Chem 207 Midterm 1 (A) 30.04.2010
advertisement

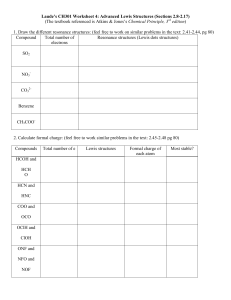
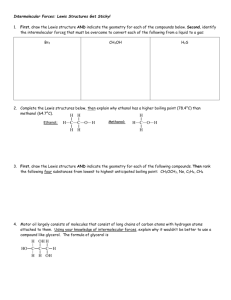
Chem 207 Midterm 1 (A) 30.04.2010 Name___________________________________ Student Number__________________________ 1) An oxygen atom has __________ valence electrons. 2) Draw a correct Lewis structure for boric acid, B(OH)3. 3) Covalent bonds may be polar or nonpolar. What property of the atoms forming a given bond determines this? 4) Which of the following choices represent(s) a pair of resonance forms? A) B) C) D) both A and C E) both B and C 5) The Lewis structure of trimethylamine is shown below. Draw the condensed structural formula which corresponds to this Lewis structure. 6) Draw an acceptable line-angle formula for cyclobutanol (shown below). 1 7) Draw a correct Lewis structure for acetaldehyde, CH3CHO. 8) Consider the set of compounds, NH3, HF, and H2O. Rank these compounds in order of increasing acidity and discuss your rationale. 9) Would you predict trifluoromethanesulfonic acid, CF3SO3H, to be a stronger or weaker acid than methanesulfonic acid, CH3SO3H? Explain your reasoning. 10) Which of the following terms comes closest to describing an electrophile? A) Lewis base B) anion C) nucleophile D) Lewis acid E) nonpolar 10) ______ 11) Consider the species CH3O-, NH2-, and CH3COO-. Rank these ions in order of increasing basicity, and explain your rationale. 2 12) When methanol (CH3OH) acts as a base, its conjugate acid is __________. A) CH4O+ 12) ______ B) -CH2OH C) CH3OH2+ D) CH3OE) CH4OH 13) Draw the important resonance forms of: 14) One or more of the atoms in the structure shown should have nonzero formal charges. Redraw the structure and indicate any such charges. 15) What kind of molecular orbital (σ, σ*, π, or π*) results when the two atomic orbitals shown below interact in the manner indicated? 16) What kind of molecular orbital (σ, σ*, π, or π*) results when the two atomic orbitals shown below interact in the manner indicated? 17) The CCO bond angle in acetone (CH3COCH3) is __________. 18) Choose the correct hybridization for the atom indicated in the molecule below. A) sp C) sp2 17) _____________ 18) ______ B) sp3 D) none of the above 3 19) Which of the molecules below is an ester? A) CH3COOCH3 19) ______ B) CH3COOH C) CH3CH2CH(CH3)2 D) HC≡CCH3 E) CH3OCH2CH2CH3 20) Which of the molecules below has the higher boiling point? Briefly explain your choice. CH3CH2CH2OH or CH3CH2OCH3 21) Which of the molecules below has the higher boiling point? Briefly explain your choice. CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3 or (CH3)2CHCH2CH3 22) Which compound is more soluble in water? Briefly explain your choice. CH3OCH3 or CH3CH2OH 23) What type of intermolecular force results from the attraction of coordinated temporary dipoles induced in adjacent molecules? 24) Draw the three-dimensional structure of chloroform (CHCl3) and show the direction of the molecular dipole moment. 4 25) What hybrid atomic orbitals are overlapping to form the carbon-oxygen s bond in acetaldehyde (CH3CHO)? Draw a bonding diagram showing the hybridization of each 25) _____________ overlapping orbital making a bond and indicate the type of each bond. 5 1) 6 2) or 3) Electronegativity 4) E 5) (CH3)3N 6) 7) 8) NH3 < H2O < HF When determining relative acidity, it is often useful to look at the relative basicity of the conjugate bases. The stronger the acid, the weaker (more stable, less reactive) the conjugate base. In this case, one would look at the relative basicity of F-, OH-, and NH2-. The relative strengths of these species can be gauged based on the electronegativity of the charged atom in each. Since fluorine is the most electronegative, F- is the most stable, least reactive base in the group. This means that its conjugate acid, HF, is the strongest. 9) Trifluoromethanesulfonic acid is a stronger acid. Compare the strengths of the conjugate bases and remember that the weaker the base, the stronger the conjugate acid. Both bases are stabilized by resonance, but in the case of the trifluoro derivative, the presence of the highly electronegative fluorine atoms serves to delocalize the negative charge to an even greater extent. This additional delocalization makes trifluoromethanesulfonate a weaker base. 10) D 11) CH3COO- < CH3O- < NH2The first factor to consider is the nature of the atom which bears the negative charge. The more electronegative the atom that bears the negative charge, the more stable the anion. Stable anions are less reactive and are hence weaker bases. Since O is more electronegative than N, the NH2- is the strongest base in the set. In the remaining two species, the negative charge is on the O, but in the case of CH3COO-, the negative charge is also delocalized by resonance. 12) C 13) 14) 6 15) σ 16) σ* 17) approximately 120° 18) C 19) A 20) CH3CH2CH2OH has the higher boiling point since it is capable of intermolecular hydrogen bonding. 21) CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3 has the higher boiling point. As the degree of branching increases, the surface area of the molecule decreases and the potential for intermolecular attraction via London forces decreases. Greater surface area leads to a more intermolecular attraction which in results in a higher boiling point. 22) CH3CH2OH is more soluble in water since it can donate a hydrogen bond to water and accept a hydrogen bond from water. CH3OCH3 can only accept a hydrogen bond from water; it does not have hydrogen which can hydrogen bond to water. 23) London dispersion forces 24) 25) carbon sp2 and oxygen sp2 7