Presentation
advertisement

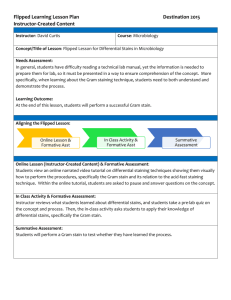
How do I know if my submission is appropriate for the Critical Thinking Question Bank (CTQB)? Samantha Elliott St. Mary’s College of Maryland CTQB Resource Session ASMCUE 2012 Bloom’s Taxonomy Knowledge Comprehension Application Analysis Synthesis Evaluation Lower-order cognitive skills Higher-order cognitive skills • To reach higher-order thinking, students must be able to complete lower order skills The Blooming Biology Tool • Crowe et al. (2008) CBE-Life Sci Ed vol 7: 368381 • 5 Bloom’s levels appropriate for multiple choice questions – All except synthesis • Appropriate for CTQB: Application, Analysis or Evaluation Lower-order cognitive skills questions (Crowe et al. 2008) • Knowledge – Recall of information – No significant distractors • Comprehension – Understanding of concept or terms – Includes significant distractors to test student misconceptions Higher-order cognitive skills questions (Crowe et al. 2008) • Application – Prediction of most likely outcome – New situation or perturbation of system • Analysis – Data interpretation and selection of best conclusion • Evaluation – Assessment of information relative to support of an argument Caveats/Suggestions • Bloom’s level can be modified depending on how the information is presented in the classroom. • Not a perfect system • Use author comments to help reviewers understand why you think the question addresses higher-order cognitive skills. Time to practice! Which of the following is the correct order of the steps of a Gram stain? 1(A). Safranin Iodine Alcohol Crystal violet 2(B). Crystal violet Iodine Alcohol Safranin 3(C). Iodine Crystal violet Alcohol Safranin 4(D). Alcohol Safranin Iodine Crystal violet 5 (E). Crystal violet Iodine Safranin Alcohol Bloom’s level: Knowledge Author’s comments: This question tests the ability of the student to recall the steps of a Gram stain. There is no higher order thinking other than memorization. Depending upon the specific reagents used in the classroom, instructors can substitute more specific terms for “Iodine” and “Alcohol.” Scientists engineer a Gram-positive bacterium to express a polysaccharide-rich outer capsule. What effect would this have on a Gram stain of this engineered organism? 1 (A). It would still stain as a Gram-positive bacterium. 2 (B). It would stain as a Gram-negative bacterium. 3 (C). It would become a Gram-indeterminate bacterium. 4 (D). It would become a Gram-variable bacterium. 5 (E). Cannot tell from the information provided. Bloom’s level: Application Author’s comments: This is a classic perturbation of the system, testing the ability of students to understand what happens to a Gram stain when you add in a polysaccharide capsule. Note that application questions can require either lower- or higher-order cognitive skills. For purposes of CTQB, we accept any multiple choice question at application level or higher according to Bloom’s taxonomy. As your final project in Microbiology lab, you are tasked with identifying a single, unknown organism. One of your friends asks you to check over her work to see if it makes sense. She hypothesizes that she has identified a gut-associated bacterium based upon the results in the table below. Based upon these results, choose the best answer in regards to your friend’s hypothesis. Gram stain negative Cell Motility? Spores? morphology short rod yes no Lactose fermentation Oxygen requirements positive facultative anaerobe 1 (A). Her hypothesis is correct. It’s definitely a gut-associated organism. 2 (B). Her hypothesis may be correct. She should run a coagulase test to be sure. 3 (C). Her hypothesis may be correct. She should grow the organism on MacConkey agar to be sure. 4 (D). Her hypothesis is incorrect. It’s definitely a soil-associated organism. 5 (E). Her hypothesis is incorrect. She should run more tests to identify the organism. Bloom’s level: Evaluation Author’s notes: This question not only requires data interpretation, but the use of this information to support a specific hypothesis, making it an evaluative item. Enteric organisms can grow in the presence of bile salts, which are present in MacConkey agar. Because this organism is already identified as a Gram-negative bacterium, MacConkey agar is an appropriate choice because it selects for growth of only Gram-negative bacteria. MacConkey agar would be inappropriate for a Gram-positive enteric organism, such as Enterococcus species. A bile esculin test would be more appropriate for those organisms. Which step of the Gram stain dissolves lipids within the cell wall? A. Crystal violet B. Iodine C. Alcohol D. Safranin E. Water Bloom’s level: Comprehension Author’s comments: This question tests the ability of students to comprehend the purpose of different steps in the Gram stain. While it is still lower-level cognition, more thought than simple memorization is required. Depending upon the specific reagents used in the classroom, instructors can substitute more specific terms for “Iodine” and “Alcohol.” Your microbiology class is characterizing a single unknown bacterium. Each member of the class performs three independent Gram stain replicates on the culture, and adds their results to the table below. Which of the following is the best conclusion about your aggregate data? Name Age of cultures Cell Morphology Gram stain results John 10-12 hours Rod, in chains Gram positive, Gram positive, Gram positive Sue 12-14 hours Rod, in chains Gram positive, Gram positive, Gram positive 12 hours Rod, in chains Gram positive, Gram negative, Gram positive Liz 12-24 hours Rod, in chains Gram positive, Gram negative, Gram negative Steve 24-36 hours Rod, in chains Gram negative, Gram negative, Gram negative Mary 1 (A). Fresh staining solutions should be made and the Gram staining performed again. 2 (B). The unknown bacterium is Gram positive. Changes in cell wall structure cause older cultures to stain differently. 3 (C). The unknown bacterium is Gram negative. Newer cultures have incomplete cell walls which cause them to stain differently. 4 (D). The unknown bacterium is Gram indeterminate. 5 (E). Students should practice their Gram staining technique on known bacteria before trying this experiment again. Bloom’s level: Analysis Author’s comments: This question requires students to interpret data and select the best outcome. The primary concept tested here is that age of culture plays a huge role in the outcome of a Gram stain. Newer cultures are better indicators of Gram type than older cultures. Your turn!