Redox Titration Lab: H2O2 Determination
advertisement

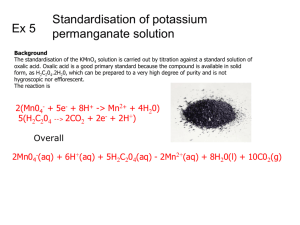
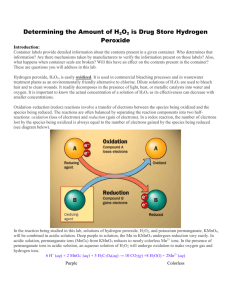
AP Chemistry L4-4 Redox Titration Lab Determination of the % H2O2 in a store bought bottle of H2O2 Purpose 1. Standardize a solution of KMnO4 by titration of oxalic acid solution. 2. Determination of the % H2O2 in a store bought bottle of H2O2 by titration with the standardized solution of KMnO4. Part 1 – Standardization of Potassium Permanganate Solution using Oxalic Acid Safety – •Wear goggles. •Wearing rubber gloves is recommended if handling chemicals. •Sulfuric acid is corrosive to skin and eyes. •Potassium Permanganate is toxic and a strong oxidizer. •Oxalic acid is slightly toxic, avoid breathing vapors. Materials •Ring stand •Buret clamp •3 125mL Erlenmeyer flasks, •Analytical balance •3M H2SO4 •50 mL buret •Small beaker •100 mL graduated cylinder •Solid oxalic acid, H2C2O4•2H2O •0.02M KMnO4 Procedure 1. On an analytical balance, mass 0.0500 g oxalic acid, H2C2O4. Place in the Erlenmeyer flask. 2. Dissolve this with 50 mL H2O that has been heated to 80°C. 3. Add 15 mL 3M H2SO4 to the flask. Swirl. 4. Fill 50 mL buret with 0.02M KMnO4 solution. 5. Record the starting volume of KMnO4to the nearest 0.05mL. 6. Slide a piece of white paper under the flask during the titration. Titrate the oxalic acid solution in the flask with the KMnO4 until a permanent pink/purple color results. 7. Record the final volume on the buret. 8. Pour waste titrant in the waste bottle. 9. Repeat procedure until you have three good results. AP Chemistry L4-4 Redox Titration Lab Determination of the % H2O2 in a store bought bottle of H2O2 Part 2 - Determination of the % H2O2 in a store bought bottle of H2O2 Materials Same as part 1, but replace oxalic acid with 3% H2O2. Procedure – 1. Place a clean Erlenmeyer flask on an analytical balance and tare (zero). 2. Remove the flask from the balance, pipette 1.0 mL H2O2 into the flask, return the flask to the balance, record the mass of the added H2O2. 3. Remove the flask from the balance, add 10 mL of 3M H2SO4 to the flask. 4. Add 50 mL of room temperature distilled water. 5. Record the starting volume of KMnO4 on the buret. 6. Slide a piece of white paper under the flask during the titration. Titrate the hydrogen peroxide solution in the flask with the KMnO4 until a permanent pink/purple color results. 7. Record the final volume on the buret. 8. Pour waste titrant in the waste bottle. 9. Repeat procedure until you have three good results. Calculations and Analysis – Part 1 – 1. The unbalanced reaction equation for Part 1 is: MnO4- + C2O4-2 Mn+2 + CO2 Balance the equation using the half reaction method. 2. Calculate moles of oxalic acid (H2C2O4) used. (Note: oxalic acid is a hydrate.) 3. Calculate moles of permanganate ion reacted. 4. Calculate the concentration (in units of Molarity) of the potassium permanganate solution. 5. Average your results. This is the concentration of the now “standardized” solution of KMnO4 that will be used in Part 2. Part 2 – 1. The unbalanced reaction equation for Part 2 is: MnO4- + H2O2 Mn+2 + O2 Balance the equation using the half reaction method. 2. Knowing the concentration of the permanganate ion and the volume used, calculate the moles of permanganate ion used. 3. Calculate the moles of hydrogen peroxide in your sample. 4. Calculate the number of grams hydrogen peroxide in your sample. 5. Calculate the percentage by mass of hydrogen peroxide in your sample. 6. Calculate the average % by mass of hydrogen peroxide from your three trials. Data Analysis and ConclusionWrite a conclusion.