A very simple tutorial
advertisement

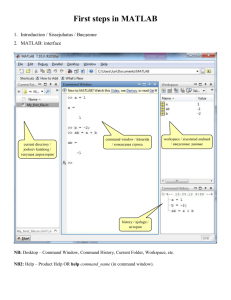
A Very Simple Introduction to Matlab Aaron N. K. Yip 01-2015 MATLAB is an interactive, matrix-based system for scientific and engineering numerical computations and visualizations. MATLAB is the short form for MATrix LABoratory. MATLAB is very user-friendly as a desk calculator, computational tool for linear algebra and matrix analysis, solver for ordinary and partial differential equations, graph plotter and much more. 1 Get Onto Matlab Matlab is becoming more and more popular. It can be found in many PC and UNIX systems. • In the various campus instructional computer labs, you can access Matlab by simply clicking its icon. (It can be found by using find.) • Matlab also exists in most UNIX systems. Just type matlab to see if it exists in the system you are using. There should be a person on duty in the Computing Center if you have problems accessing Matlab. 2 Try This.... The following is the actual screen you will see (plus some edited comments). For starters, after you have opened matlab, you can just follow the lines and see.... Jump to the next section at anytime if you wish. >> % This is the matlab prompt. >> A=[1 2 3; 4 5 6; 7 8 9] % Creating a matrix called A. A = 1 4 7 2 5 8 3 6 9 1 >> B=[ 1 2 3 5 6 1 3 -1 9 ] % Creating a matrix called B. % Note that the format is quite flexible B = 1 5 3 2 6 -1 3 1 9 >> A % To see what is A. A = 1 4 7 2 5 8 3 6 9 >> A + B % A + B = ? ans = 2 9 10 4 11 7 6 7 18 >> C = A + B % Set C = A + B C = 2 9 10 4 11 7 6 7 18 2 >> D= 2*A - 3*B % Compute D = 2*A - 3*B D = -1 -7 5 -2 -8 19 -3 9 -9 >> C=[1; 2; 3] % Create a column vector C = 1 2 3 >> R = [ 1; 2; 3] % Create a row vector R = 1 2 3 >> R=[1 2 3] R = 1 2 3 >> whos Name A B C Size % You can see what variables you have % defined and their data. Elements Bytes Density Complex 3 by 3 3 by 3 3 by 1 9 9 3 3 72 72 24 Full Full Full No No No D R ans 3 by 3 1 by 3 3 by 3 9 3 9 72 24 72 Full Full Full No No No Grand total is 42 elements using 336 bytes >> A % To see A again. A = 1 4 7 2 5 8 3 6 9 >> A(1,1) % You can see particular entry of A ans = 1 >> A(3,2) % the (3,2) entry of A is? ans = 8 >> A(2,2)=3.5 % change the (2,2) entry of A to be 3.5 A = 1.0000 4.0000 7.0000 >> A(1,3)=5.1 2.0000 3.5000 8.0000 3.0000 6.0000 9.0000 % change the (1,3) entry of A to be 5.1 A = 4 1.0000 4.0000 7.0000 2.0000 3.5000 8.0000 5.1000 6.0000 9.0000 >> P=rand(4) % create a random 4 by 4 matrix P = 0.2470 0.9826 0.7227 0.7534 0.6515 0.0727 0.6316 0.8847 0.2727 0.4364 0.7665 0.4777 >> Q=rand(3) 0.2378 0.2749 0.3593 0.1665 % create a random 3 by 3 matrix Q = 0.4865 0.8977 0.9092 >> rank(A) 0.0606 0.9047 0.5045 0.5163 0.3190 0.9866 % To find the rank of A ans = 3 >> help rand % online help for rand RAND Uniformly distributed random numbers and matrices. RAND(N) is an N-by-N matrix with random entries, ordinarily chosen from a uniform distribution on the interval (0.0,1.0). RAND(M,N) or RAND([M,N]) is an M-by-N matrix with random entries. RAND(SIZE(A)) is the same size as A. RAND with no arguments is a scalar whose value changes each time it is referenced. 5 RAND(’seed’) returns the current seed of the uniform generator. RAND(’seed’,s) sets the uniform generator seed to s. RAND(’seed’,0) resets the seed its startup value. RAND(’seed’,sum(100*clock)) sets it to a different value each time. By default, RAND samples a uniform distribution. The function RANDN generates normally distributed random matrices. RAND and RANDN have separate generators, each with its own seed. Previous versions of MATLAB allowed RAND(’normal’) to switch the prevailing distribution to normal, RAND(’uniform’) to switch back to uniform distribution, and RAND(’dist’) to return a string containing the prevailing distribution, either ’uniform’ or ’normal’. MATLAB Version 4.0 continues to allow this switch, but issues a warning message discouraging its use. See also RANDN, SPRANDN. >> help rank % online help for rank RANK Number of linearly independent rows or columns. K = RANK(X) is the number of singular values of X that are larger than MAX(SIZE(X)) * NORM(X) * EPS. K = RANK(X,tol) is the number of singular values of X that are larger than tol. >> 1+2 % simple arithmetics ans = 3 >> 2*7 ans = 6 14 >> 5/2 ans = 2.5000 >> pi ans = 3.1416 >> exp(1) ans = 2.7183 >> format long >> exp(1) % change the format to be long ans = 2.71828182845905 >> help format FORMAT Set output format. All computations in MATLAB are done in double precision. FORMAT may be used to switch between different output display formats as follows: FORMAT Default. Same as SHORT. FORMAT SHORT Scaled fixed point format with 5 digits. FORMAT LONG Scaled fixed point format with 15 digits. FORMAT SHORT E Floating point format with 5 digits. 7 FORMAT LONG E FORMAT HEX FORMAT + Floating point format with 15 digits. Hexadecimal format. The symbols +, - and blank are printed for positive, negative and zero elements. Imaginary parts are ignored. FORMAT BANK Fixed format for dollars and cents. FORMAT COMPACT Suppress extra line-feeds. FORMAT LOOSE Puts the extra line-feeds back in. FORMAT RAT Approximation by ratio of small integers. >> Q Q = 0.48651738301223 0.89765628655332 0.90920810164381 0.06056432754759 0.90465309233621 0.50452289474407 0.51629196364260 0.31903294116214 0.98664211201791 2.00000000000000 3.50000000000000 8.00000000000000 5.10000000000000 6.00000000000000 9.00000000000000 >> 3/4 ans = 0.75000000000000 >> A A = 1.00000000000000 4.00000000000000 7.00000000000000 >> format >> A % reset format to be default - short A = 8 1.0000 4.0000 7.0000 2.0000 3.5000 8.0000 5.1000 6.0000 9.0000 >> A*B % A*B, matrix multiplication ans = 26.3000 39.5000 74.0000 8.9000 23.0000 53.0000 50.9000 69.5000 110.0000 >> B*A % B*A, matrix multiplication % note that A*B is not equal to B*A ans = 30.0000 36.0000 62.0000 33.0000 39.0000 74.5000 44.1000 70.5000 90.3000 >> C C = 1 2 3 >> A*C ans = 20.3000 29.0000 50.0000 >> C*A % Matrix multiplication fails due to 9 % incompatible dimensions ??? Error using ==> * Inner matrix dimensions must agree. >> A^2 % A^A = A*A ans = 44.7000 60.0000 102.0000 49.8000 68.2500 114.0000 63.0000 95.4000 164.7000 49.8000 68.2500 114.0000 63.0000 95.4000 164.7000 >> A*A ans = 44.7000 60.0000 102.0000 >> A^3 ans = 1.0e+03 * 0.6849 1.0008 1.7109 0.7677 1.1221 1.9206 1.0938 1.5741 2.6865 0.7677 1.0938 >> A*A*A ans = 1.0e+03 * 0.6849 10 1.0008 1.7109 1.1221 1.9206 1.5741 2.6865 >> B B = 1 5 3 2 6 -1 3 1 9 >> B’ % transpose ans = 1 2 3 5 6 1 3 -1 9 >> B’’ % B transpose and transpose again ans = 1 5 3 2 6 -1 3 1 9 >> C C = 1 2 3 >> R 11 R = 1 2 3 >> C*R % column vector times row vector ans = 1 2 3 2 4 6 3 6 9 >> R*C % row vector times column vector ans = 14 >> zeros(3) % To create a 3 by 3 zero matrix ans = 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 >> zeros(5) ans = 0 0 0 0 0 >> eye(5) 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 % To create a 5 by 5 identity matrix 12 ans = 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 >> eye(3) ans = 1 0 0 >> E=rand(3,4) % To create a random 3 by 4 matrix E = 0.4940 0.2661 0.0907 0.9478 0.0737 0.5007 0.3841 0.2771 0.9138 0.5297 0.4644 0.9410 >> rref(E) % To obtain the reduced row echelon form % of E ans = 1.0000 0 0 0 1.0000 0 0 0 1.0000 0.6739 -0.2346 1.0914 >> B B = 13 1 5 3 2 6 -1 3 1 9 0 1 0 0 0 1 >> rref(B) ans = 1 0 0 >> help rref % Online help for rref RREF Reduced row echelon form. R = RREF(A) produces the reduced row echelon form of A. [R,jb] = RREF(A) also returns a vector, jb, so that: r = length(jb) is this algorithm’s idea of the rank of A, x(jb) are the bound variables in a linear system, Ax = b, A(:,jb) is a basis for the range of A, R(1:r,jb) is the r-by-r identity matrix. [R,jb] = RREF(A,TOL) uses the given tolerance in the rank tests. Roundoff errors may cause this algorithm to compute a different value for the rank than RANK, ORTH and NULL. See also RREFMOVIE, RANK, ORTH, NULL, QR, SVD. >> lookfor row % lookfor keyword row RANK Number of linearly independent rows or columns. RREF Reduced row echelon form. RREFMOVIE Movie of the computation of the reduced row echelon form. WATCHOFF Sets the current figure pointer to the arrow. FINDROW Find the rows of a matrix that match the input string. IDUIPOIN Sets and resets the window pointer to watch and arrow 14 ARROW an arrow PDEBSPLIT Splits space separated string into separate rows. >> lookfor echelon RREF Reduced row echelon form. RREFMOVIE Movie of the computation of the reduced row echelon form. >> B B = 1 5 3 2 6 -1 3 1 9 >> det(B) % determinant of B ans = -98 >> inv(B) % inverse of B ans = -0.5612 0.4286 0.2347 0.2143 0 -0.0714 0.1633 -0.1429 0.0408 >> D=inv(B) % Set D = inv(B) D = -0.5612 0.4286 0.2347 0.2143 0 -0.0714 0.1633 -0.1429 0.0408 15 >> B*D % B*D = I, of course ans = 1.0000 -0.0000 0 0.0000 1.0000 0.0000 0 0.0000 1.0000 >> D*B % D*B = I, of course ans = 1.0000 0.0000 -0.0000 -0.0000 1.0000 0.0000 -0.0000 0.0000 1.0000 >> det(D) % det(D) = ? ans = -0.0102 >> det(B)*det(D) % det(B)*det(D) = 1, of course ans = 1.0000 >> whos Name A B C D E P Size 3 3 3 3 3 4 by by by by by by Elements Bytes Density 9 9 3 9 12 16 72 72 24 72 96 128 Full Full Full Full Full Full 3 3 1 3 4 4 16 Complex No No No No No No Q R ans 3 by 3 1 by 3 1 by 1 9 3 1 72 24 8 Full Full Full No No No Grand total is 71 elements using 568 bytes >> size(P) % size of P ans = 4 4 >> size(R) % size of R ans = 1 3 >> help size SIZE Matrix dimensions. D = SIZE(X), for M-by-N matrix X, returns the two-element row vector D = [M, N] containing the number of rows and columns in the matrix. [M,N] = SIZE(X) returns the number of rows and columns in separate output variables. M = SIZE(X,1) returns just the number of rows. N = SIZE(X,2) returns just the number of columns. >> save myfile.mat % save the workspace into file called % myfile.mat >> whos Name A Size Elements Bytes Density 9 72 Full 3 by 3 17 Complex No B C D E P Q R ans 3 3 3 3 4 3 1 1 by by by by by by by by 3 1 3 4 4 3 3 2 9 3 9 12 16 9 3 2 72 24 72 96 128 72 24 16 Full Full Full Full Full Full Full Full No No No No No No No No Grand total is 72 elements using 576 bytes >> clear >> whos % clear the workspace. % now, there are no variables defined. >> load myfile % don’t worry! You can reload the % previous workspace >> whos Name A B C D E P Q R ans % See, now all the previous variables % are there. Elements Bytes Density Complex Size 3 3 3 3 3 4 3 1 1 by by by by by by by by by 3 3 1 3 4 4 3 3 2 9 9 3 9 12 16 9 3 2 Grand total is 72 elements using 576 bytes >> quit 18 72 72 24 72 96 128 72 24 16 Full Full Full Full Full Full Full Full Full No No No No No No No No No 3 Some Useful Commands It is quite useful to get acquainted with the following. Just try them out.... You can get more information about them by typing help command. 3.1 General Commands lookfor keyword look for the commands related to a key word. This is very useful if you forget the exact name of the command. help command — give online help for the command (if you know the name) diary filename — save all the screen output to the file “filename”. Default filename is “diary”. diary off will turn off the diary mode. After you are done, you can then take a look of the screen output (and edit it) at your leisure. save filename — save the whole workspace (i.e. all the variables) into a file. Default filename is “matlab.mat”. load filename — load all the variables from the file “filename” into the workspace. Default filename is “matlab.mat”. whos list information about current variables. The long form of who. clear clear the workspace. You can clear a particular variable by typing clear variablename. 3.2 Mathematical Operations and Functions You can just type help to get a list of all the types of functions available. Of particular interests to starters are: Operators and special characters. + - Plus 19 * / ’ = % - Minus Matrix multiplication division Matrix Transpose Assignment Comment Matrix analysis. rref det inv - Reduced row echelon form. - Determinant. - Matrix inverse. rank trace null orth expm - Number of linearly independent rows or columns. Sum of diagonal elements. Null space. Orthogonalization. Matrix exponential. Eigenvalues. eig poly - Eigenvalues and eigenvectors. - Characteristic polynomial. Trigonometric. sin sinh asin asinh cos cosh acos acosh tan - Sine. Hyperbolic sine. Inverse sine. Inverse hyperbolic sine. Cosine. Hyperbolic cosine. Inverse cosine. Inverse hyperbolic cosine. Tangent. 20 tanh atan atan2 atanh sec sech asec asech csc csch acsc acsch cot coth acot acoth - Hyperbolic tangent. Inverse tangent. Four quadrant inverse tangent. Inverse hyperbolic tangent. Secant. Hyperbolic secant. Inverse secant. Inverse hyperbolic secant. Cosecant. Hyperbolic cosecant. Inverse cosecant. Inverse hyperbolic cosecant. Cotangent. Hyperbolic cotangent. Inverse cotangent. Inverse hyperbolic cotangent. - Exponential. Natural logarithm. Common logarithm. Square root. - Absolute value. Phase angle. Complex conjugate. Complex imaginary part. Complex real part. Exponential. exp log log10 sqrt Complex. abs angle conj imag real Numeric. fix floor ceil - Round towards zero. - Round towards minus infinity. - Round towards plus infinity. 21 round rem sign - Round towards nearest integer. - Remainder after division. - Signum function. Polynomials. roots poly polyval polyvalm residue polyder conv deconv - Find polynomial roots. Construct polynomial with specified roots. Evaluate polynomial. Evaluate polynomial with matrix argument. Partial-fraction expansion (residues). Differentiate polynomial. Multiply polynomials. Divide polynomials. 22