ZOONOSES OF SHEEP AND GOATS
advertisement
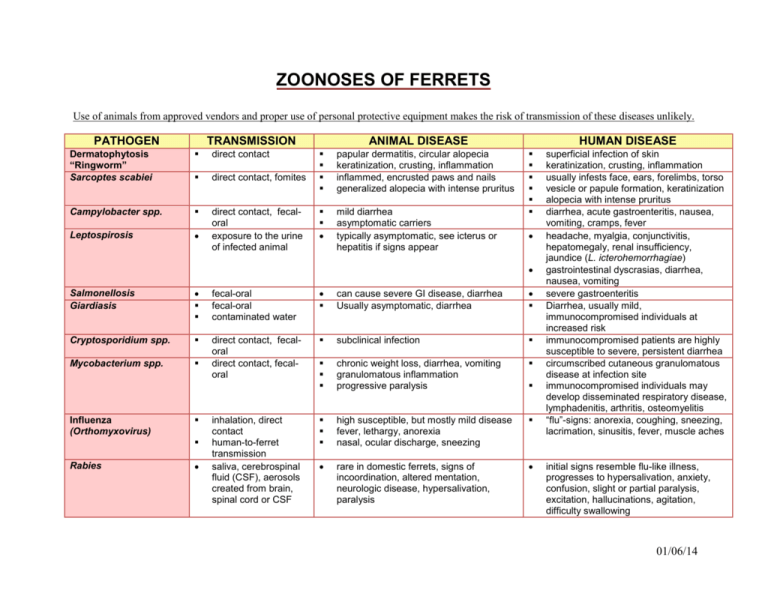
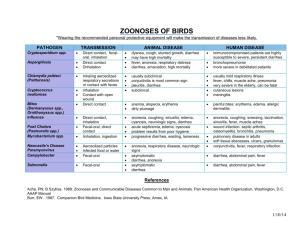
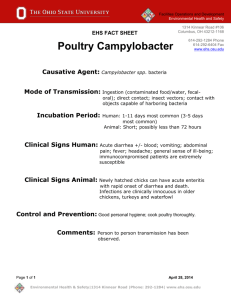
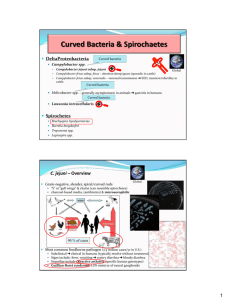
ZOONOSES OF FERRETS Use of animals from approved vendors and proper use of personal protective equipment makes the risk of transmission of these diseases unlikely. PATHOGEN TRANSMISSION Dermatophytosis “Ringworm” Sarcoptes scabiei direct contact direct contact, fomites Campylobacter spp. Leptospirosis direct contact, fecaloral exposure to the urine of infected animal ANIMAL DISEASE papular dermatitis, circular alopecia keratinization, crusting, inflammation inflammed, encrusted paws and nails generalized alopecia with intense pruritus mild diarrhea asymptomatic carriers typically asymptomatic, see icterus or hepatitis if signs appear HUMAN DISEASE Salmonellosis Giardiasis fecal-oral fecal-oral contaminated water can cause severe GI disease, diarrhea Usually asymptomatic, diarrhea Cryptosporidium spp. subclinical infection Mycobacterium spp. direct contact, fecaloral direct contact, fecaloral chronic weight loss, diarrhea, vomiting granulomatous inflammation progressive paralysis high susceptible, but mostly mild disease fever, lethargy, anorexia nasal, ocular discharge, sneezing rare in domestic ferrets, signs of incoordination, altered mentation, neurologic disease, hypersalivation, paralysis Influenza (Orthomyxovirus) Rabies inhalation, direct contact human-to-ferret transmission saliva, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), aerosols created from brain, spinal cord or CSF superficial infection of skin keratinization, crusting, inflammation usually infests face, ears, forelimbs, torso vesicle or papule formation, keratinization alopecia with intense pruritus diarrhea, acute gastroenteritis, nausea, vomiting, cramps, fever headache, myalgia, conjunctivitis, hepatomegaly, renal insufficiency, jaundice (L. icterohemorrhagiae) gastrointestinal dyscrasias, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting severe gastroenteritis Diarrhea, usually mild, immunocompromised individuals at increased risk immunocompromised patients are highly susceptible to severe, persistent diarrhea circumscribed cutaneous granulomatous disease at infection site immunocompromised individuals may develop disseminated respiratory disease, lymphadenitis, arthritis, osteomyelitis “flu”-signs: anorexia, coughing, sneezing, lacrimation, sinusitis, fever, muscle aches initial signs resemble flu-like illness, progresses to hypersalivation, anxiety, confusion, slight or partial paralysis, excitation, hallucinations, agitation, difficulty swallowing 01/06/14 References Acha, PN and B Szyfres. 1989. Zoonoses and Communicable Diseases Common to Man and Animals. Pan American Health Organization, Washington, D.C. Hillyer, EV and KE Quesenberry. 2011. Ferrets, Rabbits, and Rodents: Clinical Medicine and Surgery. WB Saunders Co., Philadelphia, PA. Fox, JG. 1988. Biology and Diseases of the Ferret. Lea & Febiger Publishing, Philadelphia, PA. Global Health Disease Fact Sheets, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 1600 Clifton Rd. Atlanta, GA 30333, USA, http://www.cdc.gov/ 01/06/14