a) Ge-H b) Ge-F c) Ge-Cl d) Ge-Br e) Ge
advertisement
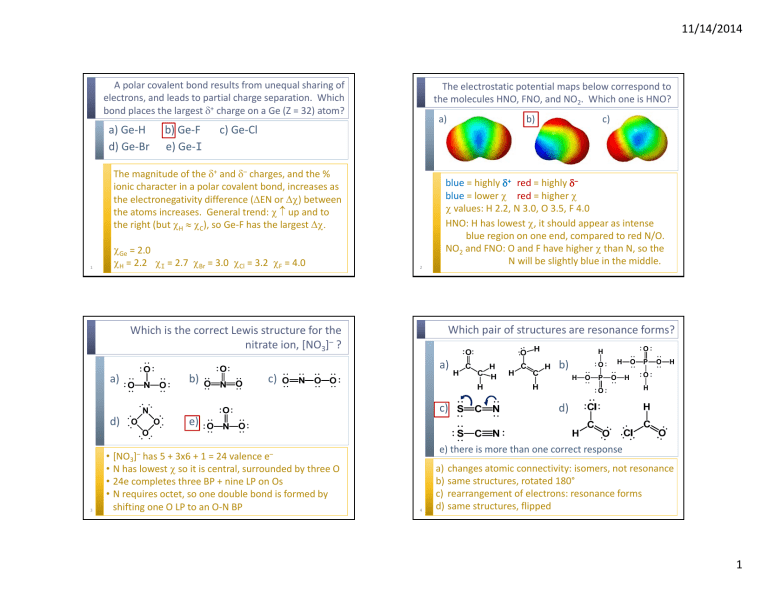
11/14/2014 A polar covalent bond results from unequal sharing of electrons, and leads to partial charge separation. Which bond places the largest δ+ charge on a Ge (Z = 32) atom? a) Ge‐H d) Ge‐Br b) Ge‐F e) Ge‐I The electrostatic potential maps below correspond to the molecules HNO, FNO, and NO2. Which one is HNO? a) c) Ge‐Cl The magnitude of the δ+ and δ– charges, and the % ionic character in a polar covalent bond, increases as the electronegativity difference (ΔEN or Δχ) between the atoms increases. General trend: χ ↑ up and to the right (but χH ≈ χC), so Ge‐F has the largest Δχ. 1 χGe = 2.0 χH = 2.2 χI = 2.7 χBr = 3.0 χCl = 3.2 χF = 4.0 2 b) blue = highly δ+ red = highly δ– blue = lower χ red = higher χ χ values: H 2.2, N 3.0, O 3.5, F 4.0 HNO: H has lowest χ, it should appear as intense blue region on one end, compared to red N/O. NO2 and FNO: O and F have higher χ than N, so the N will be slightly blue in the middle. Which pair of structures are resonance forms? Which is the correct Lewis structure for the nitrate ion, [NO3]– ? b) O H a) a) c) b) c) H O H O P O O c) N d) O O O H P O H O H d) e) O 3 • [NO3]– has 5 + 3x6 + 1 = 24 valence e– • N has lowest χ so it is central, surrounded by three O • 24e completes three BP + nine LP on Os • N requires octet, so one double bond is formed by shifting one O LP to an O‐N BP e) there is more than one correct response 4 a) changes atomic connectivity: isomers, not resonance b) same structures, rotated 180° c) rearrangement of electrons: resonance forms d) same structures, flipped 1 11/14/2014 What is the formal charge on C atom in the Lewis structure of CO? Which is the best Lewis structure for nitryl fluoride, FNO2 ? a) –2 b) –1 c) 0 d) +1 e) +2 5 a) F b) N F N O O O c) F O d) N F O CO is highly unusual. It is one of the few stable covalent molecules in which a C atom forms fewer than four bonds. With 5 neighbouring electrons, it carries a –1 formal charge, which is also unusual for stable carbon compounds. 6 Bond Order Bond Length /pm Bond Energy /kJmol–1 1 145 142 b) O3 1.5 128 303 c) O2 2 121 495 Lewis structure a) H2O2 N O a) no octet at N, large FCs (boo!) b) satisfies all octets, (–) FC on higher χ O, (+) FC on lower χ N c) (+) on highest χ F! (boo!) d) exceeds octet at N! (boo!) None of the following compounds has lone pairs on the central atom. Which has the largest bond angle? Which has the shortest O‐O bond length? a) BCl3 b) CCl4 c) PCl5 d) SF6 d) they should all be about equal length 7 O O +2 8 No LPs means all AXn structures, with shape determined by expected arrangement of atoms. AX2 – linear: 180° AX3 – trigonal planar: 120° AX4 – tetrahedral: 109.5° AX5 – trigonal bipyramidal: 120° and 90° AX6 – octahedral: 90° 2 11/14/2014 What electron pair arrangement and molecular geometry are predicted for the triiodide anion, [I3]–? a) b) c) d) e) What is the most reasonable predicted bond angle for ozone, O3 ? linear arrangement, linear geometry trigonal planar arrangement, bent geometry tetrahedral arrangement, bent geometry trigonal bipyramidal arrangement, linear geometry none of the above a) b) c) d) e) 3x7 + 1 = 22e AX2E3 is 5 electron pair regions: trigonal bipyramidal arrangement 3 LPs in the equatorial positions, leaving atoms axial: linear geometry of atoms 9 AX2E: a perfect AX3 trigonal planar arrangement would be 120°, but the LP takes up more space and causes greater repulsion than the BP electrons, so the bond angle contracts slightly. 10 Which ion has the smallest O‐N‐O bond angle? O a) [NO2]+ b) [NO2]– c) [NO3]– d) [NO4]3– 11 106° 109° 117° 120° 180° N angle BO length O N O O O 180° 2 115pm a) b) c) d) 115° 1½ 124pm N O Which compound has the largest molecular dipole? χ values: H 2.20 C 2.55 I 2.66 Br 2.96 Cl 3.16 O O O N O O 120° 1⅓ 122pm 109.5° 1 139pm Bond angle prediction requires VSEPR, and VSEPR requires a Lewis structure. Draw the Lewis structures! [NO2]+ is 16e, AX2: predicts 180° [NO2]– is 18e, AX2E: predicts <120° [NO3]– is 24e, AX3: predicts 120° [NO4]3– is 32e, AX4: predicts 109.5° 12 μ=0D CH4 CH3Cl μ = 1.90 D CH3Br μ = 1.82 D CH3I μ = 1.64 D – X + H + C H H + All these compounds have an AX4 tetrahedral geometry. The C‐H bonds are very slightly polarized with δ+ on H. As the C‐X (X = H I Br Cl) bond polarity increases, the molecular dipole also increases. The C‐Cl bond has the largest Δχ, so CH3Cl has the largest dipole moment. 3 11/14/2014 Which compound has the smallest molecular dipole? χ values: Ga 1.81 As 2.18 P 2.19 N 3.04 Cl 3.16 a) b) c) d) NCl3 μ = 0.6 D PCl3 μ = 1.0 D AsCl3 μ = 2.0 D GaCl3 μ = 0 D GaCl3 is AX3, trigonal planar with 120° angles. Individual Ga‐Cl bonds are polar, but the bond dipoles cancel, leaving the molecular non‐polar. 13 The other EX3 are pyramidal, and polar. 4

![Which is the correct Lewis structure for the nitrate ion, [NO3]– ? a) b](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/008121614_1-3f41411d21eef682c95d3c7778684719-300x300.png)