Math 55
advertisement
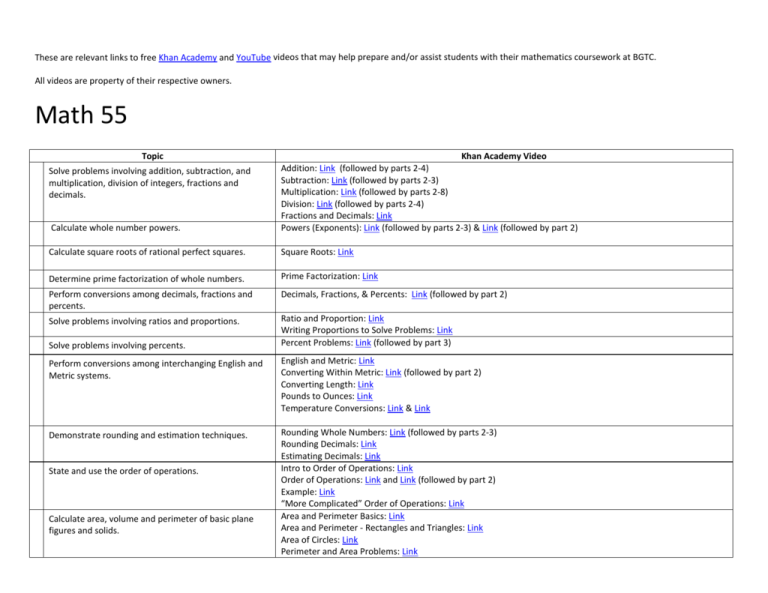
These are relevant links to free Khan Academy and YouTube videos that may help prepare and/or assist students with their mathematics coursework at BGTC. All videos are property of their respective owners. Math 55 Topic Calculate whole number powers. Khan Academy Video Addition: Link (followed by parts 2-4) Subtraction: Link (followed by parts 2-3) Multiplication: Link (followed by parts 2-8) Division: Link (followed by parts 2-4) Fractions and Decimals: Link Powers (Exponents): Link (followed by parts 2-3) & Link (followed by part 2) Calculate square roots of rational perfect squares. Square Roots: Link Determine prime factorization of whole numbers. Prime Factorization: Link Perform conversions among decimals, fractions and percents. Decimals, Fractions, & Percents: Link (followed by part 2) Solve problems involving ratios and proportions. Ratio and Proportion: Link Writing Proportions to Solve Problems: Link Percent Problems: Link (followed by part 3) Solve problems involving addition, subtraction, and multiplication, division of integers, fractions and decimals. Solve problems involving percents. Perform conversions among interchanging English and Metric systems. English and Metric: Link Converting Within Metric: Link (followed by part 2) Converting Length: Link Pounds to Ounces: Link Temperature Conversions: Link & Link Demonstrate rounding and estimation techniques. Rounding Whole Numbers: Link (followed by parts 2-3) Rounding Decimals: Link Estimating Decimals: Link Intro to Order of Operations: Link Order of Operations: Link and Link (followed by part 2) Example: Link “More Complicated” Order of Operations: Link Area and Perimeter Basics: Link Area and Perimeter - Rectangles and Triangles: Link Area of Circles: Link Perimeter and Area Problems: Link State and use the order of operations. Calculate area, volume and perimeter of basic plane figures and solids. Apply basic formulas. Read and interpret tables and graphs. Identify and apply the properties of real numbers. Solve applied problems using these competencies with real world applications. Volume of a Sphere: Link Solid Geometry Volume: Link Cylinder Volume (and Surface Area): Link Evaluate a formula using substitution: Link Algebra Tables: YouTube Video Part 1 (followed by many more videos about various tables) Reading Bar Graphs: Link Reading Line Graphs: Link Reading Pie Graphs: Link Properties of Whole Numbers: Link Absolute Values: Link Integers and Rational Numbers: Link Word Problem Solving Strategies: Link Word Problem Solving Plan: Link Application Problems involving Weight: Link MAT 65 Ch. 1 2 Topic Measurement A. Convert measurements of length, weight, and capacity within the U.S. Customary System. B. Convert measurements of length, weight, and capacity within the International System of units (metric). C. Convert U.S. Customary units to metric units. D. Convert metric units to U.S. Customary units. Algebraic Expressions A. Simplify expressions using properties of exponents. B. Evaluate variable expressions. C. Simplify variable expressions using the property of real numbers and the order of operations. D. Translate verbal expressions into variable expressions. Khan Academy Video Converting Different Units of Length: link Converting within the Metric System: link Converting Between Metric Units: link Unit Conversion: link U.S. Customary and Metric Units: link Converting Pounds to Ounces: link Gallons to Quarts, Pints and Cups: link Adding Different Units of Length: link Adding Different Units of Weight: link Exponent Properties 1: link (Click Next Video to view Exponent Properties 2-7) Understanding Exponents: link (There is a Part 2) Simplifying Expressions with Exponents: link (There is a Part 2 and 3) Variable Expressions: link Introduction to Order of Operations: link Order of Operations: link (There is a Part 2) Order of Operations: link (Also a Part 2) Order of Operations Example: link More Complicated Order of Operations Example: link Adding and Subtracting Real Numbers: link 3 Different Notations A. Perform arithmetic operations with powers of 10. B. Write numbers in scientific and engineering notation. C. Multiply and divide numbers in scientific and engineering notation. D. Add, subtract, multiply, and divide numbers with measurements of units. 4 Roots A. B. C. D. 5 6 Simplify square roots. Evaluate square roots. Simplify and evaluate cube roots. Calculate the third side of a right triangle using the Pythagorean Theorem. Equations A. Solve linear equations in one variable. B. Translate verbal problems into equations and solve. C. Solve literal equations with variables of power 1. D. Solve application problems using direct variation. E. Solve application problems using inverse variation. F. Solve applications of linear equations. Linear Inequalities A. Solve linear inequalities in one variable. B. Graph solutions. Square Roots and Real Numbers: link Word Problem Solving Strategies: link Scientific Notation: link (followed by part 2 and 3) Scientific Notation: link Scientific Notation 1: link (followed by part 2 and 3) Unit Vectors and Engineering Notation: link Adding Different Units of Length: link Adding Different Units of Weight: link Application Problems Involving Units of Weight: link Understanding Square Roots: link Simplifying Square Roots: link Approximating Square Roots: link Simplifying Cube Roots: link Finding Cube Roots: link Pythagorean Theorem 1: link (followed by part 2 and 3) Pythagorean Theorem Application: Link Linear Equations 1: link (followed by part 2-4) Word Problem Solving Strategies: link Direct and Inverse Variation: link Recognizing Direct and Inverse Variation: link Direct Variation 1: link Direct Variation Application: link Inverse Variation Application: link Solving Inequalities: link Graphing Inequalities 1: link (followed by part 2) 7 Graphing A. Plot points in the plane. B. Graph linear equations using the slope and y-intercept. C. Graphing of real world data and applications of graphing linear equations. Graphing a Basic Function: link Graphing Using X and Y Intercepts: link Graphing a Line in Slope Intercept Form: link Graphs of Linear Equations: link Graphing Lines: link Application Problem with Graph: link 8 Polynomials and Exponents Exponent Properties 1: link (Click Next Video to view Exponent Properties 2-7) A. Define and use properties of integral exponents. B. Add, subtract, and multiply polynomials. C. Divide a polynomial by a monomial. 9 Factoring A. Factor the greatest common factor from a polynomial,. 2 B. Factor a simple trinomial of the form x + bx + c. C. Factor difference of two squares. Understanding Exponents: link (There is a Part 2) Polynomials 1: link (followed by Part 2) Adding and Subtracting Polynomials: link (There is a part 2 and 3) Multiplying Polynomials: link (followed by Part 2 and 3) Polynomial Divided by Monomial: link Factor Polynomials using Greatest Common Factor (GCF): link Factoring Trinomials with a Common Factor: link Factoring Difference of Squares: link MAT 110 Ch. 3.1 Topic Statement, Negations, & Quantified Statements 3.2 Compound Statements & Connectives 3.3 5.6 Truth Tables Exponents and Scientific Notation 6.1 Algebraic Expressions & Formulas 6.2 Linear Equations & Proportions 6.3 7.1 Applications of Linear Equations Graphing & Functions 7.2 Linear Functions & their Graphs 7.3 System of Linear Equations Khan Academy Video Statements: YouTube Link Negations: YouTube Link Quantifiers: YouTube Link Compound and Simple Statements: YouTube Link Logical Connectives: YouTube Link (part 1) and YouTube Link (part 2) Truth Tables: YouTube Link Understanding Exponents 1-2: Understanding Exponents 1 (Click “Next Video” to access video 2) Exponent Properties 1-7: Exponent Properties 1 (Click “Next Video” to access videos 2-7) Scientific Notation 1-3: Scientific Notation 1 (Click “Next Video” to access videos 2-3) Simple Equations: Simple Equations Variable Expressions: Variable Expressions Algebra: Linear Equations 1-4: Algebra: Linear Equations 1 (Click “Next Video” to access videos 2-4) Understanding Proportions: Understanding Proportions Find an Unknown in a Proportion 1-2: Find an Unknown in a Proportion 1 (Click “Next Video” for Video 2) Example of Solving for a Variable: Example of Solving for a Variable Graphical Relations and Functions: Graphical Relations and Functions Evaluating Functions: Evaluating Functions Graphing a Basic Function: Graphing a Basic Function Graphing a line in slope intercept form: Graphing a Line in Slope Intercept Form Graphing Using Intercepts: Graphing Using Intercepts Graphing Using X and Y Intercepts: Graphing Using X and Y Intercepts Solving Linear Systems by Graphing: Solving Linear Systems by Graphing Systems of Equations: Systems of Equations Graphing Systems of Equations: Graphing Systems of Equations Solving Systems of Equations by Substitution: Substitution 8.1 Percent, Sales Tax, & Income Tax 8.2 8.3 Simple Interest Compound Interest 9.1 Measuring Length & the Metric System 9.2 Measuring Area & Volume 9.3 Measuring Weight & Temperature 12.1 Sampling, Frequency Distributions & Graphs 12.2 Measures of Central Tendency 12.3 12.4 Measures of Dispersion The Normal Distribution Solving Systems of Equations by Elimination: Elimination Solving Systems of Equations by Multiplication: Multiplication Percent and Decimals: Percent and Decimals Decimal, percent, and fraction 1-2: Decimal, Percent, & Fraction 1 (click “Next Video” for video 2) Basics of US Income Tax Rate Schedule: Income Tax Rate Schedule Introduction to Interest: Introduction to Interest 1 (click “Next Video” for part 2) Introduction to Compound Interest: Intro to Compound Interest Compound Interest and E: Intro to Compound Interest and E part 1 (click “Next Video” for next parts) Adding Different Units of Length: Adding Different Units of Length Converting Units of Length: Converting Units of Length Conversion Between Metric Units: Conversion Between Metric Units Area and Perimeter: Area and Perimeter Solving application problems involving units of volume: Volume Adding different units for weight: Adding Different Units for Weight Application problems involving units of weight: Units of Weight Comparing Celsius and Fahrenheit temperature scales: Comparing C and F Sampling Distribution of the Sample Mean 1-2: Sampling Distribution 1 (click “Next Video for part 2) Sampling Distribution Example Problem: Sampling Distribution Example Average or Central Tendency - Arithmetic Mean, Median, and Mode: Central Tendency Statistics - The Average: Average Range, Variance and Standard Deviation as Measures of Dispersion: Dispersion Introduction to the Normal Distribution: Intro to Normal Distribution ck12.org Normal Distribution Problems - z-score: Z-Score MAT 116 Topic Perform conversions using U. S. customary and SI (metric) measures. Khan Academy Video English and Metric: Link Converting Within Metric: Link (followed by part 2) Converting Length: Link Pounds to Ounces: Link Temperature Conversions: Link & Link Apply basic plane geometric principles of lines, angles, triangles and other polygons, circles and arcs, congruency and similarity. Lines, Segments, and Rays: Link Slope of Lines: Link Parallel Lines: Link (followed by part 2-3) Perpendicular Lines: Link (followed by part 2) Angles: Link & Link Congruent and Similar Triangles: Link , Link , Link (followed by part 2), 30-60-90 Triangles: Link (followed by part 2) Perimeter of Polygons: Link Area of a Circle: Link Radius, Diameter, and Circumference: Link Language and Notation of the Circle: Link Calculate surface area and volume of basic geometric solids. Cylinder volume and Surface Area: Link Sphere Volume: Link Solid Geometry Volume: Link Application Problems and Volume: Link Solve problems involving significant digits and accuracy and precision of numbers. Pure Numbers and Significant Digits: Link Significant Figures: Link (followed by part 2) Ratio and Proportion: Link Direct, Inverse, and Joint Variation: Link Direct Variation Application: Link Inverse Variation Application: Link Joint Variation Application: Link Solve problems involving ratio, proportion, direct, inverse and joint variation. Perform conversions between coordinate systems. Apply fundamentals of trigonometric functions and co-functions to right triangles. Apply the law of sines and the law of cosines to oblique triangles. Solve problems involving compound angles. Identify the vector concept, the components of vectors and add vectors. Use a scientific calculator. Polar Coordinates: Link Polar and Cartesian Coordinates: Link (followed by part 3) Alternate Coordinate Systems: Link Basic Trigonometry: Link Using Trig Functions: Link (followed by part 2) Proof: Law of Sines: Link Law of Cosines: Link Oblique Triangles: YouTube Link (Part 1) YouTube Link (Part 2) YouTube Link (Part 3) Compound Angles: YouTube Link (Part 1) YouTube Link (Part 2) Intro to Vectors: Link Vector Examples: Link Basic Scientific Calculator Functions: YouTube Link MAT 120 Topic Khan Academy Video Simplify & perform operations with rational expressions Simplify & perform operations with radical expressions Simplify expressions with rational exponents Simplifying Rational Expressions: Link (followed by parts 2-3) Adding and Subtracting Rational Expressions: Link (followed by parts 2-3) Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions: Link (followed by parts 2-3) Simplifying Radical Expressions: Link (parts 2-3 follow) and Link Solving Radical Equations: Link (parts 2-3 follow) Applying Radical Equations: Link (parts 2-3 follow) Multiply and Simplify a Radical Expression: Link (part 2 follows) Adding and Simplifying Radicals: Link Subtracting and Simplifying Radicals: Link Radical Equation Application: Link Rational Exponents and Exponent Laws: Link and Link Solve quadratic equations Intro to Quadratic Equation: Link (followed by part 2) Simple Quadratic Equation: Link Standard Form: Link Solve by Completing the Square: Link Solve by Factoring: Link (parts 2-3 follow) Solve by Graphing: Link Solve by Square Roots: Link Application of Quadratic Formula: Link Solve system of linear equations Solve System by Elimination: Link Solve System by Multiplication: Link System of Linear Inequalities Application: Link Linear Equations: Link (followed by parts 2-3) Standard Form: Link Point-Slope Form: Link Slope Intercept Form: Link Absolute Value Equations: Link Absolute Value Equation Examples: Link (part 2 follows) Solve linear & absolute value equations Solve linear & absolute value inequalities Graph using elementary techniques Linear Inequalities: Link Linear Inequalities in 2 Variables: Link (part 2 follows) Absolute Value Inequalities: Link Absolute Value Inequalities Example: Link Graphing Lines: Link Graphing a Basic Function: Link Graph using X and Y Intercepts: Link Graph using Intercepts: Link Slope and Y-Intercept: Link Application Problem with Graph: Link Graph Inequalities: Link (part 2 follows) Solve Linear Systems by Graphing: Link Solve Quadratic Equation by Graphing: Link Write equations of lines Use function notation Simplify & perform operations with complex numbers Equation of a Line: Link (part 2 and 3 follow) Algebra: Equation of a Line: Link Equations of Parallel and Perpendicular Lines: Link Parallel Line Equation: Link Function Notation: YouTube Link Complex Numbers: Link (part 2 follows) Adding Complex Numbers: Link Subtracting Complex Numbers: Link Multiplying Complex Numbers: Link Dividing Complex Numbers: Link Solve application problems involving all of the above Examples are included in previous videos MAT 126 Topic Solve problems involving ratios and proportions Khan Academy Video Ratio and Proportion: Link Writing Proportions: Link Proportionality: Link Understanding Proportions: Link Finding an Unknown in a Proportion: Link (followed by part 2) Solve rational equations Define triangles using the law of sines and the law of cosines Rational Equations: Link Solving Rational Equations: Link (followed by parts 2-3) and Link Applying Rational Equations: Link (followed by parts 2-3) Proof: Law of Sines: Link Law of Cosines: Link Identify the vector concept and the components of vectors and vector addition Intro to Vectors: Link Vector Examples: Link Determine the solutions to simultaneous linear equations using determinants Linear Algebra - Determinants: Link Solve quadratic equations by the process of factoring, completing the square, and the quadratic formula Intro to Quadratic Equation: Link (followed by part 2) Simple Quadratic Equation: Link Standard Form: Link Solve by Completing the Square: Link Solve by Factoring: Link (parts 2-3 follow) Solve by Graphing: Link Solve by Square Roots: Link Application of Quadratic Formula: Link Apply radians and the radian measurements including their applications to rotating objects Radians and Degrees: Link Introduction to Angular Velocity: Link Utilize phasor algebra to perform basic operations on complex numbers Complex Numbers: Link and Link Phasors: Part 1: YouTube Link (followed by MANY more parts) Utilize exponent and logarithmic equations such as population growth, time constants, and pH scale Solving Logarithmic Equations: Link Population Growth: YouTube Link pH scale: (Acid Base Introduction): Link Perform Conversions between number systems such as decimal, binary, octal, and hexadecimal Binary, Decimal, and Hexadecimal: Link Binary Numbers: Link Number Base Conversion Practice: Link Octal: YouTube Link Use a scientific calculator Scientific Calculator Basics: YouTube Link MAT 150 Sec. 2.1/2.2 Topic Piecewise Functions and The Algebra of Functions 2.3 The Compositions of Functions 2.4 Symmetry and Transformations 3.1 The Complex Number 3.2 Quadratic Equations, Functions, Zeros and Models Khan Academy Video Piecewise Functions: YouTube Link The Algebra of Functions: YouTube Link Compositions of Linear Transformations 1: link (followed by part 2) Linear Transformations: link Vector Transformations: link Complex Numbers: link Complex Numbers 1: link (followed by part 2) Adding Complex Numbers: link Subtracting Complex Numbers: link Multiplying Complex Numbers: link Dividing Complex Numbers: link Introduction to Quadratic Equation 1: link (followed by part 2) Quadratic Functions 1: link (followed by part 2 and 3) Zeros: YouTube Link 3.3 Analyzing Graphs of Quadratic Functions 3.4 Solving Rational Equations and Radical Equations 4.1 4.2 Polynomial Functions and Models Graphing Polynomial Functions 4.5 Rational Functions 5.1 Inverse Functions 5.3 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions and Graphs 5.5 Solving Exponential and Logarithmic equations 6.7 Systems of Inequalities 7.4 Non-Linear Systems of Equations/Conic Sections Identifying Quadratic Models: link Graphs of Quadratic Functions: link Graphing Quadratic Functions: link Rational Equations: link Solving Rational Equations 1: link (followed by part 2 and 3) Solving Radical Equations: link Solving Radical Equations 1: link (parts 2 and 3 follow) Polynomial Approximation of Functions : Link (parts 2-7 follow) Graph a Polynomial: YouTube Link and YouTube Link Asymptotes of Rational Functions: link Graphing Rational Functions: link and link Introduction to the Inverse of a Function: link Introduction to Function Inverses: link Exponential Growth Functions: link Exponential Decay Functions: link Logarithms: link Graphing Logarithmic Functions: link Solving Exponential Equations: link Solving Logarithmic Equations: link Systems of Linear Inequalities: link System of Inequalities Application: link Systems of Inequalities: link Non-Linear Systems of Equations 1: link (parts 2 and 3 follow) Introduction to Conic Sections: link Conic Sections: link STA 220 Topic Solve problems including discrete and continuous probability distributions using statistical methods. Identify examples of the different levels of data measurement and recognize several different types of sampling. Khan Academy Video Basic Probability: Link Probability: Link (followed by parts 2-8) Probability Density Functions: Link Binomial Distribution: Link (followed by parts 2-4) Discrete: YouTube Link and YouTube Link Continuous: YouTube Link Surveys and Samples: Link Sample Variance: Link Sample vs. Population Mean: Link Construct various types of graphical displays of data. Calculate and apply measures of central tendency, measures of dispersion, and measures of position, including the five-number summary. Apply the basic principles of probability. Graphical Relations and Functions: Link Graphical Slope of a Line: Link Graphical Systems of Inequalities: Link Graphical Systems Application Problems: Link Measures of Central Tendency: Link Measures of Dispersion: Link Intro to the Normal Distribution: Link Standard Deviation: Link Measures of Position: YouTube Link Five-Number Summary: YouTube Link Basic Probability: Link Probability: Link (followed by parts 2-8) Calculate z-scores for values in normal distribution, and find critical values for given probabilities. Binomial Distribution: Link (followed by parts 2-4) Qualitative Sense of Normal Distribution: Link Expected Value of Binomial Distribution: Link Empirical Rule: Link and Link Z-Score: Link Critical Values: YouTube Link Calculate normal approximations to binomial distributions. Normal Distribution Approximates: Link Apply the Central Limit Theorem when appropriate. Central Limit Theorem: Link Calculate point and interval estimates for large- and small-sample population means, proportions, and variances (standard deviations). Point and Interval Estimates: YouTube Link (Part 1 – Followed by parts 2 & 3) Large Sample Proportion: Link Small Sample Hypothesis Test: Link Small Sample Confidence Intervals: Link T-Statistic Confidence Interval: Link Variance of a Population: Link Standard Deviation: Link Determine adequate sample size needed to accurately estimate population means, proportions, and variances (standard deviations). Estimating the Population Mean: YouTube Link Part 1 and YouTube Link Part 2 Estimating Population Proportions: YouTube Link Part 1 and YouTube Link Part 2 Variance: Link Estimating Variance and Standard Deviation: YouTube Link Test hypotheses about means, proportions, and variances (standard deviations) for large and small samples. Testing Hypotheses: YouTube Link Test the significance of the relationship between two variables. Determine a linear regression equation. Functional Relationships: Link Testing if a Relationship is a Function: Link Regression Line Example: Line and Link Differentiate between correlation and causation. Correlation and Causality: Link Identify discrete probability distributions (including the binomial distribution) and calculate means, variances, and standard deviations for them.






