Unit I
Your responses to these questions will be scored on the basis of the accuracy and relevance of the i
Explanations should be clear and well organized. Examples and equations may be included in your
appropriate. Specific answers are preferable to broad, diffuse CH
responses.
CH SH
Ethanethiol
Bonding & Geometry Practice
3
2
(pg 1 of 12)
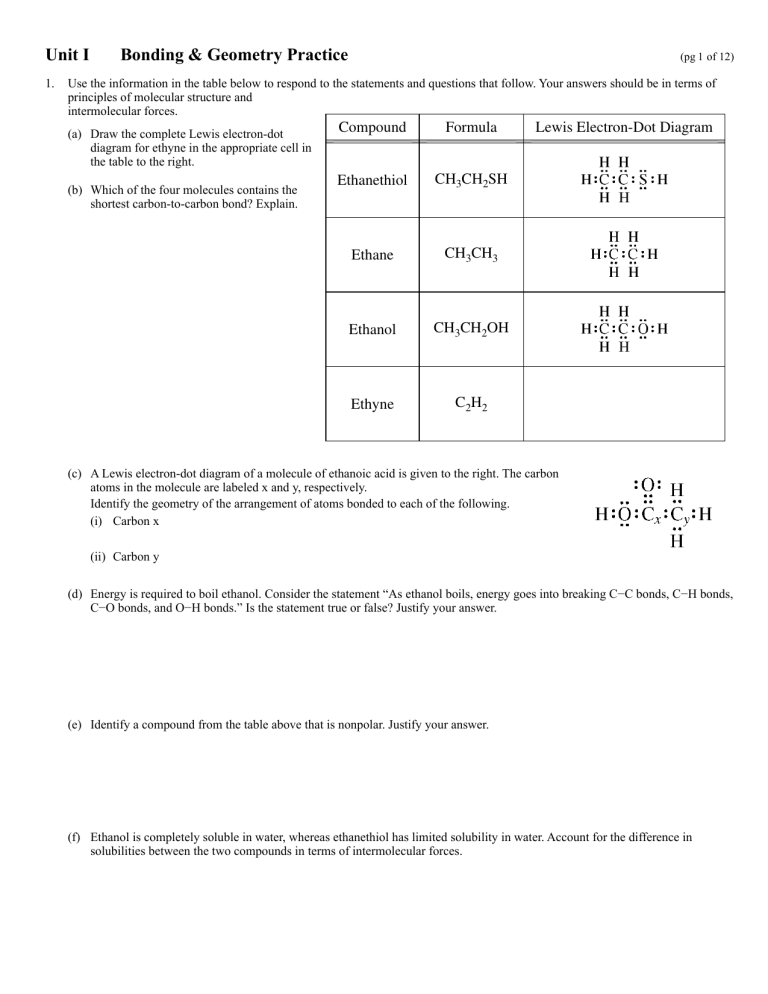
5. Use the information in the table below to respond to the statements and questions that follow. Y
1. Use the information in the
table below
respond
the statements
and questionsstructure
that follow.
Your
answers should forces.
be in terms of
should
be intoterms
oftoprinciples
of molecular
and
intermolecular
principles of molecular structure and
intermolecular forces.
(a) Draw the complete Lewis electron-dot
diagram for ethyne in the appropriate cell in
the table to the right.
(b) Which of the four molecules contains the
shortest carbon-to-carbon bond? Explain.
Compound
Formula
Ethane
Ethanethiol
CH3CH2SH
CH3
CH3Electron-Dot
Lewis
Diagram
CH3CH2OH
Ethanol
Ethane
CH3CH3
C2H2
Ethyne
Ethanol
CH3CH2OH
(a) Draw the complete Lewis electron-dot diagram for ethyne in the appro
C2H2 contains the shortest carbon-to-carbon bo
(b) WhichEthyne
of the four molecules
(c) A Lewis electron-dot diagram of a molecule of ethanoic acid is given
molecule are labeled x and y, respectively.
(c) A Lewis electron-dot diagram of a molecule of ethanoic acid is given to the right. The carbon
(a) Draw the complete Lewis electron-dot diagram for ethyne in the appropriate cell in the
atoms in the molecule are labeled x and y, respectively.
Identify the geometry(b)
of the
arrangement
atoms
bonded tocontains
each of thethe
following.
Which
of the of
four
molecules
shortest carbon-to-carbon bond? Explain.
(i) Carbon x
(ii) Carbon y
tab
(c) A Lewis electron-dot diagram of a molecule of ethanoic acid is given below. The carbon a
molecule are labeled x and y, respectively.
Identify the geometry of the arrangement of atoms bonded to each of t
(d) Energy is required to boil ethanol. Consider the
“Asx ethanol boils, energy goes into breaking C−C bonds, C−H bonds,
(i)statement
Carbon
C−O bonds, and O−H bonds.” Is the statement true or false? Justify your answer.
(ii) Carbon y
(d)geometry
Energyofis the
required
to boilofethanol.
Consider
the statement
“As ethanol
Identify the
arrangement
atoms bonded
to each
of the following.
(i) Carbon xbonds, C−H bonds, C−O bonds, and O−H bonds.” Is the statement t
(ii) Carbon
(e) yIdentify a compound from the table above that is nonpolar. Justify you
(e) Identify a compound from the table above that is nonpolar. Justify your answer.
(d) Energy is (f)
required
to boil
ethanol. Consider
thein
statement
“As ethanol
boils, energy
goes i
Ethanol
is completely
soluble
water, whereas
ethanethiol
has limite
bonds, C−H bonds,
C−O
bonds,
and
O−H
bonds.”
Is
the
statement
true
or
false?
Justify
difference in solubilities between the two compounds in terms of inter
(e) Identify a compound from the table above that is nonpolar.
Justify
answer.
© 2010
Theyour
College
Board.
Visit the College Board on the Web: www.collegeboard
(f) Ethanol is completely soluble in water, whereas ethanethiol has limited solubility in water.
difference
solubilities
between
the two
compounds
in termsforofthe
intermolecular
(f) Ethanol is completely soluble
in water,in
whereas
ethanethiol
has limited
solubility
in water. Account
difference in forces.
solubilities between the two compounds in terms of intermolecular forces.
-11© 2010 The College Board.
Visit the College Board on the Web: www.collegeboard.com.
GO ON TO THE
-11-
5
(continued)
(c) A Lewis electron-dot diagram of a Question
molecule
ethanoic
acid is given below. The carbon atoms in the
AP® ofCHEMISTRY
molecule are labeled x and y,2010
respectively.
SCORING
®
(a) Draw the complete
Lewis
electron-dot
diagram forGUIDELINES
ethyne in the appropriate cell in the table above.
APdiagram
CHEMISTRY
(c) AILewis Bonding
electron-dot
of
a
molecule
of ethanoic acid is given below. The carbon atoms in the
H2OH Unit
& Geometry Practice
SCORING
GUIDELINES
molecule 2010
are labeled
x and y, respectively.
Question 5 (continued)
ANSWER #1
See the lower right cell in the table above.
One point is earned for the correct Lewis structure.
Question 5 (continued)
(c)
A Lewis
of a molecule
of ethanoic
acid
is given
The carbon atoms in the
Identify
the electron-dot
geometry of diagram
the arrangement
of atoms
bonded to
each
of the below.
following.
molecule are labeled x and y, respectively.
H2
Lewis electron-dot
(i) diagram
Carbon xof a molecule of ethanoic acid is given below. The carbon atoms in the
(b)Which
of
the
four molecules
contains the
shortestbonded
carbon-to-carbon
bond?
Explain.
Identify
of the arrangement
of atoms
to each of the
following.
olecule are(a)labeled
x andthe
y,geometry
respectively.
One point is earned for the correct geometry.
(i) Carbon x Trigonal planar
One point is earned for the correct choice.
Ethyne,
which
contains
a triple
bond,
has the shortest
Trigonal
planar
One
for the correct geometry.
Identify
theappropriate
geometry
of
the
arrangement
of atoms bonded
topoint
each is
of earned
the following.
ot diagram for ethyne
in
the
cell
in
the
table
above.
y other molecules have single C-to-C
(ii) Carbon
C-to-C
bond. The
One point is earned for the correct
x
Carbon
entify the geometry
ofand
the
arrangement
ofshorter
atoms bonded
to each
of the following.
bonds,(i)
triple
bonds
are
than single
bonds.
explanation.
(b) Distorted
tetrahedral,
tetrahedral or trigonal pyramidal
One point is earned for the correct geometry.
y
(ii) Carbon
x
i)
Carbon
ve.
One point is earned for
the correct
Lewis structure.
Trigonal
planar
One point is earned for the correct geometry.
Distorted
tetrahedral or trigonalOne
pyramidal
One
is earned
for the correct geometry.
Trigonaltetrahedral,
planar
point is earned
forpoint
the correct
geometry.
(c(d)
i) Energy is required to boil ethanol. Consider the statement “As ethanol boils, energy goes into breaking
y bonds,
Carbon
C!H
C!O bonds, and O!H bonds.” Is the statement true or false? Justify your
C!C(ii)bonds,
the shortest carbon-to-carbon
bond?
Explain.
answer.
(d) Energy is required to boil ethanol. Consider the statement “As ethanol boils, energy goes into breaking
i) Carbon y Distorted tetrahedral, tetrahedral or trigonal pyramidal
point is earned
the correct
the statement
true orforfalse?
Justifygeometry.
your
C!C bonds, C!H bonds, C!O bonds, and O!H bonds.” IsOne
(c ii)
The
statement
is
false.
All
of
the
bonds
described
are
answer.
One pointoristrigonal
earned for
the correct©choice.
2010
The
College
Board.for the correct geometry.
orted
tetrahedral,
tetrahedral
pyramidal
One
point
is earned
One point is earned for the correct choice with
the shortest
intramolecular;
these bonds
arethenot
broken
during
Visit
College
Board
on the Web: www.collegeboard.com
ngle C-to-C vaporization.
(d) Energy
isWhen
required
to boil
ethanol.
Consider
the statementjustification.
“As ethanol boils, energy goes into breaking
ethanol
boils,
the added
energy
One
point
is
earned
for
the
correct
The statement is false. All of the bonds described are
ngle bonds. overcomes
bonds,
C!H
bonds,
C!O
bonds,
and
O!H
bonds.”
Is the
statement
true
false?
Justify
your
C!C
not
intramolecular,
forces.
intermolecular,
explanation.
One
point
is earned
fororthe
correct
choice
with
intramolecular;
these
bonds the
are statement
not broken“As
during
ergy is required
toanswer.
boil ethanol.
Consider
ethanol boils, energy goes into breaking
vaporization.
When
ethanol
boils,
the
added
energy
justification.
!C bonds, C!H bonds, C!O bonds, and O!H bonds.” Is the statement true or false? Justify your
overcomes intermolecular, not intramolecular, forces.
swer.
(d)
(e) Identify
a compound
from
abovedescribed
that is nonpolar.
Justify your answer.
The statement
is false.
Allthe
of table
the bonds
are
One point is earned for the correct choice with
intramolecular; these bonds are not broken during
statement is false.
All of the bonds
described
are the added energy
vaporization.
When
ethanol
boils,
justification.
(e)Either
Identify
a compound
from
theidentified
table above
that point
is nonpolar.
Justify
your
answer.
ethane
ethyne
may
be
asOne
nonpolar.
is earned
for the
correct
choice with
amolecular; these
bonds
areor
not
broken
during
overcomes
not intramolecular,
forces.
intermolecular,
orization. When
boils, the
added energy
justification.
Theethanol
ethane/ethyne
molecule
is nonpolar because
all of
rcomes intermolecular,
not intramolecular,
forces.
the
bond
dipoles
the molecule
cancel. as nonpolar.
Either
ethane
or in
ethyne
may be
identified
2010 The College Board.
(e)
Identify
a compound
fromisthe
table above
thatallisof
nonpolar.
OR
oard on the Web:
www.collegeboard.com
The
ethane/ethyne
molecule
nonpolar
because
Justify your answer.
AP® CHEMISTRY
One point is earned for a correct choice
the
bond
dipoles
in
the
molecule
cancel.
The ethane/ethyne
is nonpolar
because
theyour answer.
entify a compound
from the tablemolecule
above that
is nonpolar.
Justify
with justification.
2010
SCORING
GUIDELINES
molecule
is symmetric.
Either ethane
or ethyneOR
may
be identified
as nonpolar.
One point is earned for a correct choice
Explanation
must
referistois
the
shapebecause
of
the theall of
Note:
The
ethane/ethyne
molecule
nonpolar
because
The
ethane/ethyne
molecule
nonpolar
er ethane or ethyne
may
be identified
as nonpolar.
Question
5
(continued)
with justification.
molecule.
as: “all hydrocarbons
are
the bondStatements
insuch
the molecule
cancel.
molecule
isdipoles
symmetric.
ethane/ethyne
molecule“the
is nonpolar
all of by hydrogens”
nonpolar’,
carbons because
are surrounded
ORtointhe
Explanation
refer
shape
of
the ethanethiol has limited solubility in water. Account for
Note:
(f)or
Ethanol
is completely
soluble
water,
whereas
bond dipoles
in
the
molecule
“there
are
no cancel.
lonemust
pairs”
do not
earn
this
point.
(e) molecule.
Oneofpoint
is earned for
a correct choice
Statements
such as:between
“all hydrocarbons
are
the
difference
in
solubilities
the
two
compounds
in terms
intermolecular
forces.
The ethane/ethyne
molecule is nonpolar because
the
OR
nonpolar’, “the carbons are surrounded by hydrogens”
with justification.
molecule is symmetric.
One point is earned for a correct choice
“there are
lone pairs”
do not
ethane/ethyneormolecule
is no
nonpolar
because
the earn this point.
refer
to the shape
ofwith
the
Note: isExplanation
with
justification.
Ethanol
able to formmust
strong
hydrogen
bonds
ecule is symmetric.
molecule.
Statements
such
as:not
“allhave
hydrocarbons
water
whereas
ethanethiol
does
similar are
must
referThe
to
the
shape of
the
e: Explanation
nonpolar’,
“the
carbons
are
surrounded
by hydrogens”
capability.
formation
of
hydrogen
bonds
increases
© 2010 The College Board.
ecule. Statements
such
as:are
“all
are
“there
nohydrocarbons
lonemolecules
pairs”
do
not
earn
this
point.
theorattraction
between
of
ethanol
and
Visit the College Board on the Web: www.collegeboard.com
polar’, “the carbons
are surrounded
by hydrogens”
molecules
of water, making
them more soluble in
One point is earned for the correct explanation.
there are no lone
eachpairs”
other.do not earn this point.
© 2010 The College Board.
Visit the College Board on the Web: www.collegeboard.com
Note: The answer must clearly focus on the solutesolvent interaction. Just the mention of hydrogen
(f) bonding does not earn the point.
© 2010 The College Board.
Visit the College Board on the Web: www.collegeboard.com
© 2010 The College Board.
Visit the College Board on the Web: www.collegeboard.com
(pg 2 of 12)
Unit I
2.
Bonding & Geometry Practice
(pg 3 of 12)
Answer the following questions using principles of chemical bonding and molecular structure.
(a) Consider the carbon dioxide molecule, CO2 , and the carbonate ion, CO32−.
(i) Draw the complete Lewis electron-dot structure for each species.
(ii) Account for the fact that the carbon-oxygen bond length in CO32− is greater than the carbon-oxygen bond length in CO2.
(b) Consider the molecules CF4 and SF4.
(i) Draw the complete Lewis electron-dot structure for each molecule.
(ii) In terms of molecular geometry, account for the fact that the CF4 molecule is nonpolar, whereas the SF4 molecule is polar.
!
!
6789:;<=$>$
6789:;<=$>$
!
!
B*#"&3)<*
! *
B*#"&3)<*
*C4D* C&D****
*
B*#"&3)<*
* *Bonding
*
*
*
*C4D** C&D****
*ANSWER
* #2 * *
* *
*
* *
*
*
*
*
*
*
* *
* *
* *
* *
,F
* *
* *
* *
* *
* *
* *
* *
* *
E
*
*
*
*
*
* ,F
*
*
E
,F
E
!
E
E !
E
!
E
E
E
!
E
!
E
*
*
*
*
!
E
*
E
E *
*
* • E31*#"&3)*14%319*A"%*145(*G1H&<*1015)%"3F9")*<)%I5)I%1*
*
E
*
*
*
**
•
J39&54)&"3*"A*0"31*#4&%<*"A*1015)%"3<*4%1*%1KI&%19*"3*145(*<)%I5)I%1*
* • E31*#"&3)*14%319*A"%*145(*G1H&<*1015)%"3F9")*<)%I5)I%1*
E31*#"&3)*14%319*A"%*145(*G1H&<*1015)%"3F9")*<)%I5)I%1*
• L1<"34351*A"%7<*"A*!EM,−*4%1*3")*%1KI&%19*
• • J39&54)&"3*"A*0"31*#4&%<*"A*1015)%"3<*4%1*%1KI&%19*"3*145(*<)%I5)I%1*
• J39&54)&"3*"A*0"31*#4&%<*"A*1015)%"3<*4%1*%1KI&%19*"3*145(*<)%I5)I%1*
• * L1<"34351*A"%7<*"A*!EM,−*
4%1*3")*%1KI&%19*
• L1<"34351*A"%7<*"A*!EM,−*4%1*3")*%1KI&%19*
(a
i)
C&&D* J3*!E,>*)(1*!−E*&3)1%45)&"3<*4%1*9"I/01*/"39<>*"#>!*&3*!EM,−*)(1*!−E*&3)1%45)&"3<*
*
*
* J3*!E,4%1*%1<"34351*A"%7<*C"%*A&'I%1<*/10"H:D***
*
*
* *
*)(1*!−E*&3)1%45)&"3<*
C&&D*
>*)(1*!−E*&3)1%45)&"3<*4%1*9"I/01*/"39<>*"#*>!*&3*!EM* ,−,−
"#
*
C&&D*
* J3*!E
* ,>*)(1*!−E*&3)1%45)&"3<*4%1*9"I/01*/"39<>*
*
*
*
*
* >!*&3*!E
* M *)(1*!−E*&3)1%45)&"3<*
*
4%1*%1<"34351*A"%7<*C"%*A&'I%1<*/10"H:D*** *
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
**
* 4%1*%1<"34351*A"%7<*C"%*A&'I%1<*/10"H:D***
* E *
*
*
* E*
* *
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Unit
*I
* C&D****
*C4D*
E
!
E
E
E
E
! E
!
*
*
*
E
E
!
E
E
!
E
E
!
!
E
E
! E
E
E
E
*
*
*
* *
&* Geometry
Practice
* *
* *
* *
*
E
*
(pg 4 of 12)
!"#$%!
* !
!"#$%
!"#$%!
*
*
* *
&"#$!
*
&"#$!
&"#$!
E
E
*
&"#$!
*
N(1*54%/"3F"6$'13*/"39*013')(*&<*'%14)1%*&3*)(1*%1<"34351*A"%7<*)(43*&3*)(1*9"I/01*/"39<:*
&"#$!
• ! N(1*54%/"3F"6$'13*/"39*013')(*&<*'%14)1%*&3*)(1*%1<"34351*A"%7<*)(43*&3*)(1*9"I/01*/"39<:*
.<)**#"&3)*14%319*A"%*&39&54)&3'*9"I/01*/"39<*4%1*#%1<13)*&3*!E,**"#**%1<"34351*"55I%<*&3*!EM,−* &"#$!
!
,−
,39**#"&3)*14%319*A"%*$"%&*"A*)(1*4/"=1*'()!*&39&54)&3'*)(1*%104)&=1*013')(<*"A*)(1*/"39*)$#1<*
• ii).<)•**#"&3)*14%319*A"%*&39&54)&3'*9"I/01*/"39<*4%1*#%1<13)*&3*!E
(a
,**"#**%1<"34351*"55I%<*&3*!EM *
• 39
.! <)**#"&3)*14%319*A"%*&39&54)&3'*9"I/01*/"39<*4%1*#%1<13)*&3*!E,**"#**%1<"34351*"55I%<*&3*!EM,−*
**#"&3)*14%319*A"%*$"%&*"A*)(1*4/"=1*'()!*&39&54)&3'*)(1*%104)&=1*013')(<*"A*)(1*/"39*)$#1<*
• , 39
C&D*
* $"%&**"A*)(1*4/"=1*
*
* *&39&54)&3'*)(1*%104)&=1*013')(<*"A*)(1*/"39*)$#1<*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
'()!
! • ,C/D***#"&3)*14%319*A"%*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
!"#$%
!
!
C/D*
C&D*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
C/D*
C&D*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
O *
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
!"#$%
O!
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
!"#$%!
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
! E
N(1*54%/"3F"6$'13*/"39*013')(*&<*'%14)1%*&3*)(1*%1<"34351*A"%7<*)(43*&3*)(1*9"I/01*/"39<:*
E
*
E
E
!
OO
O
O
!
O
!
*
*
*
*
*
*
O
E31*#"&3)*14%319*A"%*145(*G1H&<*1015)%"3F9")*<)%I5)I%1*
O
*
*
* !"#$%&'()*+,-$
*
*
OO
O
P
P
O
O
O
OO
O
::
::: O
: OO
O
O
P
•
*
*
*
* • E31*#"&3)*14%319*A"%*145(*G1H&<*1015)%"3F9")*<)%I5)I%1*
*• G"31*#4&%<*"A*1015)%"3<*4%1*%1KI&%19*"3*145(*<)%I5)I%1*
*
*
*
*
*
*
!
•
E31*#"&3)*14%319*A"%*145(*G1H&<*1015)%"3F9")*<)%I5)I%1*
.///$*%0,)12$23)4'5)1'*$
• G"31*#4&%<*"A*1015)%"3<*4%1*%1KI&%19*"3*145(*<)%I5)I%1*
(b i) • G"31*#4&%<*"A*1015)%"3<*4%1*%1KI&%19*"3*145(*<)%I5)I%1*
!
6789:;<=$>$?@<=:AB$
!
*
B&&C* !DE*(4<*4*)1)%4(19%40*'1"71)%$>*<"*)(1*/"39*9&#"01<*543510>*0149&3'*)"*4*3"3#"04%*7"015F01:**
!"#$*
*
G&)(*A&=1*#4&%<*"A*1015)%"3<*4%"F39*)(1*513)%40*H*4)"7>*HDE*16(&/&)<*4*)%&'"340*/&#$%47&940*
!"#$**
1015)%"3&5*'1"71)%$>*I&)(*)(1*0"31*#4&%*"A*1015)%"3<:**J3*)(&<*5"3A&'F%4)&"3>*)(1*/"39*9&#"01<*
!"#$%&'()*+*,--.*/$*!"001'1*23)%4351*2647&34)&"3*8"4%9:*;00*%&'()<*%1<1%=19:*!"001'1*8"4%9>*;9=43519*?0451713)*?%"'%47>*;?>*439*)(1*45"%3*0"'"*
9"*3")*543510>*439*)(1*7"015F01*&<*#"04%:*
4%1*%1'&<)1%19*)%49174%@<*"A*)(1*!"001'1*23)%4351*2647&34)&"3*8"4%9:*
!"#$%&'()*+*,--.*/$*!"001'1*23)%4351*2647&34)&"3*8"4%9:*;00*%&'()<*%1<1%=19:*!"001'1*8"4%9>*;9=43519*?0451713)*?%"'%47>*;?>*439*)(1*45"%3*0"'"*
!
4%1*%1'&<)1%19*)%49174%@<*"A*)(1*!"001'1*23)%4351*2647&34)&"3*8"4%9:*
!"#$%&'()*+*,--.*/$*!"001'1*23)%4351*2647&34)&"3*8"4%9:*;00*%&'()<*%1<1%=19:*!"001'1*8"4%9>*;9=43519*?0451713)*?%"'%47>*;?>*439*)(1*45"%3*0"'"*
D
"#!
D
4%1*%1'&<)1%19*)%49174%@<*"A*)(1*!"001'1*23)%4351*2647&34)&"3*8"4%9:*
!
!
"#!
D
"#! !
H
D
D
•
!! (b ii)
D
*
K31*#"&3)*14%319*A"%*145(*7"015F01*A"%*#%"#1%*'1"71)%$*439*16#0434)&"3**
*
*
!
::
D
D
*
O
*
Unit I
3.
Bonding & Geometry Practice
(pg 5 of 12)
Using principles of chemical bonding and molecular geometry, explain each of the following observations.
Lewis electron-dot diagrams and sketches of molecules may be helpful as part of your explanations. For each observation, your
answer must include references to both substances.
(a) The bonds in nitrite ion, NO2−, are shorter than the bonds in nitrate ion, NO3−.
(b) The CH2F2 molecule is polar, whereas the CF4 molecule is not.
(c) The atoms in a C2H4 molecule are located in a single plane, whereas those in a C2H6 molecule are not.
(d) The shape of a PF5 molecule differs from that of an IF5 molecule.
(e) HClO3 is a stronger acid than HClO.
Using principles of chemical bonding and molecular geometry, explain each of the following observations.
1 point
earned
Lewis electron-dot diagrams and sketches of molecules may be helpful as part of your
explan
ations.for
For each
the difference in the
observation, your answer must include references to both substances.
Unit I
effective number of
bonds in both ions
Bonding & Geometry Practice
According
to thein
Lewis
two
resonance
(a) The bonds
nitriteelectron-dot
ion, NO2– ,diagram,
are shorter
than
the bondsstructures
in nitrate are
ion, NO3– .
ANSWER
required #3
to represent the bonding in the NO2– ion. The effective number of
bonds between N and O is 1.5.
According to the Lewis electron-dot diagram, two resonance structures are
required to represent the bonding in the NO2– ion. The effective number of
bonds between N and O is 1.5.
1 point earned for
the difference in the
1 point earned for
effective number of
relating the effective
bonds in both ions
number of bonds to
bond length
Three resonance structures are required to represent the bonding in theNO3–
1 point earned for
ion. The effective number of bonds between N and O is 1.33.
relating the effective
The greater the effective number of bonds, the shorter the N–O bond length.number of bonds to
bond length
AP® CHEMISTRY
2002
SCORING
GUIDELINES
(Form
Three resonance structures
are required
to represent
the bonding in the
NO3– B)
®
ion.(b)
The
effective
of bonds between
and O is 1.33.
AP NCHEMISTRY
The
CH2Fnumber
2 molecule is polar, whereas the CF4 molecule is not.
2002 SCORING
GUIDELINES
Question
6 (cont’d.) (Form B)
(a) The greater the effective number of bonds,®the shorter the N–O bond length.
AP CHEMISTRY
(c) The
in a geometry
C2H4 molecule
single
plane, whereas
those in
C2H6 molecule
Theatoms
molecular
in both are
CH2located
F2 and in
CFa46
is(cont’d.)
1 point earned
foradiscussing
the are not.
Question
2002 SCORING
GUIDELINES
(Form
B)
similarity
in
molecular
geometry
tetrahedral (or the same). The C-F bond is polar. In CF4,
Theatoms
carbon
in molecule
C2H4 is
have
a located
molecular
TheinCH
polar,
whereas
CF
molecule
is not. those in a C2H6 molecule are not.
(c) The
aatoms
arethe
inthe
a single
plane, whereas
2CF22Hmolecule
the(b)
molecular
geometry
arranges
C-F dipoles
so4that
4
1 point1earned
for thefor
bonding
Question
6 (cont’d.)
point earned
discussing the
geometry
around
each
carbon
atom
that
is
trigonal
they cancel out and the molecule is nonpolar. The C-H bond
of
the
carbon
atoms
relationship
between
molecular geometry
planar
(AX
),
so
all
six
atoms
are
in
the
same
The
carbon
in C
a molecular
is less
polar3atoms
than the
C-F
two C-H dipoles do not
2Hbond.
4 have The
and
the
C-H
and
C-F
(c) The
atoms
in
a
C
H
molecule
are
located
in
a
single
plane,
whereas
those
in
a
C
H
molecule
1
point
earned
for
the
bonding
2 each
4dipoles
2 6bond
The
molecular
geometry
in both
CH
1 point earned for discussing
the dipolesare not.
plane.
The
carbon
atoms
in
aCF
molecular
around
carbon
atom
trigonal
cancel
the
two
C-F
in C
CH
. andis
2H226FF2have
2that
4 is
(b) geometry
1 point
earned
for the structure
of
the
carbon
atoms
similarity
in
molecular
geometry
planar
(AXthat
so
six atoms
arebond
the
same
geometry
is all
tetrahedral
),inso
atoms
tetrahedral
(or), the
same).
The (AX
C-F
isthe
polar.
In are
CF4,
The carbon 3atoms in C2H4 have a4molecular
the
geometry
arranges
so that
plane.
in C2the
H6 C-F
havedipoles
a molecular
notmolecular
all The
in thecarbon
same atoms
plane.
11point
earned
for
the
bonding
1 point
earned
geometry
around
each
carbon atom
that is trigonal
point
earned
forfor
thediscussing
structurethe
they
out is
andtetrahedral
the molecule
is nonpolar.
The C-H
OR cancelthat
geometry
(AX
the atoms
arebondof the
4),inso
carbon atoms
relationship
between
molecular geometry
planar
(AX
),
so
all
six
atoms
are
the
same
is
lesscarbon-carbon
polar3than the C-F
bond.
Theintwo
C-Hresults
dipolesindoanot
The
double
bond
C2H
4
not
all in the same plane.
and the C-H and C-F bond dipoles
cancel the
C-F dipoles
F
.
plane.
Thetwo
carbon
atoms in CH
C2H
have
a
molecular
2 62
planar molecule whereas the carbon-carbon
single 1 point earned for the structure
OR
geometry that is tetrahedral (AX4), so the atoms are
bondcarbon-carbon
in C2H6 results
inCopyright
a non-planar
(tetrahedral)
The
double
bond©in2002
C2H
resultsEntrance
in a Examination Board. All rights reserved.
by4 College
not all in the
same plane.
Placement
and AP are
registered trademarks of the College Entrance Examination Board.
site at molecule
eachAdvanced
carbon
atom.the Program
planar
whereas
carbon-carbon
single
OR
bond in C2H6 results in a non-planar (tetrahedral)
The carbon-carbon
double bond in C2H4 results in a 14
(d) The
a PF5 atom.
molecule differs from that of an IF5 molecule.
site shape
at eachofcarbon
planar molecule whereas
the carbon-carbon single
Copyright
© 2002 by
College Entrance Examination Board. All rights reserved.
bond
in
C
H
results
in
a
non-planar
(tetrahedral)
2Advanced
6
In PF
geometry
isand
trigonal
Program
AP arethat
registered
of the College Entrance Examination Board.
5, the
(d) The
shape
of molecular
a PF5Placement
molecule
differs
from
of antrademarks
IF5 molecule.
at each carbon atom.
(c) site
bipyramidal
because the phosphorus atom has
14 1 point earned for discussing the
In
PFbonding
geometry and
is trigonal
five
pairs of electrons
no lone
5, the molecular
(d) The
shape
of
a
PF
molecule
differs
from
that
of
an
IF5 difference
molecule. made by the lone pair of
5
pairs of electrons.
bipyramidal
because
the phosphorus atom has
electrons
in IFfor
how it affects
1 point earned
discussing
the
IF5 has
square
pyramdal
molecular
geometry.
5 and
five
pairs
of electrons
and no
lone
In
PFbonding
5, the molecular geometry is trigonal
difference
made
by
the
lone
pair of
the
geometry
of
the
two
molecules
pairs
of electrons.
The central
iodine atom has five bonding pairs
bipyramidal
because
the phosphorusgeometry.
atom has
electrons in IF5 and how it affects
IF
has square
pyramdal
of5electrons
and
one lonemolecular
pair of electrons.
1 point earned for
discussing the
five
bonding pairs of electrons and no lone
the geometry
ofby
thethe
two
molecules
The central
presence
of the
additional
pair of
electrons difference
The
iodine
atom
has fivelone
bonding
pairs
made
lone
pair of
pairs
of electrons.
on
the
central
iodine
atom
means
the
molecular
of
electrons
and
one
lone
pair
of
electrons.
electrons
in
IF
and
how
it
affects
IF5 has square pyramdal molecular geometry.
5
geometry
is different.
The
presence
of the additional lone pair of electrons the geometry of the two molecules
The central iodine atom has five bonding pairs
on the central iodine atom means the molecular
of electrons and one lone pair of electrons.
(e)(d)HClO
geometry
different.acid than HClO.
3 is aisstronger
The presence
of the additional lone pair of electrons
on
the
central
atom means
the molecular
According
toiodine
the formula
for HOCl
and HOClO2, there are two
(e) HClO
3 is aisstronger
geometry
different.acid than HClO.
1 point earned for
additional terminal, electronegative oxygen atoms attached to the
discussing the
According
to
the
formula
for
HOCl
and
HOClO
,
there
are
two
central chlorine atom. These additional terminal
2 oxygen atom
(e) HClO3 is a stronger acid than HClO.
importance
offor
the
1
point earned
–
additional
terminal,
electronegative
atoms
attached to
stabilize the
negative
charge on the oxygen
anion ClO
to the
3 compared
electronegativity
of
discussing
the
central
chlorine
atom.
These
additional
terminal
oxygen
atom
According
the formula
for HOCl
and HOClO2attraction
, there arebetween
two
ClO–. Thetoresult
is to reduce
the electrostatic
the terminalofoxygen
importance
the
– compared to
stabilize
the
negative
charge
on
the
anion
ClO
1 point earned for
3 attached to the
additional
terminal,
the H+ and
ClOx–. electronegative oxygen atoms
atoms in the twoof
electronegativity
discussing the
–. chlorine
central
atom.
These
additional
terminal
oxygen
atom
ClO
The
result
is
to
reduce
the
electrostatic
attraction
between
structures
OR
the
terminalofand/or
oxygen
the
+ and
stabilize
the
negative
charge on
the anion ClO3O– atoms
compared
to to the importance
the
ClO
TheHtwo
additional
electronegative
bonded
the enhanced
x–. terminal
atoms
in
the
twoof
electronegativity
–. The
– pull electron
stability of
the
structures
OR
ClO
result
to3reduce
the electrostatic
attraction
chlorine
atom
of is
ClO
density away
frombetween
the central the
terminaland/or
oxygen
chlorate
vs.
the
The
two
additional
terminal
electronegative
O
atoms
bonded
to
the
the
enhanced
+
–
the
H and
ClOxThe
. net result is to weaken the H-O bond. Since atoms in the two
chlorine
atom.
– pull electron density away from the central stability
hypochlorite
ion
of
the
chlorine
atom
of
ClO
HOCl has no additional
structures and/or
OR
3 terminal O atoms, its H-O bond is
chlorate
vs.
the
stronger.
The weaker
H-O
the stronger
acid.Since
two additional
electronegative
O atoms
bonded
to the the enhanced
chlorine
atom.
Theterminal
netthe
result
isbond,
to weaken
the
H-Othe
bond.
(e) The
hypochlorite
of theion
HOCl has
no additional
terminal
O atoms,
H-Ofrom
bondthe
is central stability
chlorine
atom
of ClO3– pull
electron
densityits
away
chlorate vs. the
stronger.atom.
The weaker
H-Oisbond,
the stronger
acid.Since
chlorine
The netthe
result
to weaken
the H-Othe
bond.
hypochlorite
ion
Copyright
©
2002
by
College
Entrance
Examination
Board.
All
rights reserved.
HOCl has no additional terminal O atoms, its H-O bond is
Advanced Placement Program and AP are registered trademarks of the College Entrance Examination Board.
stronger. The weaker the H-O bond, the stronger the acid.
(pg 6 of 12)
Unit I
4.
Bonding & Geometry Practice
Using the information in the table to the right, answer the following questions
about organic compounds.
(a) For propanone,
(i) draw the complete structural formula (showing all atoms and bonds);
(pg 7 of 12)
Compound
Name
Propane
Propanone
1-propanol
Compound
Formula
CH3CH2CH3
CH3COCH3
CH3CH2CH2OH
ΔH°vap
(kJ mol–1)
19.0
32.0
47.3
(ii) predict the approximate carbon-to-carbon-to-carbon bond angle.
(b) For each pair of compounds below, explain why they do not have the same value for their standard heat of vaporization, ΔH°vap.
(You must include specific information about both compounds in each pair.)
(i) Propane and propanone
(ii) Propanone and 1-propanol
(c) Draw the complete structural formula for an isomer of the molecule you drew in part (a) (i).
(d) Given the structural formula for propyne below,
(i) indicate the hybridization of the carbon atom indicated by the arrow in the structure above;
(ii) indicate the total number of sigma (σ) bonds and the total number of pi (π) bonds in the molecule.
!/C4! (-*K!EF+!M#$%.+E+!BE-&ME&-*.!G#-$&.*!/BF#KC'D!*..!*E#$B!*'(!H#'(B4N!
!"!#$%&'()*+,#
! ABC'D!EF+!C'G#-$*EC#'!C'!EF+!E*H.+!*H#I+J!*'BK+-!EF+!G#..#KC'D!L&+BEC#'B!*H#&E!#-D*'CM!M#$%#&'(B:!
! !"##$! %&'()*'*+!)*,!-.(&'()*'/
!
-../#)$0+(12#23(4&5(1&)#
! ,#-!%-#%*'#'+J! !
/*4!
!
!
!
!
!
! 01+!#*2+&3'/+45/)&!)22&)42#6+!7'&4+8!#*!-.(&'()*'/!)&+!,#8(+&8#'*!
Bonding & Geometry
Practice
-!('#*2!7'&!4'&&+42/9!
! !/C4!
!Unit
! I!/CC4! %-+(CME!EF+!*%%-#OC$*E+!M*-H#'=E#=M*-H#'=E#=M*-H#'!H#'(!*'D.+:!
(-*K!EF+!M#$%.+E+!BE-&ME&-*.!G#-$&.*!/BF#KC'D!*..!*E#$B!*'(!H#'(B4N!
7'&4+8!)*,!19,&':+*.;'*,#*:<!01+!=>?8!#*!(&'()*'*+!)&+!,#8(+&8#'*!
6789:;<=#>#?@<=:ABCD#
#,+*2#79#*:!21+!=>?8!7'&!+)41!
!
)*,!,#('/+.,#('/+<!@#*4+!21+!#*2+&3'/+45/)&!)22&)42#6+!7'&4+8!,#77+&!#*!
ANSWER #4
3!%#C'E!G#-!M#$%.+E+!*'(!M#--+ME!BE-&ME&-*.!G#-$&.*!
85;82)*4+!
! !"##$! %&'()*'*+!)*,!-.(&'()*'/
! 21+!2A'!85;82)*4+8B!21+!+*21)/(9!'7!6)('&#C)2#'*!A#//!,#77+&<
PF+! " 2 " 2 "! H#'(!*'D.+!CB!38;# !
3!%#C'E!G#-!H#'(!*'D.+!
!
!
!
!
!
01+!#*2+&3'/+45/)&!)22&)42#6+!7'&4+8!#*!-.(&'()*'/!)&+!,#8(+&8#'*!
! ! !!
-!('#*2!7'&!4'&&+42/9!
7'&4+8!)*,!19,&':+*.;'*,#*:<!01+!=>?8!#*!(&'()*'*+!)&+!,#8(+&8#'*!
3!%#C'E!G#-!M#$%.+E+!*'(!M#--+ME!BE-&ME&-*.!G#-$&.*!
! /H4! ,#-!+*MF!%*C-!#G!M#$%#&'(B!H+.#KJ!+O%.*C'!KFQ!EF+Q!(#!'#E!F*I+!EF+!B*$+!I*.&+!G#-!EF+C-!BE*'(*-(!
"4$!! D&)A!21+!4'3(/+2+!82&5425&)/!7'&35/)!7'&!)*!#8'3+&!'7!21+!3'/+45/+!9'5!,&+A!#*!()&2!")$!"#$<!
#,+*2#79#*:!21+!=>?8!7'&!+)41!
!
)*,!,#('/+.,#('/+<!@#*4+!21+!#*2+&3'/+45/)&!)22&)42#6+!7'&4+8!,#77+&!#*!
F+*E!#G!I*%#-CR*EC#'J!!!#"#$!:!/S#&!$&BE!C'M.&(+!B%+MCGCM!C'G#-$*EC#'!*H#&E!H#EF!M#$%#&'(B!C'!+*MF!
!! !
85;82)*4+!
21+!2A'!85;82)*4+8B!21+!+*21)/(9!'7!6)('&#C)2#'*!A#//!,#77+&<
!
(a
i)
!
%*C-:4!
! !/CC4! %-+(CME!EF+!*%%-#OC$*E+!M*-H#'=E#=M*-H#'=E#=M*-H#'!H#'(!*'D.+:!
!"!#$%&'()*+,#
!
!
! ! ! !!!
-../#)$0+(12#23(4&5(1&)#
!
! ! ! ! PF+!
!!/C4!"5-#%*'+!*'(!%-#%*'#'+
2
"
2
"!
H#'(!*'D.+!CB!38;#
3!%#C'E!G#-!H#'(!*'D.+!
!"4$! !D&)A!21+!4'3(/+2+!82&5425&)/!7'&35/)!7'&!)*!#8'3+&!'7!21+!3'/+45/+!9'5!,&+A!#*!()&2!")$!"#$<!
(a ii)
! !!
-!('#*2!7'&!4'&&+42B!4'3(/+2+!82&5425&)/!
! ! !/CC4! %-+(CME!EF+!*%%-#OC$*E+!M*-H#'=E#=M*-H#'=E#=M*-H#'!H#'(!*'D.+:!
6789:;<=#>#?@<=:ABCD#
!
7'&35/)!
!"!#$%&'()*+,#
!
!
PF+!C'E+-$#.+M&.*-!*EE-*MECI+!G#-M+B!C'!%-#%*'+!*-+!
!
! ,#-!+*MF!%*C-!#G!M#$%#&'(B!H+.#KJ!+O%.*C'!KFQ!EF+Q!(#!'#E!F*I+!EF+!B*$+!I*.&+!G#-!EF+C-!BE*'(*-(!
-../#)$0+(12#23(4&5(1&)#
!"##$!
%&'()*'*+!)*,!-.(&'()*'/
/H4!
PF+!
"
2
"
2
"!
H#'(!*'D.+!CB!38;#
3!%#C'E!G#-!H#'(!*'D.+!
(CB%+-BC#'!G#-M+B!#'.Q:!PF+!TU,B!C'!%-#%*'#'+!*-+!
!
!
!
3!%#C'E!G#-!M#--+ME.Q!C(+'ECGQC'D!EF+!TU,B!
!:!/S#&!$&BE!C'M.&(+!B%+MCGCM!C'G#-$*EC#'!*H#&E!H#EF!M#$%#&'(B!C'!+*MF!
F+*E!#G!I*%#-CR*EC#'J!!!#
"#$
!
(CB%+-BC#'!*'(!(C%#.+=(C%#.+:!VC'M+!EF+!C'E+-$#.+M&.*-!
!
G#-!+*MF!B&HBE*'M+!
01+!#*2+&3'/+45/)&!)22&)42#6+!7'&4+8!#*!-.(&'()*'/!)&+!,#8(+&8#'*!
%*C-:4! *EE-*MECI+!G#-M+B!(CGG+-!C'!EF+!EK#!B&HBE*'M+BJ!EF+!+'EF*.%Q!
-!('#*2!7'&!4'&&+42B!4'3(/+2+!82&5425&)/!
6789:;<=#>#?@<=:ABCD#
-!('#*2!7'&!4'&&+42/9!
!
7'&4+8!)*,!19,&':+*.;'*,#*:<!01+!=>?8!#*!(&'()*'*+!)&+!,#8(+&8#'*!
7'&35/)! #,+*2#79#*:!21+!=>?8!7'&!+)41!
",$!
! ! E#6+*!21+!82&5425&)/!7'&35/)!7'&!(&'(9*+!;+/'AB!
!!! (b i) #G!I*%#-CR*EC#'!KC..!(CGG+-:!
/H4!
,#-!+*MF!%*C-!#G!M#$%#&'(B!H+.#KJ!+O%.*C'!KFQ!EF+Q!(#!'#E!F*I+!EF+!B*$+!I*.&+!G#-!EF+C-!BE*'(*-(!
)*,!,#('/+.,#('/+<!@#*4+!21+!#*2+&3'/+45/)&!)22&)42#6+!7'&4+8!,#77+&!#*!
! 5-#%*'+!*'(!%-#%*'#'+
! !"##$! %&'()*'*+!)*,!-.(&'()*'/
! 85;82)*4+!
! ! F+*E!#G!I*%#-CR*EC#'J!!!#
!!/C4!
!
"#$!:!/S#&!$&BE!C'M.&(+!B%+MCGCM!C'G#-$*EC#'!*H#&E!H#EF!M#$%#&'(B!C'!+*MF!
!
21+!2A'!85;82)*4+8B!21+!+*21)/(9!'7!6)('&#C)2#'*!A#//!,#77+&<
!
!
!
%*C-:4!
! 01+!#*2+&3'/+45/)&!)22&)42#6+!7'&4+8!#*!-.(&'()*'/!)&+!,#8(+&8#'*!
! PF+!C'E+-$#.+M&.*-!*EE-*MECI+!G#-M+B!C'!%-#%*'+!*-+!
!!! ! 7'&4+8!)*,!19,&':+*.;'*,#*:<!01+!=>?8!#*!(&'()*'*+!)&+!,#8(+&8#'*! -!('#*2!7'&!4'&&+42/9!
#,+*2#79#*:!21+!=>?8!7'&!+)41!
!!/C4!
5-#%*'+!*'(!%-#%*'#'+
)*,!,#('/+.,#('/+<!@#*4+!21+!#*2+&3'/+45/)&!)22&)42#6+!7'&4+8!,#77+&!#*!
E#6+*!21+!82&5425&)/!7'&35/)!7'&!(&'(9*+!;+/'AB!
"#%Q-CDFE!W!8;;7!HQ!"#..+D+!X'E-*'M+!XO*$C'*EC#'!Y#*-(:!Z..!-CDFEB!-+B+-I+(:!
4$!!",$!
D&)A!21+!4'3(/+2+!82&5425&)/!7'&35/)!7'&!)*!#8'3+&!'7!21+!3'/+45/+!9'5!,&+A!#*!()&2!")$!"#$<!
(CB%+-BC#'!G#-M+B!#'.Q:!PF+!TU,B!C'!%-#%*'#'+!*-+!
85;82)*4+!
!
3!%#C'E!G#-!M#--+ME.Q!C(+'ECGQC'D!EF+!TU,B!
!
ZI*C.*H.+!*E!*%M+'E-*.:M#..+D+H#*-(:M#$:!
21+!2A'!85;82)*4+8B!21+!+*21)/(9!'7!6)('&#C)2#'*!A#//!,#77+&<
(CB%+-BC#'!*'(!(C%#.+=(C%#.+:!VC'M+!EF+!C'E+-$#.+M&.*-!
(b
ii)
!
!
! G#-!+*MF!B&HBE*'M+!
*EE-*MECI+!G#-M+B!(CGG+-!C'!EF+!EK#!B&HBE*'M+BJ!EF+!+'EF*.%Q!
!
"#$!#*,#4)2+!21+!19;&#,#C)2#'*!'7!21+!4)&;'*!)2'3!#*,#4)2+,!;9!21+!)&&'A!#*!21+!82&5425&+!);'6+F!
-.#
#G!I*%#-CR*EC#'!KC..!(CGG+-:
! PF+!C'E+-$#.+M&.*-!*EE-*MECI+!G#-M+B!C'!%-#%*'+!*-+!
!
!
!
(CB%+-BC#'!G#-M+B!#'.Q:!PF+!TU,B!C'!%-#%*'#'+!*-+!
3!%#C'E!G#-!M#--+ME.Q!C(+'ECGQC'D!EF+!TU,B!
!
"4$!
D&)A!21+!4'3(/+2+!82&5425&)/!7'&35/)!7'&!)*!#8'3+&!'7!21+!3'/+45/+!9'5!,&+A!#*!()&2!")$!"#$<!
(CB%+-BC#'!*'(!(C%#.+=(C%#.+:!VC'M+!EF+!C'E+-$#.+M&.*-!
G#-!+*MF!B&HBE*'M+!
-!('#*2!7'&!4'&&+42B!4'3(/+2+!82&5425&)/!
!
!
!*EE-*MECI+!G#-M+B!(CGG+-!C'!EF+!EK#!B&HBE*'M+BJ!EF+!+'EF*.%Q!
"#!19;&#,#C)2#'*
!
-!('#*2!7'&!4'&&+42!19;&#,#C)2#'*!
!
7'&35/)!
!!
#G!I*%#-CR*EC#'!KC..!(CGG+-:
!
!!
!
"#$!#*,#4)2+!21+!19;&#,#C)2#'*!'7!21+!4)&;'*!)2'3!#*,#4)2+,!;9!21+!)&&'A!#*!21+!82&5425&+!);'6+F!
!
"#%Q-CDFE!W!8;;7!HQ!"#..+D+!X'E-*'M+!XO*$C'*EC#'!Y#*-(:!Z..!-CDFEB!-+B+-I+(:!
! !! !(c)
!
ZI*C.*H.+!*E!*%M+'E-*.:M#..+D+H#*-(:M#$:!
!"##$!#*,#4)2+!21+!2'2)/!*53;+&!'7!8#:3)!"!$!;'*,8!)*,!21+!2'2)/!*53;+&!'7!(#!""$!;'*,8!#*!21+!
!
-!('#*2!7'&!4'&&+42B!4'3(/+2+!82&5425&)/!
!
3'/+45/+<!
7'&35/)!
! !
"#!19;&#,#C)2#'*
! -.# -!('#*2!7'&!4'&&+42!19;&#,#C)2#'*!
(d i)
!
,$! E#6+*!21+!82&5425&)/!7'&35/)!7'&!(&'(9*+!;+/'AB!
!
"#%Q-CDFE!W!8;;7!HQ!"#..+D+!X'E-*'M+!XO*$C'*EC#'!Y#*-(:!Z..!-CDFEB!-+B+-I+(:!
!
!
!
ZI*C.*H.+!*E!*%M+'E-*.:M#..+D+H#*-(:M#$:!
!
! ! !!
! ! -!('#*2!7'&!4'&&+42!*53;+&!'7!8#:3)!;'*,8!
G!8#:3)!;'*,8!
! !"##$!#*,#4)2+!21+!2'2)/!*53;+&!'7!8#:3)!"!$!;'*,8!)*,!21+!2'2)/!*53;+&!'7!(#!""$!;'*,8!#*!21+!
! -.#
! ! 3'/+45/+<!
H!(#!;'*,8!
-!('#*2!7'&!4'&&+42!*53;+&!'7!(#!;'*,8
! ! (d
! ii)",$! E#6+*!21+!82&5425&)/!7'&35/)!7'&!(&'(9*+!;+/'AB!
!
! !
!
!
!
! "#$!#*,#4)2+!21+!19;&#,#C)2#'*!'7!21+!4)&;'*!)2'3!#*,#4)2+,!;9!21+!)&&'A!#*!21+!82&5425&+!);'6+F!
!
-!('#*2!7'&!4'&&+42!*53;+&!'7!8#:3)!;'*,8!
G!8#:3)!;'*,8!
!
! !
H!(#!;'*,8!
-!('#*2!7'&!4'&&+42!*53;+&!'7!(#!;'*,8
I'(9&#:12!J!HKKL!;9!I'//+:+!M*2&)*4+!MN)3#*)2#'*!O')&,<!P//!&#:128!&+8+&6+,<!
!
!
P6)#/);/+!)2!)(4+*2&)/<4'//+:+;')&,<4'3<!
!
!
!-!('#*2!7'&!4'&&+42!19;&#,#C)2#'*!
!
!
"#!19;&#,#C)2#'*
!
!
-E#
"#$!#*,#4)2+!21+!19;&#,#C)2#'*!'7!21+!4)&;'*!)2'3!#*,#4)2+,!;9!21+!)&&'A!#*!21+!82&5425&+!);'6+F!
!
!
!!
!
I'(9&#:12!J!HKKL!;9!I'//+:+!M*2&)*4+!MN)3#*)2#'*!O')&,<!P//!&#:128!&+8+&6+,<!
!"##$!#*,#4)2+!21+!2'2)/!*53;+&!'7!8#:3)!"!$!;'*,8!)*,!21+!2'2)/!*53;+&!'7!(#!""$!;'*,8!#*!21+!
P6)#/);/+!)2!)(4+*2&)/<4'//+:+;')&,<4'3<!
"#!19;&#,#C)2#'*
!
-!('#*2!7'&!4'&&+42!19;&#,#C)2#'*!
3'/+45/+<!!
!
!
!
!
-E#
! ! ! ! !!
!
!
!
!"##$!#*,#4)2+!21+!2'2)/!*53;+&!'7!8#:3)!"!$!;'*,8!)*,!21+!2'2)/!*53;+&!'7!(#!""$!;'*,8!#*!21+!
!
-!('#*2!7'&!4'&&+42!*53;+&!'7!8#:3)!;'*,8!
G!8#:3)!;'*,8
!
3'/+45/+<!
!
H!(#!;'*,8!
-!('#*2!7'&!4'&&+42!*53;+&!'7!(#!;'*,8
!
!
!
!
!
G!8#:3)!;'*,8!
H!(#!;'*,8!
!
!
-!('#*2!7'&!4'&&+42!*53;+&!'7!8#:3)!;'*,8!
-!('#*2!7'&!4'&&+42!*53;+&!'7!(#!;'*,8
!
(pg 8 of 12)
Unit I
5.
Bonding & Geometry Practice
(pg 9 of 12)
Explain each of the following in terms of the electronic structure and/or bonding of the compounds involved.
(a) At ordinary conditions, HF (normal boiling point = 20°C) is a liquid, whereas HCl (normal boiling point = -114°C) is a gas.
(b) Molecules of AsF3 are polar, whereas molecules of AsF5 are nonpolar.
(c) The N-O bonds in the NO2¯ ion are equal in length, whereas they are unequal in HNO2.
(d) For sulfur, the fluorides SF2, SF4, and SF6 are known to exist, whereas for oxygen only OF2 is known to exist.
Unit I
Bonding & Geometry Practice
(pg 10 of 12)
ANSWER #1
(a) Both molecules have dispersion forces, but HF exhibits the stronger hydrogen bonding
while HCl only has dipole-dipole interactions.
(note: only 1 pt if simply stated that HF has greater IMF than HCl.
1 pt
1 pt
(b) AsF3 has a trigonal pyramid shape and the polar bonds do NOT cancel out
(it is an asymmetric molecule)
AsF5 has a trigonal bipyramid shape and its polar bonds Do cancel out
(it is a symmetric molecule)
(note: explanation must refer to the shape to earn the points, 1 point earned only if correct Lewis structures are given,
1 pt
(c) NO2-1 has resonance structures, resulting in equal length bonds
1 pt
HNO2 has no resonance structures
(note: only 1 point if only the correct Lewis structure is given including the correct resonance structure.)
(d) For SF4, and SF6 the sulfur has an expanded octet, and sulfur can access the 3d orbitals
oxygen has no access to d orbital since no d’s can exist in oxygen’s 2nd valence shell.
Page 2
Page 2
1 pt
1 pt
1 pt
1 pt
Unit I
6.
Bonding & Geometry Practice
Use simple structure and bonding models to account and explain for each of the following.
(a) The bond length between the two carbon atoms is shorter in C2H4 than in C2H6. (2)
(b) The H−N− H bond angle is 107.5° in NH3.
(2)
(c) The bond lengths in SO3 are all identical and are shorter than a sulfur-oxygen single bond. (2)
(d) The I3¯ ion is linear.
(2)
(pg 11 of 12)
Unit I
Bonding & Geometry Practice
(pg 12 of 12)
ANSWER #6
(a) Make two Lewis structure sketched. C2H4 contains a C−C double bond, while C2H6 is a single bond. Double bonds are shorter
than single bonds.
(b) Draw a Lewis structure for NH3 as well as a 3-D sketch to show the shape. State that the shape of NH3 is trigonal pyramid
because the tetrahedral set of domains with one unshared pair of electrons results in trigonal pyramid. Further, the expected
109.5º bond angle, is shorter, at 107º because the un-bonded pair of electrons requires more space and repels the bonding pair of
electrons away, closing up their bond angles.
(c) Sketch a Lewis structure, then sketch the 2 other resonance structures. Resonance supports the experimental observation by
indicating the bonds are a blend of double and single character and will thus be shorter than a single, but longer than a double
and all three identical.
(d) Draw a Lewis structure as well as a 3-D sketch that indicates three unshared pairs in the equatorial positions. The five domains
around the central I atom requires trigonal bipyramidal, with it’s three unshared pairs in the equatorial positions, resulting in a
linear molecule.