BI SC 004
advertisement

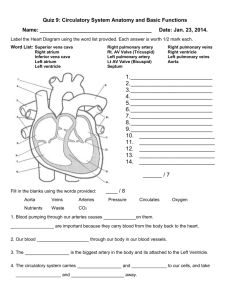
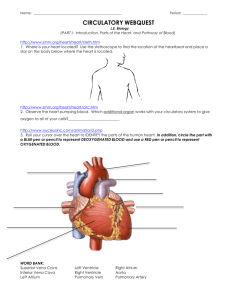
BI SC 004 Human Body: Form and Function STUDY GUIDE The Cardiovascular System: The Heart, Blood Vessels and Circulation Dr. Martha Aynardi aynardi@psu.edu The Heart, Blood Vessels, and Circulation Chapter Learning Objectives ` Upon completion of this chapter, you should be able to: ◦ Differentiate between the types of blood vessels on the basis of structure and function. ◦ Explain the mechanisms that regulate blood flow through arteries, capillaries, and veins. ◦ Describe the role of the precapillary sphincters. ◦ Recall the largest artery and vein. ◦ Define atherosclerosis and recall some of its causes. ◦ Differentiate between systolic and diastolic pressure. ◦ Describe the functions of the systemic and pulmonary circuits. ◦ Recall the flow of blood through the systemic and pulmonary circuits. ◦ Explain the factors which influence venous return from the lower extremities. ◦ Define cardiac output. ◦ Describe the basic anatomical features of the heart and the heart wall. Be sure to include the following key terms in your description: vena cava; right atrium; tricuspid valve; right ventricle; pulmonary arteries; pulmonary veins; left atrium; mitral (bicuspid valve); left ventricle; aorta; SA node; AV node; bundle of His (AV bundle); Purkinje fibers; myocardium, and coronary arteries. ◦ Recall the flow of blood through the heart. (Be sure to identify the major blood vessels, chambers, and heart valves.) ◦ Identify the sequential events of the cardiac conduction system that result in a heartbeat (cardiac contraction). ◦ Recall what the electrocardiogram is used to determine. Also, differentiate between the P wave, the QRS complex, and the T wave. ◦ Recall what the sphygmomanometer is used to determine. ◦ Define a myocardial infarction. ◦ Define a heart murmur. ◦ Recall what the purpose of coronary bypass surgery is. The Heart, Blood Vessels, and Circulation ` Differentiate between the types of blood vessels on the basis of structure and function (pg. 414-418). ◦ Arteries – blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart and toward a capillary. ◦ Arterioles – small arteries; connect larger arteries to capillary networks. ◦ Capillaries – the smallest blood vessels which are the sites of nutrient and waste exchange for the body’s cells. ◦ Venules – small, thin walled veins that receive blood from capillaries. ◦ Veins – collect blood from venules and return it to the heart. ` FIGURE 13-2 on page 414 of your textbook illustrates the structure of the various types of blood vessels. ` Describe the role of the precapillary sphincters (pg. 417). ◦ A precapillary sphincter is a band of smooth muscle that regulates blood flow from an arteriole into a capillary. The contraction of these smooth muscle fibers reduces the flow of blood . The relaxation of the muscle allows blood to enter the capillary more rapidly. ` Name the largest artery and vein (pg. 414 & 418). ◦ The largest artery is the aorta. ◦ The largest vein is the venae cavae. ` Define atherosclerosis and identify some of its causes (pg. 416). ◦ Atherosclerosis is the formation of lipid deposits in the tunica media associated with damage to the endothelial lining of the blood vessel. ◦ Factors which may contribute to its cause: x ` Age x Sex x High blood cholesterol levels x High blood pressure x Cigarette smoking x Diabetes mellitus x Obesity x Stress Measurement of Blood Pressure: ◦ Differentiate between systolic and diastolic pressure (pg. 420). x Systolic pressure refers to the force with which blood pushes against artery walls when the heart muscle contracts (especially the ventricles). x Diastolic pressure is the blood pressure in the arteries during relaxation phase of the cardiac conduction cycle when the heart chamber relaxes and fills with blood. ` Describe the functions of the systemic and pulmonary circuits (pg. 389; 429-430). ◦ Systemic circuit – this circuit transports oxygenated blood and nutrients from the left side of the heart to the organs and tissues of the body and then returns deoxygenated blood from these structures to the right side of the heart. ◦ Pulmonary circuit – this circuit transports deoxygenated blood from the right side of the heart to the lungs where it is oxygenated and then returns it to the left side of the heart. ` Recall the flow of blood through the systemic and pulmonary circuits. ` Explain the mechanisms that regulate blood flow through arteries, capillaries, and veins (pg. 418-419). ◦ Define cardiac output ◦ Define peripheral resistance. ◦ How do cardiac output and peripheral resistance influence blood pressure? ◦ Describe how vasoconstriction and vasodilation regulate blood pressure? ◦ What is the function of precapillary sphincters? ◦ What factors influence venous return (to the heart)? ` Explain the factors which influence venous return from the lower extremities (pg. 405 & 418). ◦ The factors which influence blood flow are pressure and resistance. ` Define cardiac output (pg. 404-405). ◦ Cardiac output refers to the amount of blood pumped by each ventricle in 1 minute. ◦ Factors that regulate cardiac output: x Blood volume reflexes x Autonomic innervation x ` Hormones Describe the basic anatomical features of the heart and the heart wall. Be sure to include the following key terms in your description: vena cava; right atrium; tricuspid valve; right ventricle; pulmonary arteries; pulmonary veins; left atrium; mitral (bicuspid valve); left ventricle; aorta; SA node; AV node; bundle of His (AV bundle); Purkinje fibers; myocardium, and coronary arteries. ` Recall the flow of blood through the heart (pg. 389; 397). Be sure to identify the major blood vessels, chambers, and heart valves. ` Identify the sequential events of the cardiac conduction system that result in a heartbeat (cardiac contraction) (pg. 389-401). ` Recall what the electrocardiogram is used to determine. Also, differentiate between the P wave, the QRS complex, and the T wave (pg. 401-403). ` Recall what the sphygmomanometer is used to determine (pg. 422). ◦ A sphygmomanometer is a devise used for measuring blood pressure. ` Define a myocardial infarction (pg. 397). ◦ A myocardial infarction, or heart attack is when the coronary circulation becomes blocked, and cardiac muscle cells die from a lack of oxygen. ` Define a heart murmur (pg. 395). ◦ A heart murmur is the soft, distinctive sound of swirling blood that usually results from a leaky heart valve. ` Recall what the purpose of coronary bypass surgery is (pg. 442 & lecture). ◦ Coronary bypass surgery provides a way to bypass blocked arteries, restoring normal blood flow to the heart. Key Terms ` Precapillary sphincters ` Atherosclerosis ` Systolic ` Diastolic pressure ` Systemic ` Pulmonary circuits ` Cardiac output ` Vena cava ` Right atrium ` Tricuspid ` Valve ` Right ventricle ` Pulmonary arteries ` Pulmonary veins ` ` Left atrium Aorta SA node AV node Bundle of His Myocardium Cardiac conduction system Electrocardiogram P wave QRS complex ` ` ` ` ` ` ` ` ` ` ` ` ` ` ` ` ` T wave Sphygmomanometer Myocardial infarction Heart murmur Coronary bypass surgery Coronary arteries Mitral Purkinje fibers Left ventricle Chapter Review Questions ` Can you answer the following questions? ◦ Can you differentiate between the types of blood vessels on the basis of structure and function? ◦ What are the mechanisms that regulate blood flow through arteries, capillaries, and veins? ◦ What is the role of the precapillary sphincters? ◦ What is the largest artery and vein? ◦ What is atherosclerosis and can you name some of its causes? ◦ What is the difference between systolic and diastolic pressure? ◦ What are the functions of the systemic and pulmonary circuits? ◦ Can you describe the flow of blood through the systemic and pulmonary circuits? ◦ What are the factors which influence venous return from the lower extremities? ◦ What is cardiac output? ◦ Can you describe the basic anatomical features of the heart and the heart wall? Be sure to include the following key terms in your description: vena cava; right atrium; tricuspid valve; right ventricle; pulmonary arteries; pulmonary veins; left atrium; mitral (bicuspid valve); left ventricle; aorta; SA node; AV node; bundle of His (AV bundle); Purkinje fibers; myocardium, and coronary arteries. ◦ Can you describe the flow of blood through the heart? (Be sure to identify the major blood vessels, chambers, and heart valves.) ◦ What are the sequential events of the cardiac conduction system that result in a heartbeat (cardiac contraction)? ◦ What is the electrocardiogram used to determine? Can you differentiate between the P wave, the QRS complex, and the T wave? ◦ What is the sphygmomanometer used to determine? ◦ What is a myocardial infarction? ◦ What is a heart murmur? ◦ What is the purpose of coronary bypass surgery? Questions to consider when studying for the exam ` How does structure relate to function? ` Are you able to recognize examples and apply knowledge? ` Do you know the sequential steps of any mechanisms discussed?