Midterm exam #2 of BIO3124 : General microbiology Name : Student
advertisement

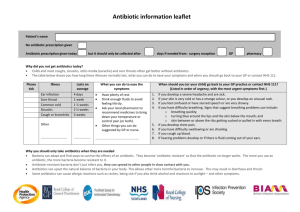
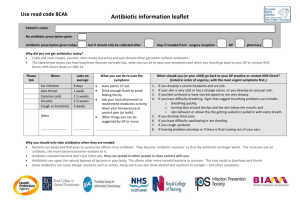
Midterm exam #2 of BIO3124 : General microbiology Name : Student number : Cet examen comporte deux parties. La première partie d’une valeur de 25 points consiste de 25 questions à choix de réponses. La deuxième partie d’une valeur de 15 points comporte 4 questions à courtes réponses. Assurez-vous de répondre à SEULEMENT 3 DES 4 questions sinon seulement les trois premières questions répondues seront corrigées. Formules : 𝑵 = 𝑵𝟎 𝟐𝒏 𝑵 = 𝒕/𝒈 𝒏 = 𝟑. 𝟑(𝒍𝒐𝒈𝑵 − 𝒍𝒐𝒈𝑵𝟎 ) 𝝁= ((𝒍𝒐𝒈𝑵 − 𝒍𝒐𝒈𝑵𝟎 )𝟐. 𝟑𝟎𝟑) (𝒕 − 𝒕𝟎 ) 𝝁 = 𝒍𝒏𝟐/𝒈 −𝒌𝒕 = 𝐥𝐧( 𝑵𝟎 ) 𝑵 𝑫 = 𝒕/(𝒍𝒐𝒈𝑵𝟎 − 𝒍𝒐𝒈𝑵) 𝑫𝒃 𝒍𝒐𝒈 ( ) = (𝑻𝒂 − 𝑻𝒃 )/𝒛 𝑫𝒂 Parti1. Multiple choice questions 1. The addition of a macrolide during which growth phase would prolong its duration? a. b. c. d. Exponential. Lag. Stationary. Death. 2. Biotin is optional for E.coli since when required these bacteria can synthesize this nutrient. What would be the observed effect on the growth profile of this bacterium once biotin was exhausted from a given medium? a. b. c. d. We would observe a reduction in the exponential rate of growth. The cells would enter stationary phase since biotin is essential for growth. The cells would enter the death phase. A second lag phase would be initiated. 3. A bacterial culture went from 1 X 103 to 1 X 106 cells/ml in 12 hours. According to this data what are the total number of generations, the generation time and the growth rate constant respectively? a. b. c. d. ~10 generations, ~72 minutes and ~0.83 generation/hour. ~12 generations, ~60 minutes and ~1.0 generation/hour. ~15 generations, ~75 minutes and ~0.80 génération/hour. ~20 generations, ~36 minutes and ~1.7 generation/hour. 4. A bacterium has a growth rate constant of 3 and 2 generations/hour in growth media « A » and « B » respectively. The initial density on both media is 1 X 108 cells/mL. How much time would be required for growth in medium « B » in order to reach the same cell density which would be expected in medium « A » after 2 hours of growth? a. b. c. d. 2h 4h 3.0 h 3.5 h 5. Which of the following statements about viruses is false? a. b. c. d. All viruses have a DNA or an RNA genome that can be either single or double stranded. Viral surface proteins determine which cell they can infect. Amongst other things, viruses are classified according to the type of genomes they have. Enveloped viruses are less sensitive to phenols than are naked viruses. 6. The optical density of a B. subtilis broth (a large rod) is compared to that of an E.coli broth (a small rod). Which of the following conclusions is valid if both have the same optical density? a. b. c. d. The number of bacteria in both broths must be the same. The B. subtilis broth must contain more cells than the E.coli broth. The E. coli broth must contain more bacteria than the B. subtilis broth. None of these conclusions are valid. 7. What class of germicides would be effective against Clostridium spores? a. b. c. d. Aldehydes. Halogenes. Alcohols. Deteergents. 8. Two different bacterial cultures, « A » and « B », have TDT at 100oC of 5 and 10 minutes respectively. If the initial cell densities are the same, which of the following conclusions is TRUE? a. The inactivation facttor achieved after 5 minutes for bacteria « A » must be greater than the one obtained after 10 minutes for bacteria « B ». b. The D100 value of bacteria a must be less than that of bacteria « B ». c. The TDP of bacteria « A » must be greater than that of bacteria « B ». d. The z value of bacteria « A » must be greater than that of bacteria « B ». 9. To verify the efficacy of a quinolone treatment against a known pathogen, you wish to determine whether the treatment results in a reduction in the number of bacteria in blood. Which method would be most appropriate? a. b. c. d. A viable count. Turbidity measurements. A direct count. A and C. 10. A microscopic examination of a yogurt sample is illustrated. Which of the following conclusions is valide according to what is observed on the image? a. b. c. d. The yogurt is contaminated. The yogurt is not contaminated. The yogurt is not sterile. None of these conclusions can be drawn according to what is shown on this image. 11. Ad drug with the lowest a. b. c. d. Toxic dose. Therapeutic index. Therapeutic dose. Selective toxicity. ? would be best for therapeutic purposes. 12. Which of the following statements about HIV and Influenza is TRUE? a. b. c. d. Both use an DNA dependent RNA polymerase. Cell entry in both cases involves fusion of their envelopes with the cell membrane. Their genomes are replicated in the cytoplasm. All these statements are false. 13. A combination of a bacteriophage and an aminoglycoside is used to treat a bacterial infection. What would be the predicted effect on the bacteriophage based treatment? a. b. c. d. The antibiotic would have an anatgonistic effect on the bacteriophage based treatment. The antibiotic would have a synergistic effect on the bacteriophage based treatment. The antibiotic would have no effect on the bacteriophage based treatment The effect cannot be predicted. 14. This image represents a sensitivity test by the disk diffusion method of a bacteria to different antibiotics. All the antibiotics are from a natural source with the exception of « A1 » which represents a chemically modified version of « A ». Based on these results, what can be concluded about antibiotics « A » and « A1 »? a. b. c. d. A A1 B C The modification increases the MIC of « A1 ». The modification decreases the MIC of « A1 ». The modification increases the MBC of « A1 ». The modification confers a broader action spectrum to « A1 ». 15. According to the results of the Kirby bauer assay shown above, which of the antibiotics would be best to treat an infection? a. b. c. d. A or A1. This conclusion cannot be drawn from these results. C. B. 16. If all these antibiotics have equivalent toxic doses, which one would therefore have the lowest therpeutic index? a. b. c. d. A. B. C. A1. 17. A bacterium « A » can grow in close proximity to a bacterium « B » on an agar plate containing tetracycline. However, bacterium « A » cannot grow if it is grown alone on tetracycline. What is the possible resistance mechanism used by bacterium « B »? a. b. c. d. Impermeability. Degradation of the antibiotic. Transport Modification of the antibiotic’s target. 18. The acquired resistance of a bacterium « A » to an antibiotic can be transferred to a bacterium « B » when these are grown together in the same broth. The filtrate obtained after the filtration of the « A » broth culture through a filter of 0.10μm retains the capacity to transmit the resistance to bacterium « B ». What is the possible mode of transfer of the resistance? a. b. c. d. Transduction or transformation. Transduction. Transformation. Conjugation. 19. Viable counts of Micrococcus luteus and of Staphylocoocus aureus were 1 X 108 CFU/mL. What possible interpretation can be made from these results? a. b. c. d. The number of cells per m Lis the same for both bacteria. The number of cells per mL of Staphylococcus is higher than that of Micrococcus. The number of cells per mL of Micrococcus is higher than that of Staphylococcus. None of these interpretations are valid. 20. Which characteristic (s) is (are) desirable for antiseptics and disinfectants? a. b. c. d. A small quantity for a high efficacy. A low toxicity. A pleasant odor. All of the above 21. There many more antibacterial drugs as compared to antifungal drugs; why? a. Beause fungi are very similar to human cells making it difficult to have drugs with an acceptable selective toxicity. b. Because fungi do not cause infections in humans. c. Because fungi are not sensitive to antimicrobials. d. Because the number of cellular targets in fungi is much lower than that in bacteria. 22. Most enveloped viruses acquire their envelope during their release by exocytosis from the cell. Which of these viruses is an exception to this rule? a. b. c. d. Influenza HIV HPV None of these viruses 23. Which of the foloowing statements about broad spectrum antibiotics is FALSE? a. b. c. d. They include Carbapenems. They include monobactams. They generally have a low therapeutic index. They are not recommended if the identity of the infectious agent is known. Kirby Bauer E-Test a b d c i ii iii 24. The above E-Test was done with antibiotics « a », « b » et « c » shown on the Kirby Bauer assay illustrated. Choose the correct association. a. b. c. d. a = ii, b = i, et c = iii a = i, b = ii et c = iii a=ii, b=iii et c= i a = iii, b = ii et c = i 25. Choose the order of drugs representing the highest therapeutic index to the lowest. a. b. c. d. Chloramphenicol, polymixin B, imidazole, a nucleoside analogue. Imidazole, polymixin B, a nucleoside analogue, chloramphenicol. A nucleoside analogue, chloramphenicol, imidazole, polymixin B Polymixin B, a nucleoside analogue, chloramphenicol, imidazole. Viable count X 106 CFU/mL Part 2. Only answer 3 of the 4 questions, or else only the first three will be graded. (5 points/question) 1. Time (Minutes) 1a. What is the growth rate (µ) of this culture? 0.035 cels/minutes 1b. How many CFUs/mL are predicted after 250 minutes of growth? Approx. 1.6 X 1011 1c. A direct count was done as follows on a sample collected after 20 minutes of growth. A volume of 0.1mL was applied to a counting chamber with the following dimensions: 1mm X 2mm X 0.05mm. If the chamber has 100 squares, what average number of cells would be per square? (Assume that one CFU = 1 cell) 50 1d. If D120 is equal to 10 seconds, what is the minimum amount of time required to sterilize this culture in the lab at 120oC starting from the number of cells obtained at 40 minutes? Approx. 140 sec. 1e. If the z value of this culture is 20oC, what is the TDT (thermal death time) at 100oC for a sample collected after 40 minutes? Use the D value obtained in the previous question. 800 sec. or 13.3 minutes 2. Make the most appropriate combination of the structures below with the descriptions given in the table. Choose only ONE structure for each description. Enter "X" if none of the structures corresponds to the description given. The same choice can be used more than once. A B C Cefalexin carbapenem quinolone cephalosporin D E F tetracycline G glycopeptide H I macrolide phenol aminoglycoside imidazole Description Cefalexin Glycopeptide antibiotic used to treat MRSA. Broad spectrum bacteriostatic antibiotic. Drug that target the cell membrane of eucaryotes Class of antibiotics that targets RNA synthesis Description B Broad spectrum beta lactam of the last generation. E Narrow spectrum beta lactam. A X D Narrow spectrum antibiotic with the same target as tetracycline. H DNA synthesis inhibitor F F G Aminoglycoside C 3. Match each of the terms or statements from list « A » to those of list « B ». Each term of list « B » can only be used once. List A List B I Iodophor A. Plasma membrane G Innate antibiotic resistance B. Prophylactic O Growth yield (Y) C. Mercury F Antifungal paint D. Monobactam A Polymixin B E. Glycopeptide D Beta-lactamase F. Heavy metal N Hemmaglutinine G. Streptomycetes H Partial food sterilization H. Pasteurization M Integrase I. Halogen B Taking antibiotics in the absence of infection J. Exponential phase K. Emulsifier L. Empirical M. HIV N. Tropism O. Stationary phase P. VRE Q. HEPA Filter 200 Inhibition diameter (mm) 4. 20 2.0 0.2 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 MIC (μg/mL) Ab A B C D Cmin-Cmax (μg/mL) 40-80 50 - 100 100 -300 40 - 60 LD50 (μg/mL) 25 200 150 100 Diameters (mm) 6.0 10.0 3.0 1.0 Sensitivity RI S S R 4a. The above graph shows the diameters corresponding to the MICs of a pathogen isolated from a patient. The table shows the physiological data of different antibiotics and the diameters of inhibition obtained on a Kirby Bauer test. Indicate in the table if the pathogen is resistant ("R"), sensitive ("S"), or has an intermediate resistance ("IR") to each of antibiotics. (2 points) 4b. Which antibiotic would be best to treat the patient? (1 point) B 4c. Give two reasons why this antibiotic was chosen rather than the others. (2 points) The bacteria are sensitive to antibiotics B and C. The therapeutic index of B is higher than that of C (4.5 Vs 2.5) The toxic dose of B is higher than the maximum concentration whereas C’s is lower.