinse the reaction flask with ~ 3 mL of water and pour into the separatory funnel. 6. Then rinse the reaction flask with 5 mL of ether and pour into the separatory funnel. 7. Add 15 mL of ether to the separatory funnel and briefly shake it to extract the product into the ether layer. 8. Remove the lower aqueous layer and discard. 9. Add another 10 mL of water to the separatory funnel, shake briefly and then drain and discard the lower water layer. 10. In the following manner check the composition of your crude ether extract by TLC analysis using silica gel TLC plates and a developing system of Ethyl Acetate:Hexane (1:9). You may use a 250 mL beaker covered with a watch glass as your TLC chamber. a. Using a TLC spotting capillary tube, place a spot of the 2-naphthol starting material dissolved in ethyl acetate (this TLC reference solution is available in the community hood) on the TLC plate. b. Using a clean TLC spotting capillary, place a spot of the ether layer in the separatory funnel next to the starting material on the TLC plate. c. Develop the TLC plate using the Ethyl Acetate:Hexane (1:9) mixture and view the plate under short wave UV light. d. Is all of the starting material gone from your reaction product which was extracted into the ether?? 11. While the TLC plate is developing, place the ether layer remaining in the separatory funnel into a 50 mL Erlenmeyer flask. Add a boiling stone and carefully warm and continuously agitate the flask on a steam bath to boil off the ether. After most of the ether is removed, vigorously heat the liquid residue in the Erlenmeyer on the steam bath to remove the last traces of ether. 12. After the ether is removed, allow the flask to cool briefly and then add 3 mL of 95% ethanol to the residue in the flask. A clear slightly colored solution should be obtained. 13. Cool the flask in an ice bath. While the flask is cooling, continually stir and scratch the flask’s contents with a glass stirring rod. Crystals should begin to form. Be patient! It may take 5 -10 minutes or longer before crystallization starts. Keep the flask in the ice bath for this entire recrystallization process. 14. If no crystals form after 10 minutes of cooling and scratching, see your instructor or TA and s/he will provide some seed crystals to attempt to initiate the crystallization process. Once the crystallization process starts, cool and scratch (with a glass rod) the flask for an additional 5 – 10 minutes. 15. After no more crystals appear to be forming, use vacuum filtration to collect the solids on a Hirsch or Buchner funnel. Be sure that you keep all mixtures and washes ice cold during the recrystallization/filtration processes. If not kept cold, you will lose product! 16. Immediately wash the collected crystals (while on the Hirsch/Buchner funnel and under suction) with two 2 mL portions of ICE COLD 85% (Note: 85% not 95%) ethanol. 17. Allow the crystals to air dry on the Hirsch or Buchner funnel by continuing to suck air through the crystals until the crystals appear to be dry and free flowing. 18. Weigh the crystals to determine your % yield. 19. Dissolve a few crystals of your recrystallized product in 10 drops of ethyl acetate in a test tube and determine the purity of this material using TLC analysis as in Step 10. Are there any differences in the TLCs when comparing your crude and recrystallized materials? 20. Take a MP of the product and compare to the expected literature value. 21. Compare the IR and 1H NMR spectra of both starting material and product (provided as handouts); interpret the spectra (including assignable NMR splitting patterns) and indicate key absorption bands/peaks which distinguish between starting material and product. TMBare (2/5/2010) Page 2 of 2