AMB Country Risk Report
August 18, 2015
Our Insight, Your Advantage.
Australia
Country Risk Tier
• The Country Risk Tier (CRT) reflects A.M. Best’s assessment
of three categories of risk: Economic, Political and Financial
System Risk.
CRT-1
• Australia is a CRT-1 country with very low levels of economic,
political and financial system risk.The Australian economy
has experienced over 20 years of uninterrupted economic
expansion, which includes the global financial crisis.
Economic Risk
Finland
• Australia’s strong economic position before the global
economic slowdown and the aggressive monetary and fiscal
policies implemented
throughout helped to make the slowdown
Russia
relatively mild for the country. Growth is expected to continue
at a rate of 2.8% in 2015 and accelerate to 3.2% in 2016.
Moderate
Low
Estonia
High
Russia
Latvia
Lithuania
Belarus
Very Low
Poland
Slovakia
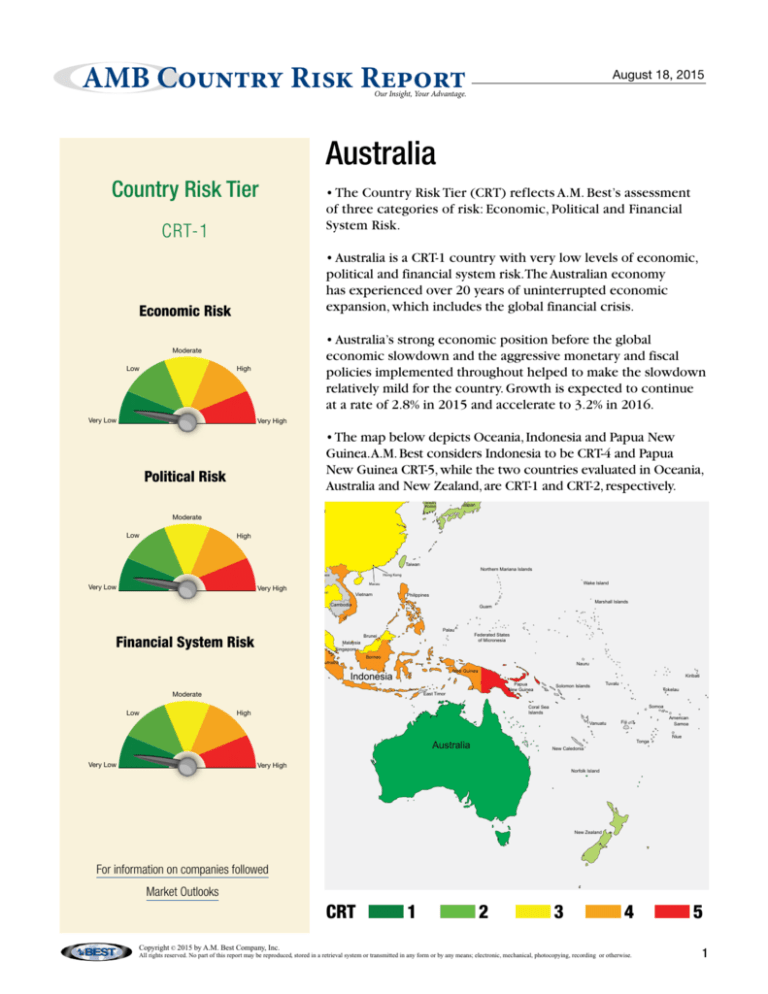
• The map below depicts Oceania, Indonesia and Papua New
Guinea.A.M. Best considers Indonesia to be CRT-4 and Papua
New Guinea CRT-5, while the two countries evaluated in Oceania,
Australia and New Zealand, are CRT-1 and CRT-2, respectively.
Kazakhstan
Republic of
Moldova
Hungary
Sakhalin
Very High
Ukraine
Mongolia
Romania
a
a & Serbia
vina
ontenegro
Political Risk
Russia
Bulgaria
Georgia
Macedonia
Armenia
Albania
Kyrgyzstan
Azerbaijan
Uzbekistan
Turkey
Greece
Cyprus
Turkmenistan
Syria
Lebanon
Iraq
Israel
Low
Kuwait
ya
Pakistan
Bahrain
Egypt
Nepal
Sudan
Bhutan
Bangladesh
Myanmar
India
Very Low
Very High
Yemen
Eritrea
Japan
High
U.A.E.
Oman
had
South
Korea
China
Qatar
Saudi Arabia
Taiwan
Northern Mariana Islands
Hong Kong
Laos
Wake Island
Macau
Thailand
Vietnam
Philippines
Cambodia
Somalia
Sri Lanka
l Africa Republic
Uganda
Financial System Risk
ia
Brunei
Sumatra
Tanzania
Moderate
Malawi
Comoros
Zimbabwe
Low
East Timor
Kiribati
Papua
New Guinea
Solomon Islands
Tuvalu
Tokelau
Somoa
Coral Sea
Islands
High
Australia
Reunion
Very Low
Very High
Lesotho
Cook
Islands
American
Samoa
Fiji
Mauritius
Madagascar
Swaziland
Nauru
New Guinea
Vanuatu
Mozambique
Botswana
Federated States
of Micronesia
Borneo
Indonesia
Seychelles
Zambia
Palau
Malaysia
Singapore
Kenya
Rwanda
Dem. Republic
Burundi
of Congo
a
Marshall Islands
Guam
Dijbouti
Ethiopia
s
nd
la
Is
North Korea
Tajikistan
Afghanistan
Moderate
Iran
Jordan
ril
Ku
Tonga
Niue
New Caledonia
Norfolk Island
South Africa
New Zealand
For information on companies followed
Market Outlooks
CRT 1 2 3 4 5
Copyright © 2015 by A.M. Best Company, Inc.
All rights reserved. No part of this report may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system or transmitted in any form or by any means; electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise.
1
AMB Country Risk Report
Australia
Regional Summary: Oceania
• Oceania, whose largest two nations,
Australia and New Zealand, make up
the vast majority of economic activity,
is located in the South Pacific Ocean.
Australia and New Zealand have strong
political and cultural ties with the United
Kingdom, enjoy high living standards and
benefit from an educated population.
• Australia and New Zealand have close
economic ties with Southeast Asia. In
2009 the ASEAN-Australia and New
Zealand Free Trade Area (AANZFTA) was
established which has been successful in
increasing trade throughout the region,
representing over 620 million people and
$4.1 trillion USD.
• The region is expected to grow
modestly in the coming years, with both
Australia and New Zealand forecasted to
grow in the range of 2.5 to 3.5% in 2015
and 2016. Growth will likely be driven
by accommodative monetary policy, low
inflation, currency depreciation boosting
exports and weak fuel prices.
Vital Statistics 2014
Nominal GDP
Population
GDP Per Capita
Real GDP Growth
Inflation Rate
Premiums Written (Life)
Premiums Written (Non-Life)
Premiums Growth (2013 - 2014)
Country Risk Tier
CRT-1
CRT-4
CRT-2
CRT-3
CRT-2
CRT-1
Australia
Indonesia
Japan
Malaysia
New Zealand
Singapore
Source: IMF, Axco, Swiss Re and A.M. Best
Economic Growth
• The Australian economy is dominated
by its services sector, which accounts
for nearly 70% of GDP. The largest
components are finance, property, and
business services.
5
Real GDP
CPI Inflation
4.5
4
3.5
3
%
2.5
2
1.5
1
0.5
0
• With strong institutions, a flexible
economy and supportive monetary policy
it is likely the commodity lead weakness
will be short-lived.
1444.19
23.6
61,219
2.7
2.5
56,151
31,924
12.4
Regional Comparison
Economic Risk: Very Low
• Atypically slower growth of about 2.5%
is expected in 2015 due to a weakened
mining sector, low non-mining sector
investment, and slower external demand
as China cools and the eurozone remains
weak. Further monetary easing is
possible if the economy does not show
signs of improvement.
USD bn
mil
USD
%
%
USD mil
USD mil
%
2006
2007
2008
2009
2010
2011
2012
2013
2014
2015
2016
2017
2018
2019
2020
Source: IMF World Economic Outlook and A.M. Best
2
AMB Country Risk Report
Australia
Political Risk: Very Low
Political Risk Summary
• Most of Australia’s population and
economic activity is concentrated along
the country’s eastern coast.
Score 1 (best) to 5 (worst)
Australia
World Average
International Transactions
Policy
5
4
Legal System
• Australia’s legal system is very strong,
stable and transparent with minimal
corruption.The stable regulatory
environment and fair treatment of foreign
investors make the country a destination
for foreign direct investment.
Monetary Policy
3
2
1
Regional Stability
Fiscal Policy
0
Social Stability
Business Environment
Government Stability
• Projected weaker fiscal revenues in the
2015 budget will leave an estimated AUD
52 billion shortfall.The government still
hopes to reach a balanced budget by 2020
through budget initiatives, stronger tax
revenues with a recovery in commodity
prices and some fiscal conservatism. While
not ideal, Australia does have the financial
flexibility currently to run a budget deficit.
Labor Flexibility
Source: A.M. Best
GDP Per Capita and Population
for Selected Countries
Financial System Risk: Very Low
300
70,000
GDP Per Capita
• According to the World Bank, Australia’s
business environment is ranked #10 out of
189 countries in terms of their 2015 Ease
of Doing Business survey.
Population
60,000
250
50,000
200
• The Australian Prudential Regulation
Authority (ARPA) and the Australian
Securities and Investment Commission
(ASIC) are the ultimate regulatory
authorities for the insurance industry in
Australia. ARPA is the prudential regulator
of the entire financial services industry
and conforms to international standards.
USD
Millions
40,000
150
30,000
100
20,000
50
10,000
0
• Australian banks are sufficiently
capitalized and profitable; however, under
a stressed scenario, they have an outsized
exposure to the housing market through
mortgage lending.
Australia
Indonesia
Source: IMF and A.M. Best
Japan
Malaysia
New Zealand
Singapore
0
• The Reserve Bank of Australia lowered
the base lending rate by 50 basis points
to a rate of 2% in the first half of 2015 in
response to slower growth, low inflation
and weaker commodity prices.There is
potential for further cuts.
3
AMB Country Risk Report
Australia
GUIDE TO BEST’S COUnTry rISk TIErS
A.M. Best defines country risk as the risk that country-specific factors could adversely affect the claims-paying ability of an insurer. Country risk is
evaluated and factored into all Best’s Credit Ratings. Countries are placed into one of five tiers, ranging from “CRT-1” (Country Risk Tier 1), denoting
a stable environment with the least amount of risk, to “CRT-5” (Country Risk Tier 5) for countries that pose the most risk and, therefore, the greatest
challenge to an insurer’s financial stability, strength and performance.
A.M. Best’s Country Risk Tiers are not credit ratings and are not directly comparable to a sovereign debt rating, which evaluates the ability and
willingness of a government to service its debt obligations.
Country risk Tiers
Country risk Tier
Definition
CRT-1
Predictable and transparent legal environment, legal system and business infrastructure; sophisticated financial
system regulation with deep capital markets; mature insurance industry framework.
CRT-2
Predictable and transparent legal environment, legal system and business infrastructure; sufficient financial system
regulation; mature insurance industry framework.
CRT-3
Developing legal environment, legal system and business environment with developing capital markets; developing
insurance regulatory structure.
CRT-4
Relatively unpredictable and nontransparent political, legal and business environment with underdeveloped capital
markets; partially to fully inadequate regulatory structure.
CRT-5
Unpredictable and opaque political, legal and business environment with limited or nonexistent capital markets; low
human development and social instability; nascent insurance industry.
Country risk reports
A.M. Best Country Risk Reports are designed to provide a brief, high-level explanation of some of the key factors that determine a country’s Country
Risk Tier assignment. It is not intended to summarize A.M. Best’s opinion on any particular insurance market or the prospects for that market.
Categories of risk
Country Risk Reports provide scores for three categories of risk for each country. These scores are (1) Very Low; (2) Low; (3) Moderate; (4) High
and (5) Very High.
Category of risk
Definition
Economic Risk
The likelihood that fundamental weaknesses in a country’s economy will cause adverse developments for an insurer.
A.M. Best’s assessment of economic risk evaluates the state of the domestic economy, government finances and
international transactions, as well as prospects for growth and stability.
Political Risk
The likelihood that government or bureaucratic inefficiencies, societal tensions, inadequate legal system or
international tensions will cause adverse developments for an insurer. Political risk comprises the stability of the
government and society, the effectiveness of international diplomatic relationships, the reliability and integrity
of the legal system and of the business infrastructure, the efficiency of the government bureaucracy, and the
appropriateness and effectiveness of the government’s economic policies.
Financial System Risk
Financial system risk (which includes both insurance and non-insurance financial system risk) is the risk that financial
volatility may erupt due to inadequate reporting standards, weak banking system or asset markets, and/or poor
regulatory structure. In addition, it includes an evaluation of whether the insurance industry’s level of development and
public awareness, transparent and effective regulation and reporting standards, and sophisticated regulatory body will
contribute to a volatile financial system and compromise the ability of an insurer to pay claims.
Political risk Summary
To provide additional detail on the political risk in a given domicile the Country Risk Reports include the Political Risk Summary. The Political Risk
Summary is a radar chart that displays scores for nine different aspects of political risk scored on a scale of one to five with one being the least
amount of risk and five being the highest amount of risk.
Category
Definition
International Transactions
Policy
Measures the effectiveness of the exchange rate regime and currency management.
Monetary Policy
Measures the ability of a country to effectively implement monetary policy.
Fiscal Policy
Measures the ability of a country to effectively implement fiscal policy.
Business Environment
Measures the overall quality of the business environment and ease of doing business.
Labor Flexibility
Measures the flexibility of the labor market, including the company’s ability to hire and fire employees.
Government Stability
Measures the degree of stability in a government.
Social Stability
Measures the degree of social stability, including human development and political rights.
Regional Stability
Measures the degree of stability in the region.
Legal System
Measures the transparency and level of corruption in the legal system.
Country risk Tier Disclosure
A Country Risk Tier (CRT) is not a credit rating, rather it represents a component of A.M. Best’s Credit Rating Methodology that is applied to all
insurers. A CRT is not a recommendation to purchase, hold or terminate any security, insurance policy, contract or any other financial obligation
issued by a government, an insurer or other rated issuer, nor does it address the suitability of any particular policy, contract or other financial
obligation for a specific purpose or purchaser.
Copyright © 2015 by A.M. Best Company, Inc.
Version 091714
Copyright © 2015 by A.M. Best Company, Inc.
All rights reserved. No part of this report may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system or transmitted in any form or by any means; electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise.
4









