BIO 141 Exam 4 Study Guide What vessels carry blood away from
advertisement

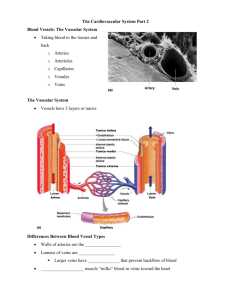
BIO 141 Exam 4 Study Guide What vessels carry blood away from the heart? What vessels carry blood to the heart? What vessels are the turn around point and site of exchange? Describe the three main layers that make up the walls of blood vessels? Tunica Interna Tunica Media Tunica Externa What are the characteristics of arteries? What are the characteristics of elastic arteries? What are the characteristics of muscular arteries? What are anastomoses? What are the characteristics of arterioles? What are the characteristics of capillaries? What vessels lead to the capillaries? What vessels lead away from capillaries? What is a capillary bed? What are the two types of flow through a capillary bed? Describe the characteristics of the different types of capillaries. Continuous Capillaries Fenestrated Capillaries Sinusoids What is portal circulation? What are the characteristics of venules? What are the characteristics of veins? What are anastomose veins? What are superficial veins? What are deep veins? Where is the greatest amount of blood found at any given time in your body? What is capillary exchange? How does capillary exchange occur? How does it cross the capillary wall? What molecules cross with each? Intercellular Clefts Fenestrations Endothelial Cell Membranes Sinusoids What is trancytosis? How does it work? What type of molecules can cross this way? What is bulk flow? How does it work? What type of molecules can cross this way? What is filtration? What is reabsorption? What is Starling’s Law of the Capillaries? How does it work? What is hemodynamics? What determines blood pressure in arteries? Where is the highest blood pressure found? What is systolic blood pressure? What is considered “normal”? What is diastolic blood pressure? What is considered “normal”? Where is the lowest blood pressure found? What is mean arterial pressure? What is vascular resistance? What 3 factors affect resistance? Where would you find the highest resistance? Where would you find the lowest resistance? What is venous return? What controls venous return? Where is blood flow fastest? Where would you expect it to be slowest? What is circulation time? What interconnected negative feedback systems control blood pressure and flow? Where is your cardiovascular center located? Describe the function of each area of the cardiovascular center? Cardiostimulatory Area Cardioinhibitory Area Vasoconstrictor Area Vasodilation Area Where can nervous inputs come from to control flow and pressure? What outputs create the effects? What nerves carry input to the brain to regulate blood pressure? What parts of the body are affected by the output from the cardiovascular center? Is this regulation a negative or positive feedback loop? Where are chemoreceptors located to control blood pressure? What do they sense? What is hypoxia? What is acidosis? What is hypercapnia? Describe the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone (RAA) System? What does it affect? How does it work? How does epinephrine/norepinephrine work to control blood pressure? How does the antidiuretic hormone work to control blood pressure? How does natriuretic peptide work to control blood pressure? What does a pulse rate measure? What is considered normal at rest for adult? What is tachycardia? What is bradycardia? Name come common pulse points. What is shock? Name and describe the 3 types of shock. What are the responses to shock? What are the signs and symptoms of shock? Describe the 3 circulation routes? Systemic Circulation Pulmonary Circulation Fetal What is the upper respiratory system? What is the lower respiratory system? What is the conducting zone? What is the respiratory zone? What is the function of the nose? Describe the structures of the nose. External Nose Internal Nose Where does the nose open in to? What is the function of the pharynx? Describe the structures of the pharynx. Nasopharynx Oropharynx Laryngopharynx What is the function of the larynx? What are the nine pieces of the cartilage that make up the pharynx, and where are they located? What part of the larynx is responsible for voice production? Where is it located? Where can the sound be resonated? What is the function of the trachea? What are the 4 layers of the trachea, what are they composed of? What are the bronchi? What is the structure? Describe the right bronchus Describe the left bronchus What is the carina? What are the secondary bronchi? What are the tertiary bronchi? What are bronchioles? Where are they located? What is their structure? What are terminal bronchioles? Where are they located? What is their structure? What is the bronchial tree? What structural changes occur with branching of the bronchial tree? What is the function of your lungs? What is the pleural membrane? What is the parietal pleura? What is the visceral pleura? What is the pleural cavity? What is pleurisy? What is pleural effusion? What is a hemothorax? What is pneumothorax? Describe the surface anatomy of the lungs. Base Apex Costal surface Mediastinal surface What is the hilum? Cardiac notch Which lung is larger? What is the oblique fissure? Describe it on the left lung Describe it on the right lung What is the horizontal fissure? Where is it found? Be able to label the diagrams on 24/25 What is an alveoli? What are they supplied by? What are alveolar sacs? What are the 2 types of epithelium in an alveoli? What is the respiratory membrane? Where do the lungs receive blood from? Pulmonary Bronchial What is the process of pulmonary ventilation? What are the 3 steps of pulmonary ventilation? How do pressure changes affect the movement of air in and out of the lungs? What factors affect ventilation? Surface Tension Compliance Airway resistance How does gas exchange occur? Where does gas exchange occur? What is Dalton’s Law, and how does it affect gas exchange? What is Henry’s Law and how does it affect gas exchange? How is oxygen transported in the blood? How much is dissolved? How much is carried on hemoglobin? What is full saturation of hemoglobin? What is partial saturation of hemoglobin? Where is oxygen loaded on to hemoglobin? Where does oxygen dissociate from hemoglobin? Be able to label the oxygen dissociation curve under Normal conditions Acidic conditions In response to carbon dioxide In response to temperature In response to BPG What is the difference between adult and fetal hemoglobin? How is carbon dioxide carried in the blood? How much is dissolved? How much is carried on hemoglobin? How is carbon dioxide attached to hemoglobin? How much is in the bicarbonate ion? What part of your brain controls respiratory rate? Describe each of the areas in the respiratory center? Medullary Rhythmicity Center Pneumotaxic Area (pons) Apneustic Area What are the cortical influences on the respiratory rate? Where are peripheral chemoreceptors located? What do they detect? How do proprioceptors control respiratory rate? What is the inflation reflex? What can send signals to the respirator center? Limbic System Temperature Pain Stretching Anal Sphincter Irritation of Airways Blood Pressure