Curved Bacteria & Spirochaetes
advertisement
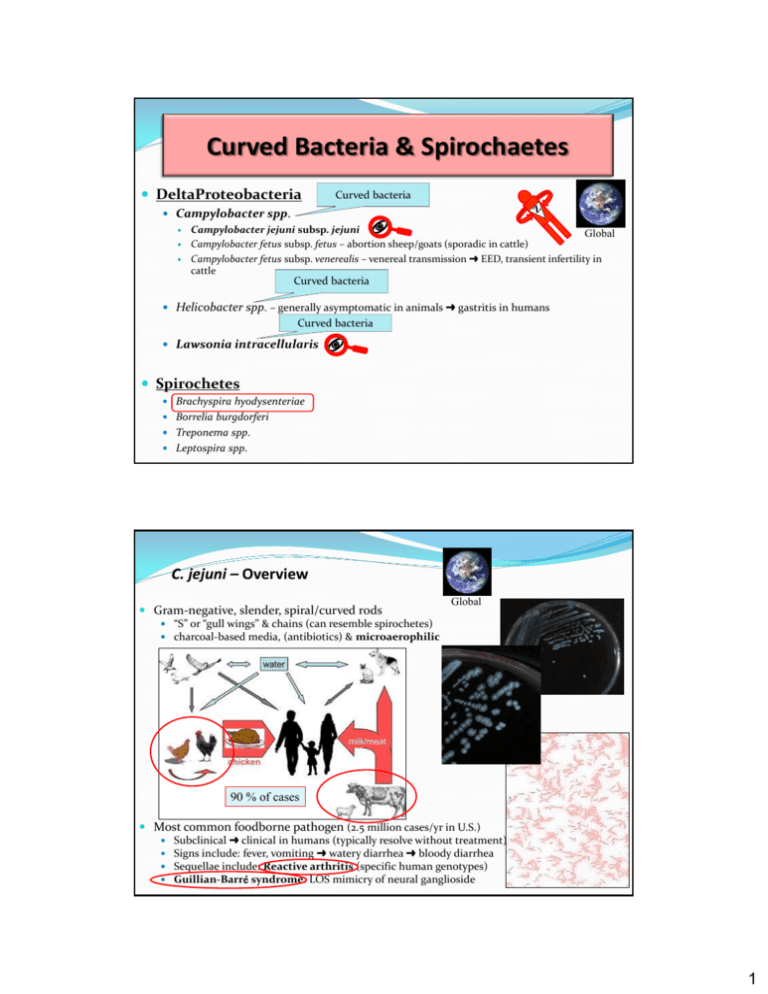
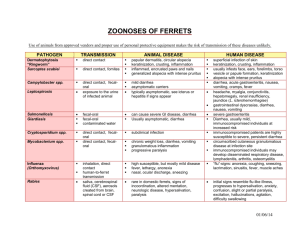
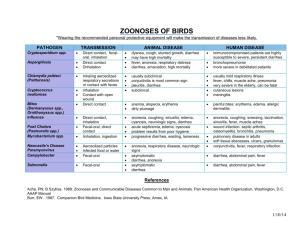
Curved Bacteria & Spirochaetes DeltaProteobacteria Curved bacteria Campylobacter spp. Campylobacter jejuni subsp. jejuni Global Campylobacter fetus subsp. fetus – abortion sheep/goats (sporadic in cattle) Campylobacter fetus subsp. venerealis – venereal transmission EED, transient infertility in cattle Curved bacteria Helicobacter spp. – generally asymptomatic in animals gastritis in humans Curved bacteria Lawsonia intracellularis Spirochetes Brachyspira hyodysenteriae Borrelia burgdorferi Treponema spp. Leptospira spp. C. jejuni – Overview Gram-negative, slender, spiral/curved rods Global “S” or “gull wings” & chains (can resemble spirochetes) charcoal-based media, (antibiotics) & microaerophilic 90 % of cases Most common foodborne pathogen (2.5 million cases/yr in U.S.) Subclinical clinical in humans (typically resolve without treatment) Signs include: fever, vomiting watery diarrhea bloody diarrhea Sequellae include: Reactive arthritis (specific human genotypes) Guillian-Barr syndrome: LOS mimicry of neural ganglioside 1 C. jejuni (CJ) & C. fetus (CFF): Ovine Abortion Global CJ & CFF leading cause of ovine abortions “In contrast to other diarrhea-causing pathogens .. does not express a large number of classical virulence factors.” Virulence factors: GIT epithelium FIP Flagella – colonization, host-cell invasion LOS – adhesin, host-cell invasion CadF – fibronectin-binding protein Cytolethal Distending Toxin (CDT) – host-cell DNA Pathogenesis: CJ > CFF Lamb fetus liver - Focal hepatic necrosis Dx & Intervention Smear-stain (carbol fuchsin) Fetal abomasal contents Fetal hepatic lesions Sample PCR &/or Culture Ingestion entry into GIT epithelium translocation into submucosa phagocyte uptake dissemination to uterus/placenta necrotizing placentitis Manage sources of infection Quarantine, placenta/lamb Abx in feed? Vaccination CFF & CJ Other Campylobacter spp. & Misc. Infections C. jejuni Canine diarrhea (~ 1/3 of non-viral diarrhea cases) – human-to-dog or dog- to-human can occur (Abx - Erythromycin/Tylosin) Avian Vibrionic Hepatitis – uncommon in chickens & turkeys C. coli – swine GIT human enterocolitis FYI C. upsaliensis – canine diarrhea FYI 2 Lawsonia intracellularis: Proliferative Enteropathy Gram -ve, campylobacter-like shape Tissue culture only Swine, horses & hamsters (not humans). Global Virulence – not much known Obligate intracellular Polar flagella Type Three Secretory System LPS Gebhart, Path. Bact. Infect. Animals. 2010 Porcine Proliferative Enteropathy (PPE/PIA) economically important ’d larger herds After Erythromycin Horses – less prevalent (CVJ, 09,2007) Protein Losing Enteropathy <1 year “Wet-tail disease” in juvenile hamsters C. difficile in adults L. intracellularis: PPE/PIA Enterocyte hyperplasia 2-5 month old pigs - fecal-oral, (carrier rats) Ileum crypt Enterocytes Spread to jejunum, cecum & colon Proliferation of crypt enterocytes Thickened, firm intestinal wall & corrugated serosa Chronic form: < 4 months mild diarrhea & poor ADG/FCE CMI & sIgA clearance of pathogen Acute Form: > 4 months Silver Stained crypt Dx & Intervention PCR &/or FA Proliferative Hemorrhagic Enteropathy (PHE) Distal ileum proximal colon lumen blood clots Dysentery death Vaccination ’s pathology Abx in feed/H2O Tiamulin Tylosin 3