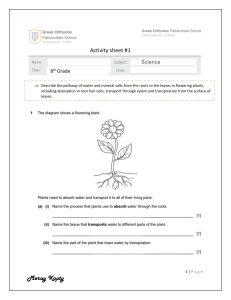
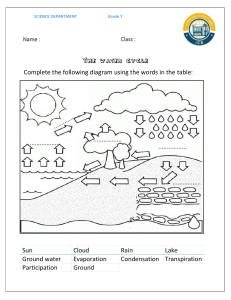
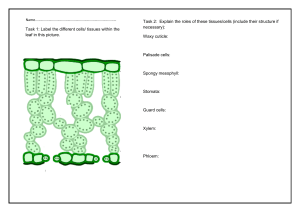
Wednesday 12 June 2024 Revision exercise: Transport in plants 1 (a) Explain why a maize plant is classified as a monocotyledonous plant. - Parallel veined leaves - Fibrous root system - Flower parts arranged in threes - One food store - Leaves attached to the stem by a sheath (b) Describe how plants that grow in arid areas are adapted to minimise water loss. - Succulent leaves - Reduced leaf surface area - Hairs on leaves - Sunken stomata/curled leaves - Thick cuticle - Reduced number of stomata [4] [6] [5] 2 (a) Explain why a plant wilts on a dry and sunny day. - High temperature increases evaporation of water off the plant - Low humidity creates more space for evaporation of water from plants - High light intensity opens more stomata and allows more water to be lost from the plant. - Dry conditions may mean less amount of water in the soil - The plant roots may not be able to absorb water from the soil fast enough to replace water lost through transpiration - As the plant cells lose water, the concentration of solutes increase leading to cell shrinkage and wilting (b) Describe and explain how xylem vessels are adapted for transport of water, and for support in a plant. [4] - Hollow/no protoplasm/no end walls – forms a continuous passage of water up the stem - Has side walls made of cellulose and lignin – provide extra support to the plant; prevent the xylem collapsing due to the pressure inside - Has pits in side walls – allow lateral movement of water into the xylem - Made up of dead cells [1] (c) What is the main force responsible for the upward movement of water in plants? - transpiration pull