Graphical Analysis of Motion Speed
advertisement
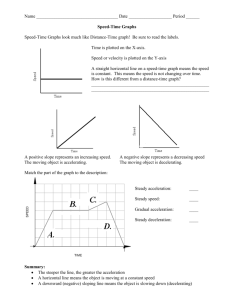
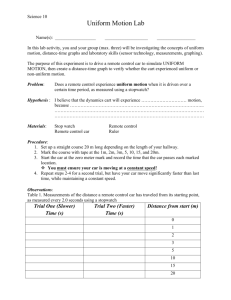
Graphical Analysis of Motion Objectives • Plot and interpret distance-time and speed-time graphs • Deduce from the shape of a distance-time graph when a body is: (i) at rest; (ii) moving with uniform speed; (iii) moving with non-uniform speed. • Deduce from the shape of a speed-time graph when a body is: (i) at rest; (ii) moving with uniform speed; (iii) moving with uniform acceleration; (iv) moving with non-uniform acceleration. • Calculate the area under a speed-time graph to find the distance travelled at uniform speed or uniform acceleration. Graphical Analysis of Motion • If the car is travelling in only one direction, s/m • its distance-time graph is also the displacement-time graph • Gradient = velocity t/s • its speed-time graph is also the velocity-time graph • Gradient = acceleration v/ms-1 t/s Graphical Analysis of Motion Distance-time Graph d/m Distance of car from reference point Reference point Position of car Note: Gradient of graph gives the speed of car Gradient = speed = Distance Time t/s Graphical Analysis of Motion Distance-time Graph Graphical Analysis of Motion Distance-time Graph Graphical Analysis of Motion Distance-time Graph • Both objects, A and B, are moving with constant speed (straight lines) distance/m A faster slower • Speed of A > Speed of B (grad of A > grad of B) B time/s Graphical Analysis of Motion Speed-time Graph Note: No change in speed, therefore no acceleration. Graphical Analysis of Motion Speed-time Graph Graphical Analysis of Motion Speed-time Graph Graphical Analysis of Motion Speed-time Graph • Not all objects move with constant acceleration. Most vehicles move with accelerations that keep changing. • The acceleration or deceleration of the object at any point in time is still given by the gradient of the graph at that point. speed/m s-1 stop stop time/s speed-time graph of a car on a straight road where it has to stop twice because of traffic lights Graphical Analysis of Motion Speed-time Graph Describe the motion of the car O Summary • If the car is travelling in only one direction, s/m • its distance-time graph is also the displacement-time graph • Gradient = velocity t/s v/ms-1 • its speed-time graph is also the velocity-time graph • Gradient = acceleration t/s Area Under Speed-Time Graph Graphical Analysis of Motion Area under a Speed-time Graph • The area under a speed-time graph gives the distance travelled. Distance = speed x time = 20 x 5 = 100 m Graphical Analysis of Motion Area under a Speed-time Graph • The area under a speed-time graph gives the speed/m s distance travelled. -1 Distance = area under graph V=5 = area of the triangle = ½ x 10 x 5 = 25 m time/s t1= 10 Graphical Analysis of Motion Distance covered in A = ½ x 10 x 30 = 150m Distance covered in B = 20 x 30 = 600m v/ms-1 30 Total distance travelled B = 150 + 300 + 150 = 900m A C 10 Or ½ (sum of parallel sides) height = ½ (20 + 40)30 20 30 40 Graphical Analysis of Motion Average speed = Total Distance Total Time = 900/40 v/ms-1 30 = 22.5ms-1 B A C 10 20 30 40 Summary • If the car is travelling in only one direction, s/m • its distance-time graph is also the displacement-time graph • Gradient = velocity • its speed-time graph is also the velocity-time graph • Gradient = acceleration • Area under graph = distance travelled t/s v/ms-1 t/s