Chapter 14 Study Guide
advertisement

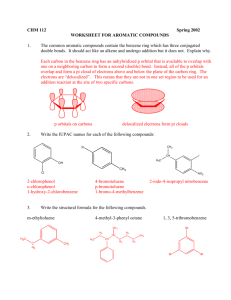
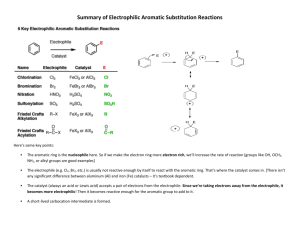
1 Chapter 14 Study Guide 1825 Michael Faraday discovers benzene. 1834 Mitscherlich synthesizes benzene from benzoic acid. The new compound has an index of hydrogen deficiency(I.H.D.) of 4. IE. 6 carbon structure should have 14 hydrogens(C n H2n+2 ). Benzene only has 6 hydrogens. Therefore, it is missing 8 hydrogens or IHD = 4. Each index is equal to a double bond or ring. Therefore this is a highly unsaturated compound. This led to classification of all organics as aliphatic or aromatic. Kekule def. of aromatic— Know structures page 624— Ortho/para/meta—only refer to disubstituted benzenes. If the two substituents are next to each other it is ortho. If the two substituents are separated by one carbon it is meta. If the two substituents are opposite each other it is para. If both of the substituents are methyl groups the molecule is called xylene. Nomenclatue—substituents are listed alphabetically. If more than two substituents then they are numbered to have the lowest possible number. If benzene is a substituent it is called phenyl. The benzyl group is a benzene with a CH2 attached. Benzene is non-reactive to ordinary alkene chemical reactions. 2 More Nomenclature notes CH3 OH Toluene NH2 Phenol SO3H Aniline Benzenesulfonic acid O CH3 COOH Benzoic Acid o-xylene O Acetophenone Anisole m-xylene p-xylene 3 Kekule structure of benzene Benzene only reacts by substitution not addition. Search for other nonbenzene aromatics led to cyclooctatetraene(COT). COT reacts by addition not substitution. Therefore it is not aromatic. Comparison of ∆H of benzene to its predicted ∆H leads to discovery of resonance stabilization energy. Modern structure of benzene Benzene is a planar molecule with a high degree of delocalization as per MOT. Modern theory of Aromaticity—Huckel’s rule(4N+2) To be aromatic, a compound must be planar, cyclic with alternating single and double bonds and must follow Huckel’s rule(i.e. have 2, 6, 10, 14, 18…pi electrons). By MOT, all pi electrons must be in bonding orbitals and not anti-bonding orbitals(p. 633). Annulenes— [10] annulene is not aromatic because it can’t be planar. By NMR, if all aromatic hydrogens show as one peak then they are equivalent and aromatic. See p. 636 also. 4 Other Aromatics Ions Cyclopentadienyl(636) and tropylium ions. empty p-orbital due to cation Aromatic, antiaromatic, nonaromatic ∆H comparison of cyclic to straight chain. Benzenoid/Nonbenzenoid Aromatic compounds Page 640-643 Heterocyclic aromatic compounds Page 644-645 Sunscreen 5 Other Aromatic Compounds Benzenoid pyrene C16H10 Benzo[a]pyrene C20H12 Dibenzo[a,l]pyrene C24H14 8 double bonds = 16 pi electrons? Internal double bond (red) does not participate. Only 14 pi electrons. 6 Br2/CCl4 Br Br [14]Annulene Nonbenzenoid Aromatic Compounds 5 perimeter double bonds = 10 pi electrons Huckel # = aromatic 7 pyridine N pyrrole furan N O thiophene S H Pyridine has 3 Pyrrole, furan and thiophene all have 2 double bonds double bonds and and 4 pi electrons. Therefore one lone pair is needed to 6 pi electrons so the achieve aromaticity. lone pair does not participate in aromaticity 8 9 Chapter 14 and 15 Practice 1. Assuming the following are planar, tell if they are aromatic are not. Also explain your answer. 2 single bonds destroys aromaticity. B A C Ring A is aromatic. It is cyclic, planar, has 14 Π electrons and alternating double and single bonds. Ring B is aromatic. It is cyclic, planar, has 10 Π electrons, and because of + charge has alternating double and single bonds. Ring C is not aromatic. Although planar, cyclic and 18 Π electrons it does not have alternating double and single bonds. 2. Give a spectroscopic values for the following. H H NMR ___6-9.5_ _ Major UV peaks ____205 and 250-275_ C NMR __100-170_ Major IR peaks above 1200 _______3030 and 4 peaks from 1450-1600___________________ 10 HOMEWORK Determine if the following are aromatic, explain your answers Reason: Reason: Reason: Reason: Reason: 11 HOMEWORK--KEY Aromatic Aromatic Nonaromatic Reason: Reason: Reason: Negative anion contributes to pi-electrons. 6 pielectrons = aromatic sp2 hybridized carbocation Allows for delocalization of pi-electrons Not cyclic Aromatic Not Aromatic Reason: Reason: 18 pi electrons. 2 internal double bonds do not contribute to aromaticity. 20 pi electrons is not a Huckel number.