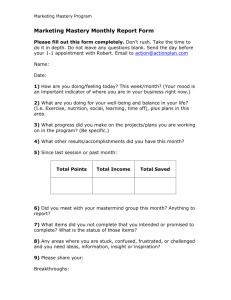
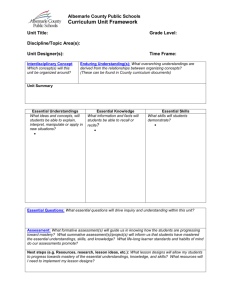
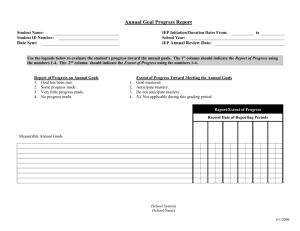
Grade 11
advertisement

GRADE LEVEL 11 STANDARD 11.1a The student will analyze and explain the contacts between American Indians and European settlers during the Age of Discovery, in terms of economic and cultural characteristics of the groups. Essential Understandings Essential Questions Essential Knowledge The differences between North American Indians and European settlers were fundamental. How did American Indians and Europeans differ economically and culturally? North American Indians (not to be named specifically) Belief systems Spiritual relationship with the Earth and nature Political structure A range from simple tribal units to confederations to empires Economic systems Communal control of land Life in harmony with the land, using it to sustain life and not to create wealth Roles of men and women Technology Bows, arrows, spears, and tomahawks Subsistence farming and hunting tools and weapons Cultural differences often lead to conflict. Essential Skills Explain simple charts. (M) Explain charts comparing two or more concepts. (M) Europeans Belief systems Christianity and the missionary spirit I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 1 GRADE LEVEL 11 STANDARD 11.1a (continued) The student will analyze and explain the contacts between American Indians and European settlers during the Age of Discovery, in terms of economic and cultural characteristics of the groups. Essential Understandings Essential Questions Essential Knowledge Essential Skills Political structure Monarchies and limited monarchies Evolving legal and political concepts of democracy and respect for individual rights and liberties Economic systems Belief in private ownership of property Combined labor with property to create wealth Roles of men and women Technology Advanced weaponry, including guns, cannons, and armor Navigational abilities I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 2 GRADE LEVEL 11 STANDARD 11.1b The student will analyze and explain the contacts between American Indians and European settlers during the Age of Discovery, in terms of motives and strategies of the explorers and settlers. Essential Understandings Essential Questions Essential Knowledge *European explorers and settlers were motivated by the same forces, although their strategies differed. Why and how did Europeans explore and settle North America? Motives Gold, Glory, and God Political expansion of territories for emerging European nationstates Expansion of markets and accumulation of wealth Spread of Christianity Many sought better economic opportunity and religious freedom * It is not intended that test items identify explorers by name because of such testing at grades 3, 4/5, 8, & World History to 1000 A.D. Essential Skills Collect, organize, and record information. (MC) Gather, classify, and interpret information. (MC) Strategies Governmental sponsorship of exploration and colonization Colonization Joint stock companies (Charters of the the Virginia Company) Trading posts Role of the church: conversion of Native Americans and establishment of missions I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 3 GRADE LEVEL 11 STANDARD 11.1c The student will analyze and explain the contacts between American Indians and European settlers during the Age of Discovery, in terms of impact of European settlement on the American Indians. Essential Understandings Many encounters between settlers and North American Indians were characterized by intolerance and misunderstanding leading to conflict, violence, migration, and death for the Indians. Essential Questions How were the lives of North American Indians changed by the arrival of European settlers? Essential Knowledge European encroachment on land caused successive waves of North American Indian migrations. Europeans introduced new diseases, triggering epidemics, which led to widespread Indian fatalities. While wars among North American Indians were common before European colonization, violence and warfare escalated as Indians confronted their European rivals. Europeans encouraged the North American Indians to adopt Christianity, European customs, and various farming techniques. I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material Essential Skills Explain cause and effect relationships. (MC) Compare and contrast differing sets of ideas, values, personalities, behaviors, and institutions. (MC) 4 STANDARD 11.1c (continued) GRADE LEVEL 11 The student will analyze and explain the contacts between American Indians and European settlers during the Age of Discovery, in terms of impact of European settlement on the American Indians. Essential Understandings Essential Questions Essential Knowledge Essential Skills *When teaching the above essential knowledge, the teacher should include 11.15dUnderstand the settlement patterns, migration routes, and cultural influence of various racial, ethnic, and religious groups. 11.15fAnalyze the political, social, and economic implications of demographic changes in the nation over time. I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 5 GRADE LEVEL 11 STANDARD 11.1d The student will analyze and explain the contacts between American Indians and European settlers during the Age of Discovery, in terms of legacies of contact, cooperation, and conflict from that period. Essential Understandings Europeans imposed their culture on, as well as borrowed ideas from, the North American cultures. The North American Indians resisted giving up their cultural identity. Essential Questions What were the consequences of contact between North American Indians and European settlers during the Age of Discovery? Essential Knowledge Economic exchange Formal and informal trade of goods including fruits, vegetables, grains, livestock, and fur Essential Skills Draw conclusions and make generalizations about data. (MC) Exchange of ideas Exchange of religious beliefs, economic ideas and practices, and technology Indian resistance to the exchange The Indians used a variety of strategies to resist dominance by Europeans, including farming alliances, open hostility, including violent attacks on settlers, and migration to new lands. Opechancanoughs Wars King Philips War I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 6 GRADE LEVEL 11 STANDARD 11.2a The student will compare the colonization of Virginia with that of other American colonies, in terms of motivations of ethnic, religious, and other immigrants and their influences on the settlement of colonies. Essential Understandings The different motives of various groups resulted in three distinct settlement patterns. Essential Questions What motivated Europeans to settle in the English colonies? How did their motivations influence their settlement patterns? Essential Knowledge Motivations New England Freedom from religious persecution Opportunity to found a Christian society Economic opportunity Middle Freedom from religious persecution for several religious groups Economic opportunity Virginia and other Southern colonies Economic opportunity Economic opportunities through land grants from the Crown Essential Skills Locate areas (regions) on maps and globes. (MC) Gather, classify, and interpret information . (MC) Draw conclusions and make generalizations about data. (MC) Influences on settlement New England Covenant community (Mayflower Compact) Citizen participation I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 7 GRADE LEVEL 11 STANDARD 11.2a (continued) The student will compare the colonization of Virginia with that of other American colonies, in terms of motivations of ethnic, religious, and other immigrants and their influences on the settlement of colonies. Essential Understandings Essential Questions Essential Knowledge Essential Skills Middle Tolerant society Commercial centers Virginia and other Southern colonies Agricultural economy Landed gentry Royalist cavaliers(Virginia) vs. New England Puritans Social reform (Georgia) *When teaching the above essential knowledge, the teacher should include the following standards: 11.15aLocate and explain the location and expansion of the original colonies. I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 8 GRADE LEVEL 11 STANDARD 11.2b The student will compare the colonization of Virginia with that of other American colonies, in terms of economic activity. Essential Understandings The New England and Middle colonies developed their economies primarily around commerce while Virginia and other Southern colonies built their economies around agriculture. Essential Questions How did the economic activity of the three colonial regions reflect their geography? Why was African slavery introduced into the colonies? Essential Knowledge New England Shipbuilding, shipping, fishing, rum trading, lumbering, live stock trading, subsistence farming Middle Colonies Trading of food commodities, shipbuilding, farming Essential Skills Explain simple charts. (MC) Explain charts comparing two or more concepts. (MC) Identify regional patterns on maps and globes. (MC) Virginia and other Southern colonies Tobacco, wheat, cattle, furs, rice, indigo Plantation economy Indentured servitude/slavery Forced migration of Africans (Middle Passage) *When teaching the above essential knowledge, the teacher should include following standard: 11.15eCompare patterns of agricultural and industrial development in different regions as they relate to natural resources, markets, and trade. I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 9 STANDARD 11.2c GRADE LEVEL 11 The student will compare the colonization of Virginia with that of other American colonies, in terms of political developments. Essential Understandings Essential Questions Essential Knowledge Early American colonists practiced self-government in a variety of ways. How do the three colonial regions compare in their political systems? New England Religious covenant (Mayflower Compact) Puritan theocracy Town meetings Royal governors Middle Colonies Combination of approaches used in New England and the South Less structured relationship between the church and state Royal governors Virginia and other Southern colonies Commercial agreements (Virginia Charters) Establishment of the Church of England Houses of Burgesses in Virginia and other colonial legislatures Royal governors Bacons Rebellion I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material Essential Skills Explain simple charts. (MC) Explain charts comparing two or more concepts. (MC) 10 STANDARD 11.2d GRADE LEVEL 11 The student will compare the colonization of Virginia with that of other American colonies, in terms of social customs, the arts, and religious beliefs. Essential Understandings Religious beliefs and economic necessities influenced the social customs and arts of the colonies. The Great Awakening had social and political as well as religious effects. Essential Questions How did the religious and economic necessities influence the social customs and the arts of the colonies? Essential Knowledge New England Hierarchy based on religious standing Functional architecture Puritan dissenters Salem witch trials Middle Colonies More flexible social structure Mixture of architecture styles Multiple religious groups, including Catholics and Quakers Virginia and other Southern colonies Hierarchy based on social status and ownership of land Plantation architecture and classical architecture Primarily Church of England Essential Skills Explain simple charts. (MC) Explain charts comparing two or more concepts. (MC) The student will develop skills in discussion, debate, and persuasive writing with respect to enduring issues and determine how divergent viewpoints have been addressed and reconciled. Such issues include problems of intolerance toward religious groups in American Society. (11.18f) Great Awakening Series of religious revivals Increased participation by women I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 11 GRADE LEVEL 11 STANDARD 11.3a The student will analyze and explain events and ideas of the Revolutionary Period, with emphasis on changes in British policies that provoked the American colonists. Essential Understandings The British government began to interfere more directly than ever before in the political and economic life in the colonies. British interference sparked deep anger and resentment among many colonists. Essential Questions Why do people revolt? Why did the British government impose taxes and restrictions on the colonies? Essential Knowledge Essential Skills British policy of mercantilism Navigation Acts Explain cause and effect relationships. (MC) French and Indian/Seven Years War Sequence events in chronological order. (MC) Colonists taxed to pay for defense Sugar Act Stamp Act Townsend Act Restructuring of settlement areas Proclamation of 1763 Privacy issues Writs of Assistance Quartering of Troops Quartering Act I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 12 STANDARD 11.3b GRADE LEVEL 11 The student will analyze and explain events and ideas of the Revolutionary Period, with emphasis on the debate within America concerning separation from Britain. Essential Understandings The ideas of the Enlightenment and the perceived unfairness of British policies provoked debate and resistance by the American colonists. Essential Questions Why do people revolt? How did both sides perceive the relationship between the mother country and colonies, especially on the question of representation? Were the American colonists justified in their hostility to British policy? Essential Knowledge Events concerning separation Stamp Act Congress Boston Massacre Committees of Correspondence Boston Tea Party First Continental Congress Interference with colonial governments Ideas supporting separation Natural Rights of Man Social Contract Theory Taxation without Representation Ideas against separation Taxation of colonists was justified to pay French and Indian War debts. Colonists were virtually represented in Parliament. Support for law and order Not all Americans supported separation from England. Definition of patriot and loyalist. I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material Essential Skills Distinguish fact from fiction. (MC) The student will develop skills for historical analysis, including the ability to analyze documents, records, and data (such as artifacts, diaries, letters, photographs, journals, newspapers, historical accounts, etc.). develop perspectives of time and place, including the construction of various time lines of events, periods, and personalities in American history. (11.17a, d) (M) The student will develop skills in discussion, debate, and persuasive writing with respect to enduring issues and determine how divergent viewpoints have been addressed and reconciled. Such issues include the evolution of rights, freedoms, and protections through political and social movements. (11.18g) (M) 13 GRADE LEVEL 11 STANDARD 11.3c The student will analyze and explain events and ideas of the Revolutionary Period, with emphasis on the Declaration of Independence and Common Sense. Essential Understandings Essential Questions The key documents of Common Sense and the Declaration of Independence defined the basic principles which justified the rebellion. What is the importance of Common Sense and the Declaration of Independence? What are the essential principles expressed in the Declaration of Independence? Essential Knowledge Common Sense Widely distributed pamphlet which aroused support for independence among colonists Author, Thomas Paine Declaration of Independence Inalienable rights of life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness All men are created equal. Governmental authority derives from consent of the governed. Right of resistance Author, Thomas Jefferson I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material Essential Skills Distinguish fact from fiction. (MC) Distinguish between primary and secondary sources. (MC) The student will develop skills for historical analysis, including the ability to analyze documents, records, and data (such as artifacts, diaries, letters, photographs, journals, newspapers, historical accounts, etc.). (11.17a) (M) 14 STANDARD 11.3d GRADE LEVEL 11 The student will analyze and explain events and ideas of the Revolutionary Period, with emphasis on individuals, including Virginians, who provided leadership in the Revolution. Essential Understandings A variety of people played different roles, all critical to the success of the American Revolution. Essential Questions Who were the significant leaders during the American Revolution and why were they significant? Essential Knowledge Virginians Patrick Henryone of the earliest and most passionate spokesmen for independence Richard Henry Leehis resolution led to the drafting of the Declaration of Independence Thomas Jeffersonauthor of the Declaration of Independence George WashingtonCommander of the Continental Army Non-Virginians Benjamin Franklinpatriot who persuaded France to ally itself with the American independence movement Sam Adamsorganizer of the Committees of Correspondence John Adamspersistent and outspoken supporter of independence who encouraged others to join the movement Marquis de LafayetteFrench officer who persuaded France to contribute troops to the American Revolution I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material Essential Skills The student will develop skills for historical analysis, including the ability to develop perspectives of time and place, personalities in American history. (11.17d) (M) 15 GRADE LEVEL 11 STANDARD 11.3e The student will analyze and explain events and ideas of the Revolutionary Period, with emphasis on key battles, military turning points, and key strategic decisions. Essential Understandings Essential Questions The Patriots defeated the British because of superior leadership and control of the countryside. Why did the British lose the Revolutionary War against the Patriots? The key to success was the ability of the Patriots to outlast the British. Why did the Americans win? Essential Knowledge Key battles Lexington and Concord Bunker Hill Trenton Turning points Saratoga Yorktown Essential Skills Collect, organize, and record information. (MC) Draw conclusions and make generalizations about information. (M) Strategic decisions Patriots adopted guerrilla warfare The French alliance contributed troops and leadership Treaty of Paris signed I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 16 STANDARD 11.4a GRADE LEVEL 11 The student will analyze the events and ideas of the Constitutional Era, with emphasis on new constitutions in Virginia and other states, the Virginia Statute for Religious Freedom, the Virginia Declaration of Rights, and the Articles of Confederation. Essential Questions Essential Knowledge Prior to the Constitutional Era, Americans had begun the process of defining the new form of government as a system for protecting individual rights, which would evolve into a democratic republic. What role did the state constitutions and other documents play in defining new forms of government and establishing the rights of citizens? The American political order is based on constitutional and ethical foundations. How did state constitutions differ? State Constitutionswritten documents approved by voters Established states and defined and limited their powers Declared the basic rights of citizens Limited the power of the executive branch and gave more power to the legislative branch, reflecting desire to retain power in the hands of the people Essential Understandings What is republicanism? What rights did women and minorities have? Essential Skills Distinguish fact from fiction. (MC) The student will develop skills for historical analysis, inlcuding the ability to analyze documents, records, and data (such as artifacts, diaries, letters, photographs, journals, newspapers, historical accounts, etc.). (11.17a) (M) Virginia Declaration of Rights (1776) Established the premise of basic human rights which cannot be violated by governments Virginia Statute for Religious Freedom (1786) Ended the official relationship between the church and state Established the principle of religious liberty (also see 11.16) I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 17 GRADE LEVEL 11 STANDARD 11.4a (continued) The student will analyze the events and ideas of the Constitutional Era, with emphasis on new constitutions in Virginia and other states, the Virginia Statute for Religious Freedom, the Virginia Declaration of Rights, and the Articles of Confederation. Essential Understandings Essential Questions Essential Knowledge Essential Skills Articles of Confederation (1781) Established idea of governmental bodies sharing power and created a national government Limited the power of the national government and reserved substantive power to the states Established a single chamber legislature, a weak executive branch, and no judicial branch Established the idea of limited national sovereignty I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 18 STANDARD 11.4b GRADE LEVEL 11 The student will analyze the events and ideas of the Constitutional Era, with emphasis on issues and policies affecting relations among existing and future states, including the Northwest Ordinance. Essential Understandings Even before the U.S. Constitution was written, states were working together to plan for the orderly growth of the new nation. Essential Questions Essential Knowledge Essential Skills What policies outlined a plan for the growth and democratic development of the new nation? Northwest Ordinance Settled portions of the Northwest territories; could enter the Union on an equal basis. Locate areas on maps and globes. (MC) How did policies concerning future states promote the orderly growth of the new nation? Interpret maps and globes. (MC) Explain cause and effect relationships. (M) The student will develop skills for historical analysis, including the ability to analyze documents, records, and data (such as artifacts, diaries, letters, photographs, journals, newspapers, histori cal accounts, etc.). (11.17a) (M) I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 19 GRADE LEVEL 11 STANDARD 11.4c The student will analyze the events and ideas of the Constitutional Era, with emphasis on the Constitutional Convention, including the leadership of James Madison and George Washington. Essential Understandings Essential Questions The Constitution established a government that allowed for powers to be shared between the national government and state governments, the rights of states and individuals to be protected, and a system for orderly change through amendments to the Constitution itself. Why was a Constitutional Convention called? The U.S. Constitution is the most enduring and successful blueprint for self-government in human history. What were the problems the Constitutional Convention addressed? What important ideas about government came out of the Constitiutional Convention? What role did Virginia leaders and ideas play in establishing the new Constitution? Essential Knowledge Reasons for the Constitutional Convention Weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation Shays Rebellion Key issues and their resolution Authority of states and national government (division of power) Power of large states and small states in the legislature (The Virginia Compromise) Counting of the population (3/5 Compromise) Free flow of commerce among states (commerce clause) Essential Skills Explain cause and effect relationships. (MC) The student will develop skills in discussion, debate, and persuasive writing with respect to enduring issues and determine how divergent viewpoints have been addressed and reconciled. Such issues include the tension between majority rule and minority rights. (11.18e) (M) Key principles of the Constitution Federalism (division of powers) Separation of powers (checks and balances) Process for amending the Constitution Independent and co-equal judicial branch I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 20 STANDARD 11.4c (continued) GRADE LEVEL 11 The student will analyze the events and ideas of the Constitutional Era, with emphasis on the Constitutional Convention, including the leadership of James Madison and George Washington. Essential Understandings Essential Questions Essential Knowledge Essential Skills Key leaders George Washington: Chairman of the convention James Madison: Father of the Constitution I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 21 GRADE LEVEL 11 STANDARD 11.4d The student will analyze the events and ideas of the Constitutional Era, with emphasis on the struggle for ratification of the Constitution, including the Federalist Papers and the arguments of the Anti-Federalists. Essential Understandings Groups argued strongly for and against the ratification of the Constitution, but the framers had designed a procedure which favored its ratification. The debate over ratification of the Constitution was a debate over the role of the federal governmenta debate that continues today. Essential Questions What procedure allowed for the ratification of the Constitution? What were the arguments for and against the ratification of the Constitution? Essential Knowledge Federalist position Favored a strong national government sharing power with the states Believed that separation of powers (three branches of government) had built in checks and balances Believed that federal powers were needed to manage trade, defense and foreign relations Believed that factions balanced each others power Believed that citizens rights were implied in Constitution Essential Skills Gather, classify, and interpret information. (MC) Draw conlcusions and make generalizations about information. (MC) Compare and contrast differing sets of ideas. Select and defend positions. (M) Anti-Federalist position Believed that federal government would favor the interests of the rich and powerful and ignore the rights of the less privileged masses Believed that one central government would be too powerful and would threaten individual rights and liberties I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 22 STANDARD 11.4d (continued) GRADE LEVEL 11 The student will analyze the events and ideas of the Constitutional Era, with emphasis on the struggle for ratification of the Constitution, including the Federalist Papers and the arguments of the Anti-Federalists. Essential Understandings Essential Questions Essential Knowledge Essential Skills Believed that individual rights must be protected in a Bill of Rights. Ratification process Process established by framers Debatethe Federalist Papers published Delegates elected to state conventions to accept or reject the Constitution (bypassed state legislatures) Acceptance by nine states to ratify the Constitution I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 23 GRADE LEVEL 11 STANDARD 11.4e The student will analyze the events and ideas of the Constitutional Era, with emphasis on the addition of the Bill of Rights to the Constitution. Essential Understandings The efforts of the Anti-Federalists led to the early inclusion of a Bill of Rights through the adoption of the first ten amendments, which protected individual rights and liberties from government encroachment. Essential Questions Why was a Bill of Rights added to the Constitution? Through what process was the Bill of Rights added? Essential Knowledge Essential Skills The Bill of Rights guaranteed the rights of individual citizens, which the new federal government could not take away. The student will develop skills in discussion, debate, and persuasive writing with respect to enduring issues and determine how divergent viewpoints have been addressed and reconciled. Such issues include the tension between majority rule and minority rights. (11.18e) (M) Without the addition of the Bill of Rights, the U.S. Constitution would not have been ratified. Note: Assessment items should not reflect individual rights by number, with the exception of the following: The First Amendment guaranteed freedom of speech and freedom of religion. Based on the Virginia Statute for Religious Freedom. I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 24 GRADE LEVEL 11 STANDARD 11.5a The student will analyze and explain events of the Early National Period, with emphasis on organization of the national government under the new Constitution. Essential Understandings The Early National Period is defined as the time from 1789-1824. The Founding Fathers created a unique relationship between the central government and the state governments. It is called federalism. The Constitution divided power among three branches of the national government to prevent the abuse of power. Essential Questions How does the organization of the national government reflect the interests and concerns of the Early National Period? Essential Knowledge Federal system of government A form of government with governmental powers divided between a central government and various state governments Essential Skills Draw conclusions and make generalizations about data. (MC) Three branches of government Guiding principles Separation of powers Checks and balances Reasons for separation of powers and checks and balances Legislative Branch Congress (bicameral) House of Representatives (based on population) Senate (2 senators) per state Powers: delegated and reserved Reasons for this structure Executive Branch The President Electoral College Powers: veto and nomination Reasons for this structure Judicial Branch The Supreme Court Reasons for this structure I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 25 GRADE LEVEL 11 STANDARD 11.5b The student will analyze and explain events of the Early National Period, with emphasis on major domestic and foreign affairs issues facing the first presidents and Congress. Essential Understandings The Early National Period is defined as the time from 1789-1824. The decisions made by the early presidents strengthened the role of the national government. The U.S. managed to maintain its neutrality and avoid war. Foreign policy matters triggered divisions among the two emerging political parties. Essential Questions Essential Knowledge How did the first presidents and Congress deal with divisive issues? Domestic affairs George Washington Three executive departments created: State, Treasury, and War The Judiciary organized Public debt paid off National Bank established Excise tax and Whiskey Rebel lion John Adams Alien and Sedition Act Election of 1800 Essential Skills Gather, classify, and interpret information. (MC) Sequence events in chronological order. (MC) Draw conclusions and make generalizations about information. (MC) Foreign affairs Washingtons Farewell Address I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 26 STANDARD 11.5c GRADE LEVEL 11 The student will analyze and explain events of the Early National Period, with emphasis on the development of political parties. Essential Understandings The political differences between Hamilton and Jefferson gave rise to a two-party system which remains a characteristic of American politics today. Essential Questions How and why did a two-party system develop? What were Hamiltons and Jeffersons visions for America? Essential Knowledge Federalists (Hamilton) Favored the rich, educated, and well-born who should rule; wanted to raise voting qualifications Favored a strong central government Wanted a balanced economy of agriculture, trade, finance, and manufacturing Supported by bankers, manufacturers, merchants, and by wealthy farmers in New England and along the Atlantic coast Favored national assumption of state debt Were pro-British Democratic-Republicans (Jefferson) Favored the common people; wanted to lower voting qualifications Favored a weak central government and strong state governments I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material Essential Skills Explain simple charts. (MC) Explain charts comparing two or more concepts. (MC) Select and defend positions. (M) The student will develop skills in discussion, debate, and persuasive writing with respect to enduring issues and determine how divergent viewpoints have been addressed and reconciled. Such issues include the relationship of government to the individual in economic planning and social programs. (11.18c) (M) 27 GRADE LEVEL 11 STANDARD 11.5c (continued) The student will analyze and explain events of the Early National Period, with emphasis on the development of political parties. Essential Understandings Essential Questions Essential Knowledge Essential Skills Thought agriculture should be the backbone of the country Supported by artisans, shop keepers, frontier settlers, and small farmers from the South and the Southwest and along the frontier Favored small public debt I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 28 STANDARD 11.5d GRADE LEVEL 11 The student will analyze and explain events of the Early National Period, with emphasis on the impact of Supreme Court decisions affecting interpretation of the Constitution, including Marbury v. Madison and McCulloch v. Maryland. Essential Understandings Essential Questions The Supreme Court asserted its authority to interpret the Constitution. How was the distribution of power within the federal government and between the federal government and state governments changed in the Early National period? Supreme Court decisions expanded the power of the federal government. Essential Knowledge Definition of judicial review Chief Justice John Marshall (a Virginian) Served as guiding force of the early Supreme Court Essential Skills Gather, classify, and interpret information. (MC) Draw conclusions and make generalizations about information. (MC) Marbury v. Madison Established the power of the federal courts to declare laws unconstitutional (judicial review) McCulloch v. Maryland Reviewed the necessary and proper clause of the Constitution, which gives Congress powers not expressly written in the Constitution, but limited by necessity (in this case, the power to establish a national bank) Power to tax is the power to destroy. States may therefore not tax instruments of the federal government, such as a national bank. I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 29 GRADE LEVEL 11 STANDARD 11.5e The student will analyze and explain events of the Early National Period, with emphasis on foreign relations and conflicts, including the War of 1812 and the Monroe Doctrine. Essential Understandings The U.S. attempted to assert its rights and power as an independent nation in the eyes of its European rivals. Essential Questions How did the U.S. assert nationalism in foreign affairs in the Early National Period? Essential Knowledge Causes of the War of 1812 Neutrality in European conflicts Harassment of American ships on the high seas by the British and French Impressment of American sailors Pressure by war hawks to force Britain to stop supporting Indians in West and to cede Canada to the U.S. Essential Skills Explain cause and effect relationships. (MC) Gather, classify, and interpret information. (MC) Draw conclusions and make generalizations about information. (MC) Monroe Doctrine Warned Europe to stay out of the Americas I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 30 STANDARD 11.5f GRADE LEVEL 11 The student will analyze and explain events of the Early National Period, with emphasis on the Louisiana Purchase and the acquisition of Florida. Essential Understandings The purchase and acquisition of land set the stage for continued westward expansion and provided security from European threats. Essential Questions What was the significance of the land purchases and acquisitions between 1800 - 1820? Essential Knowledge Essential Skills Louisiana Purchase Extent of territory purchased from France Advancement of the frontier, the territorial expansion of the U.S., and the influence of the physical environment (11.15b) Jefferson and legality of the purchase Lewis and Clarke expedition Locate areas (regions) on maps and globes. (MC) Interpret information from maps and globes. (M) Locate places on maps using longitude/latitude. (M) Acquisition of Florida Acquired by treaty with Spain Provoked by Indian skirmishes and migration of American settlers to this area *When teaching the above essential knowledge, the teacher should include the following standards: 11.15bTrace the advance of the frontier and the territorial expansion of the United States and explain how it was influenced by the physical environment. 11.15cLocate new states as they were added to the Union. I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 31 GRADE LEVEL 11 STANDARD 11.5g The student will analyze and explain events of the Early National Period, with emphasis on economic development, trade, tariffs, taxation, and trends in the national debt. Essential Understandings The Industrial Revolution transformed the ways Americans worked, lived, and bought and sold products. The Industrial Revolution was fueled by new power sources, internal improvements, the availability of capital, and a protective tariff. Essential Questions What stimulated the Industrial Revolution between 1789 and 1824? Why were Americans moving west? What role did government play in fostering economic development? Essential Knowledge Economic development Industrial Revolutionchange from handmade goods produced at home to machine-made goods produced in factories (textile mills in New England) Switch from water to steam power and its effects on transportation Eli Whitneys cotton gin and its effects on westward expansion and slavery State banks easy credit policy for land purchases; National Bank chartered to ensure a stable financial system Migration westwardFederal Land Laws Panic of 1819 Essential Skills Draw conclusions and make generalizations about data. (MC) The student will develop skills in discussion, debate, and persuasive writing with respect to enduring issues and determine how divergent viewpoints have been addressed and reconciled. Such issues include the relationship of government to the individual in economic planing and social programs. (11.18c) (M) Trade and tariffs American system Protective tariff instituted to protect American manufacturers I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 32 STANDARD 11.5g (continued) GRADE LEVEL 11 The student will analyze and explain events of the Early National Period, with emphasis on economic development, trade, tariffs, taxation, and trends in the national debt. Essential Understandings Essential Questions Essential Knowledge Essential Skills Federal funding for internal improvements Building of roads: National Road Building of canals: Erie Canal National debt Alexander Hamilton Favored assumption of state debts, funding domestic debts and imposing a tariff Thomas Jefferson Wanted to cut the cost and size of the government *When teaching the above essential knowledge, the teacher should include the following standards: Compare patterns of agricultural and industrial development in different regions as they relate to natural resources, markets, and trade. (11.15e) I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 33 GRADE LEVEL 11 STANDARD 11.6a The student will analyze the causes and effects of major events of the Civil War and Reconstruction, including slavery. Essential Understandings Essential Questions There is historical disagreement as to the centrality of slavery as a cause of the Civil War. How did abolitionists and Southern slave owners differ in their attitudes toward slavery? The South seceded after Lincolns election in 1860 because Southerners perceived a threat to the survival of their institutions, including slavery. How did slavery produce a divided Americaeconomically, culturally, and constitutionally? Was preserving slavery the primary reasons Southern states seceded? Essential Knowledge Positions on slavery Defense of slavery and slave codes Extent of slaveholding in the South Abolitionist -Garrison and The Liberator -Stowe and Uncle Toms Cabin -Underground Railroad -Frederick Douglass -Free-Soil Movement Lincoln: Opposed expansion of slavery beyond states in which it already existed. Not originally for abolition. Southern fear of slave uprisings (Nat Turners Rebellion) Essential Skills Evaluate information for accuracy and separate fact from fiction. (MC) Compare and contrast differing sets of ideas, values, personalities, behaviors, and institutions. (MC) The student will develop skills for historical analysis, including the ability to formulate historical questions and defend findings based on inquiry and interpretation. (11.17c) (M) The student will develop skills in discussion, debate, and persuasive writing with respect to enduring issues and determine how divergent viewpoints have been addressed and reconciled. Such issues include slavery and its impact. (11.18b) (M) Explain cause and effect relationships. (M) I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 34 STANDARD 11.6b GRADE LEVEL 11 The student will analyze the causes and effects of major events of the Civil War and Reconstruction, including States Rights Doctrine. Essential Understandings Essential Questions Americans disagreed about the sovereignty of states and the supremacy of the National Government. How central was the States Rights debate as a cause of the Civil War? Do states that freely enter the Union have the right to secede? Essential Knowledge Definitions of States Rights Lincoln No state may leave the Union after it has joined. United States is one nation, not a collection of independent states. Essential Skills Gather, classify, and interpret information. (M) Select and defend positions. (M) Explain cause and effect relationships. (M) Southern position States freely entered the Union; they may freely leave. States formed the federal government, not vice versa. I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 35 GRADE LEVEL 11 STANDARD 11.6c The student will analyze the causes and effects of major events of the Civil War and Reconstruction, including tariffs and trade. Essential Understandings There were fundamental economic differences between the North and the South. Essential Questions What were the fundamental economic differences between the North and the South? Why were the economies of the North and the South different? Essential Knowledge Economic differences between the North and the South The South Devoted to agriculture, few cities developed Valued King Cotton Shipped staple crops to distant markets in Northeast and Europe Favored low protective tariffs Essential Skills Explain charts containing two or more concepts. (MC) Construct and explain simple charts. (MC) The North Encouraged rise of manufacturing and large cities Enjoyed a diversified economy Favored high protective tariffs (manufacturing interests favored tariffs) I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 36 STANDARD 11.6d GRADE LEVEL 11 The student will analyze the causes and effects of major events of the Civil War and Reconstruction, including settlement of the West. Essential Understandings Before the Civil War, pro-Northern and pro-Southern groups and settlers moved into some areas of the West to gain eventual free or slave status for future statehood. A series of crises took place over the admission of new states during the decades before the Civil War. The issue was always whether the number of free states and slave states would be balanced, affecting power in the Congress. Essential Questions How was settlement of the West a factor in the Civil War? How did the Missouri Compromise, the Compromise of 1850, and the Kansas-Nebraska Act deal with the issue of the admission of free or slave states? Essential Knowledge Understand the following events and terms Missouri Compromise Manifest Destiny Settlement and annexation of Texas Mexican War (causes and results) Compromise of 1850 Kansas-Nebraska Act Birth of Republican Party Bloody Kansas John Brown Lincoln-Douglas debates and popular sovereignty (allowing people in each new state to choose on the issue of slavery) California Gold Rush *When teaching the above essential knowledge, the teacher should include the following standards: Trace the advance of the frontier and the territorial expansion of the United Staes and explain how it was influenced by the physical environment. (11.15b) Locate new states as they were added to the Union. (11.15C) I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material Essential Skills Locate areas (regions) on maps and globes. (MC) Interpret maps and globes. (MC) Locate places on maps and globes using longitude and latitude. (MC) The student will develop skills for historical analysis, including the ability to develop perspectives of time and place, including the construction of various time lines of events, periods, and person alities in American history communicate findings orally, in brief analytical essays, and in a comprehensive paper. (11.17d, e) (M) 37 GRADE LEVEL 11 STANDARD 11.6d (continued) The student will analyze the causes and effects of major events of the Civil War and Reconstruction, including settlement of the West. Essential Understandings Essential Questions Essential Knowledge Essential Skills Understand the settlement patterns, migration routes, and cultural influence of various racial, ethnic, and religious groups. (11.15d) Analyze the political, social, and economic implications of demographic changes in the nation over time. (11.15f) I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 38 STANDARD 11.6e GRADE LEVEL 11 The student will analyze the causes and effects of major events of the Civil War and Reconstruction, including secession. Essential Understandings Essential Questions The secession of the Southern States triggered the Civil War. How did secession lead to Civil War? Lincolns view and the Southern view of the nature of the Union were not subject to compromise. Why did Southern states secede? Lincolns Gettysburg Address said that the United States was one nation, not a federation of independent states. That was what the Civil War was about for Lincoln: to preserve the Union as a nation of the people, by the people, and for the people. Lincoln believed the Civil War was fought to fulfill the promise of the Declaration of Independence, and was a Second American Revolution because it laid out a different vision for the United States from the one that had prevailed from 1787 to the Civil War. Did any state have a right to leave the Union? Was Lincoln right to use military force to keep the Union intact? What was Lincolns vision of the American nation as professed in the Gettysburg Address? How did the Gettysburg Address set out a Second American Revolution? Essential Knowledge Essential Skills Lincolns election in 1860 led to secession of South Carolina followed by other Southern states. Secession of South Carolina Creation of the Confederate States of America Fort Sumter attacked by Confederate forces (beginning of the Civil War) Differentiate between historical facts and historical interpretations. (MC) Lincolns position on secession: No state may leave the Union once it has joined. Explain cause and effect relationships. (MC) Compare and contrast differing sets of ideas, values, personalities, behaviors, and institutions. (MC) Select and defend positions. (M) Documents Declaration of Independence Gettysburg Address I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 39 GRADE LEVEL 11 STANDARD 11.6f The student will analyze the causes and effects of major events of the Civil War and Reconstruction, including military advantages of the Union and the Confederacy. Essential Understandings Though the Confederate military surpassed the Union in skills, the Unions advantages in manpower, technology, industry, and economic strength resulted in the defeat of the Confederacy. The North had to conquer the South; the South had only to survive. Essential Questions What were the military advantages of the Union? What were the military advantages of the Confederacy? Why did the Union win? Essential Knowledge Union advantages More resourcesfinances More industryrailroads More population for recruiting soldiers Saved border states from secession Not all Southerners supported secession (Southwest Virginia, Eastern Tennessee, Western North Carolina) Essential Skills Gather, classify, and interpret information. (MC) Draw conclusions and make generalizations about data. (MC) Confederate advantages Generals better trained Soldiers more experienced with guns, horses, and the terrain Soldiers defending their own land I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 40 STANDARD 11.6g GRADE LEVEL 11 The student will analyze the causes and effects of major events of the Civil War and Reconstruction, including threat of foreign intervention. Essential Understandings The possibility of British support for the Confederacy led to Lincolns issuing the Emancipation Proclamation. Great Britain remained neutral during the Civil War for two reasons: economic interests and opposition to slavery. Essential Questions Why did Great Britain decide to remain neutral during the Civil War? Essential Knowledge The British had connections with the Southern cotton economy and received imports of Northern grains. There were attempts to establish a British-Confederate alliance. The Emancipation Proclamation may be seen as a foreign policy strategy to assure British neutrality. Essential Skills Gather, classify, and interpret information. (MC) Explain cause and effect reltionships. (MC) Draw conclusions and make generalizations about data. (MC) Interpret the significance of the Gettysburg Address. (11.16) (M) The Battles of Antietam and Gettysburg influenced the British decision to remain neutral. The Trent Incident threatened British intervention in the Civil War. I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 41 GRADE LEVEL 11 STANDARD 11.6h The student will analyze the causes and effects of major events of the Civil War and Reconstruction, including economic and political impact of the war. Essential Understandings The Civil War had a significant impact on the economies of both the Union and the Confederacy. The Norths industry generally improved, and U.S. government policies moved to favor business and expansion. The Souths economy was ruined by the Civil War. The defeat of the Confederacy preserved the Union and ended slavery in the South. Essential Questions What impact did the Civil War have on the North economically and politically? What impact did the Civil War have on the South economically and politically? Was the Civil War a revolution? Essential Knowledge Economy of the North Economic prosperity and westward expansion Federal subsidies of railroads Homestead Act Morrill Land Grant Act for new universities Essential Skills Gather, classify, and interpret information. (MC) Explain cause and effect reltionships. (MC) Draw conclusions and make generalizations about data. (MC) Economy of the South Economic distress Loss of land and revenue Generations of poor farmers Few industries Politics of the North The Emancipation Proclamation and the role of the Radical Republicans Federal powers increased Politics of the South Strong national government necessary despite the creation of a confederacy I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 42 STANDARD 11.6h (continued) GRADE LEVEL 11 The student will analyze the causes and effects of major events of the Civil War and Reconstruction, including economic and political impact of the war. Essential Understandings Essential Questions Essential Knowledge Essential Skills Move by some former slaves to Union territory; enlistment of others in Union army States Rights defenders found a home in the Democratic Party, which dominated the South for the next century. *When teaching the above essential knowledge, the teacher should include the following standards: Compare patterns of agricultural and industrial development in different regions as they relate to natural resources, markets, and trade (11.15e) I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 43 GRADE LEVEL 11 STANDARD 11.6i The student will analyze the causes and effects of major events of the Civil War and Reconstruction, including roles played by individual leaders. Essential Understandings Essential Questions The Confederacy possessed superior military leadership. What leaders emerged during the Civil War? Lincoln and Lee were men of integrity whose views of the nature of the United States were different, leading to an unavoidable conflict. What was the significance of the military leaders during the course of the War? How did Lincolns view of the nature of the Union differ from Lees? Essential Knowledge The North Abraham Lincoln/Gettysburg Address (also 11.16); determined to preserve the Union, by force if necessary. Believed the U.S. was one nation, not a collection of independent states. Ulysses Grant William Tecumseh Sherman George McClellan Essential Skills Gather, classify, and interpret information. (MC) Explain cause and effect relationships. (MC) Draw conclusions and make generalizations about data. (MC) The South Jefferson Davis Robert E. Lee; offered command of the Union forces at the beginning of the war, but would not fight against Virginia. Lee opposed secession but did not believe the Union should be held together by force. Stonewall Jackson I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 44 STANDARD 11.6j GRADE LEVEL 11 The student will analyze the causes and effects of major events of the Civil War and Reconstruction, including impact of Reconstruction policies on the South. Essential Understandings The severity of Reconstruction resulted in Southern resentment and distrust of the North, which continued for a long time. The economic and political gains of former slaves in the South were temporary. The creation of the Solid South (supporting only the Democratic Party) was the rule in the South for almost 100 years. Essential Questions What was the impact of Reconstruction on the South? Why did Reconstruction fail? Essential Knowledge Lincolns plan for Reconstruction Johnsons plan for Reconstruction Radical Republican planWadeDavis Bill Policies: Freedmans Bureau, 13th, 14th, and 15th Amendments, military occupation of the South Scalawags Carpetbaggers Compromise of 1877 Essential Skills Gather, classify, and interpret information. (MC) Explain cause and effect relationships. (MC) Draw conclusions and make generalizations about data. (MC) Long term impact Black codes Sharecropping/tenant farming Ku Klux Klan Jim Crow laws initiated in 1880s Role of blacks Political participation Education Johnsons opposition to Civil Rights legislation Andrew Johnsons impeachment I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 45 GRADE LEVEL 11 STANDARD 11.7a The student will analyze the impact of immigration on American life, in terms of contributions of immigrant groups and individuals. Essential Understandings Economic hardships along with political and religious persecution led immigrants to the U.S. in the late 1800s. Patterns of immigration changed as Americans distinguished between earlier and later immigrants. Essential Questions From which countries did most immigrants come between 1871 and 1930? Why did immigrants come to the U.S. in the late 1800s? How were those immigrants different from earlier waves of immigrants? What were their contributions? Essential Knowledge Prior to 1871, immigrants came from northern and western Europe (Germany, Great Britain, Ireland, and Sweden). New immigrants came from southern and eastern Europe (Italy, Greece, Poland, and Russia) as well as Asia (China and Japan). Essential Skills Gather, classify, and interpret information. (MC) Explain cause and effect relationships. (MC) Draw conclusions and make generalizations about data. (MC) Reasons for immigration Push factors (reasons to leave) Religious and political persecution Agricultural poverty Relaxation of emigration laws Pull factors (reasons to come) Promise of freedom and hope Network of family and friends in U.S. Need for and recruitment of cheap labor Contributions of immigrants Broadened the cultural life of American cities through new I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 46 STANDARD 11.7a (continued) GRADE LEVEL 11 The student will analyze the impact of immigration on American life, in terms of contributions of immigrant groups and individuals. Essential Understandings Essential Questions Essential Knowledge Essential Skills music (Irving Berlin, George & Ira Gershwin), scientific concepts (Enrico Fermi, Albert Einstein), new languages (Slavic, Yiddish, Italian, Chinese, Japanese), diverse religious beliefs (Catholic, Jewish, Buddhist) and a variety of new foods and customs Provided a cheap labor force for the factories *When teaching the above essential knowledge, the following standards should also be included: 11.15d: Understand the settlement patterns, migration routes, and cultural influence of various racial, ethnic, and religious groups. 11.5f: Analyze the political, social, and economic implications of demographic changes in the nation over time. I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 47 GRADE LEVEL 11 STANDARD 11.7b The student will analyze the impact of immigration on American life, in terms of ethnic conflict and discrimination. Essential Understandings Immigrants experienced many difficulties after their arrival in the U.S. Immigrants were torn between old traditions and the new American culture. Essential Questions To what extent did immigrants assimilate into American life? Essential Knowledge Essential Skills Assimilation factors Experiences at Ellis Island Interpret ideas, concepts, or events. (MC) Attempts to limit the number of immigrants by means of quotasChinese Exclusion Act, and Immigration Restriction Act of 1921 The student will develop skills for historical analysis, including the ability to analyze documents, records, and data (such as artifacts, diaries, letters, photographs, journals, newspapers, historical accounts, etc.) (11.17a) (M) formulate historical questions and defend findings based on inquiry and interpretation. (11.17c) (M) Mounting religious, racial, and cultural prejudices Resentment by many workers against new immigrants who worked for less pay than Americans Ethnic neighborhoods Learning the English language American customs such as going to school, becoming a citizen I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material The student will develop skills in discussion, debate, and persuasive writing with respect to enduring issues and determine how divergent viewpoints have been addressed and reconciled. Such issues include problems of intolerance toward religious groups in American society. (11.17 a, c) (11.18 f) (M) 48 STANDARD 11.7b (continued) GRADE LEVEL 11 The student will analyze the impact of immigration on American life, in terms of ethnic conflict and discrimination. Essential Understandings Essential Questions Essential Knowledge Essential Skills *When teaching the above essential knowledge, teachers should include the following standards Analyze the political social, and economic implications of demographic changes in the nation over time. (11.15f) I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 49 GRADE LEVEL 11 STANDARD 11.8a The student will summarize causes and effects of industrial development, with emphasis on new inventions and industrial production methods. Essential Understandings Essential Questions Essential Knowledge Between the Civil War and World War I, the United States was transformed from a mostly rural and agricultural nation to a mostly urban and industrial nation. How did new inventions and industrial production methods stimulate the Industrial Revolution in America? Inventions and industrial production methods Light bulb Electricity as a source of light and power (Thomas A. Edison) Bessemer process (Henry Bessemer) Assembly line (Henry Ford) The technological revolution changed forever the ways people worked, played, traveled, and communicated. What impact did these inventions and new production methods have on Americans at home and in the workplace? Essential Skills Gather, classify, and interpret information. (MC) Explain cause and effect relationships. (MC) Draw conclusions and make generalizations about data. (MC) A new power source and new production methods stimulated the expansion of American industry after the Civil War. I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 50 STANDARD 11.8b GRADE LEVEL 11 The student will summarize causes and effects of industrial development, with emphasis on new technologies in transportation and communication. Essential Understandings Railroads provided industrial access to markets and raw materials. Developments in communication altered American life in the workplace and the home. Essential Questions Essential Knowledge How did new technologies in transportation and communications stimulate the industrial development in America? Transportation Railroads (Cornelius Vanderbilt) Model T Ford (Henry Ford) Airplane (the Wright Brothers) What impact did these inventions and new production methods have on Americans at home and in the workplace? Communications Telephone (Alexander Graham Bell) Typewriter Radio I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material Essential Skills Gather, classify, and interpret information. (MC) Explain cause and effect relationships. (MC) Draw conclusions and make generalizations about data. (MC) 51 GRADE LEVEL 11 STANDARD 11.8c The student will summarize causes and effects of industrial development, with emphasis on incentives for capitalism and free enterprise. Essential Understandings Essential Questions Corporations were combined and restructured to maximize profits. How did individuals attain wealth during the period 1870 - 1917? Big business produced staggering wealth for owners, thus prompting controversy over the methods. Were the industrial leaders robber barons or captains of industry? Essential Knowledge Organizations Corporate structure (horizontal and vertical consolidations) Trusts Leaders Andrew Carnegie John D. Rockefeller J. P. Morgan I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material Essential Skills Gather, classify, and interpret information. (MC) Explain cause and effect relationships. (MC) Draw conclusions and make generalizations about data. (MC) 52 STANDARD 11.8d GRADE LEVEL 11 The student will summarize causes and effects of industrial development, with emphasis on the impact of immigration on the labor supply and the movement to organize workers. Essential Understandings Essential Questions An abundant immigrant labor supply contributed to an industrial boom after the Civil War. What were the effects of the immigrant labor supply on the Industrial Revolution (1870 - 1917)? Rapid industrialization led to a variety of problems and harsh and dangerous working conditions. How did labor respond to rapid industrialization? Conditions in factories and industries led to the rise of American labor unions. What role did the government play in the labor strikes? Essential Knowledge Immigrant labor supply (also 11.7a) Influx of Chinese workers to build the railroads Immigrants to work in textile factories in the northeast Slavs and Poles to supply labor for mines in the East Low pay for all labor Working conditions Dangerous working conditions Child labor Long hours, low wages, no job security, no benefits Company towns Employment of women Labor organizations Knights of Labor American Federation of Labor (Samuel Gompers) I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material Essential Skills The student will develop skills for historical analysis, including the ability to formulate historical questions and defend findings based on inquiry and interpretation develop perspectives of time and place, including the construction of various time lines of events, periods, and personalities in American history. (11.17 c, d) (M) Gather, classify, and interpret information. (MC) Explain cause and effect relationships. (MC) Draw conclusions and make generalizations about data. (MC) 53 GRADE LEVEL 11 STANDARD 11.8d (continued) The student will summarize causes and effects of industrial development, with emphasis on the impact of immigration on the labor supply and the movement to organize workers. Essential Understandings Essential Questions Essential Knowledge Essential Skills American Railway Union (Eugene V. Debs) Industrial Ladies Garment Workers Union Labor strikes Haymarket Square Homestead Strike Pullman Strike *When teaching the above essential knowledge, the teacher should include the following standards: Understand the settlement patterns, migration routes, and cultural influence of various racial, ethnic, and religious groups. (11.15d) I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 54 STANDARD 11.8e GRADE LEVEL 11 The student will summarize causes and effects of industrial development, with emphasis on government policies affecting trade, monopolies, taxation, and money supply. Essential Understandings The Federal government responded to the industrialization of the late 1800s by enacting legislation to regulate business. Essential Questions How did the federal government respond to rapid industrialization? Essential Knowledge Government policies on Trade Tariffs for protectection of American industry Interstate Commerce Commission (ICC) Railroad regulation Federal Trade Commission (FTC) Monopolies Sherman Anti-Trust Act Clayton Act Taxation 16th Amendment authorized a graduated federal income tax. Money Supply Federal Reserve Act Essential Skills The student will develop skills in discussion, debate, and persuasive writing with respect to enduring issues and to determine how divergent viewpoints have been addressed and reconciled. Such issues include the relationship of government to the individual in economic planning. (11.18c) (M) Gather, classify, and interpret information. (MC) Explain cause and effect relationships. (MC) Draw conclusions and make generalizations about data. (MC) State regulation Virginia State Corporation Commission (SCC) I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 55 GRADE LEVEL 11 STANDARD 11.8f The student will summarize causes and effects of industrial development, with emphasis on expansion of international markets. Essential Understandings Overproduction of American goods led to demand for foreign markets. Economic expansion led to a demand for foreign markets and political involvement by Americans. Essential Questions Why did U.S. businesses expand into international markets? Essential Knowledge U.S. access to foreign markets facilitated by Completion of Panama Canal Roosevelt CorollarySpeak softly and carry a big stick. (11.16) Creation of U.S. naval bases in Hawaii Essential Skills Gather, classify, and interpret information. (MC) Explain cause and effect relationships. (MC) Draw conclusions and make generalizations about data. (MC) Creation of international markets Open Door Policy Dollar diplomacy Internationalization of American corporations Growth in international trade from the late 1800s to World War I was the first era of a true global economy. I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 56 GRADE LEVEL 11 STANDARD 11.8g The student will summarize causes and effects of industrial development, with emphasis on the impact of industrialization, urbanization, and immigration on American society. Essential Questions Essential Knowledge American society was changed by industrialization, urbanization, and immigration. What impact did industrialization have on American society between 1870 - 1917? The impact of the Industrial Revolution inspired a Progressive Reform Movement to address new conditions. What impact did urbanization have on American society between 1870 - 1917? Impact of industrialization Muckrakers Progressive reform efforts (Meat Inspection, Pure Food and Drug Act) National Parks and Child Labor Laws Essential Understandings What impact did immigration have on American society between 1870 - 1917? What caused the Progressive Reform Movement? Impact of urbanization African-American migration to the North from the South Growth of cities Development of tenements and slums Necessity for services (education, sanitation) Suburban development Power of political machines Reform effort Settlement houses 17th and 19th Amendments Essential Skills The student will develop skills for historical analysis, including the ability to evaluate the authenticity, authority, and credibility of sources. (11.17b) (M) Gather, classify, and interpret information. (MC) Explain cause and effect relationships. (MC) Draw conclusions and make generalizations about data. (MC) Impact of immigration Nativism Job competition Chinese Exclusion Act I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 57 GRADE LEVEL 11 STANDARD 11.8g (continued) The student will summarize causes and effects of the industrial development, with emphasis on the impact of industrialization, urbanization, and immigration on American society. Essential Understandings Essential Questions Essential Knowledge Essential Skills Leadership Theodore Roosevelt Woodrow Wilson Booker T. Washington W.E.B. DuBois Jane Addams I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 58 STANDARD 11.9a GRADE LEVEL 11 The student will analyze and explain the importance of World War I, in terms of the end of the Ottoman Empire and the creation of new state in the Middle East. Essential Understandings European powers determined new political boundaries and controlled new Middle Eastern countries. Essential Questions How was the Ottoman Empire divided? Essential Knowledge Essential Skills The Treaty of Versailles divided the Ottoman Empire into mandates. Gather, classify, and interpret information. (MC) The mandates included French mandatesSyria and Lebanon British mandatesIraq, Palestine, and Trans-Jordan Explain cause and effect relationships. (MC) I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material Draw conclusions and make generalizations about data. (MC) 59 GRADE LEVEL 11 STANDARD 11.9b The student will analyze and explain the importance of World War I, in terms of the declining role of Great Britain and the expanding role of the United States in world affairs. Essential Understandings The U.S. assumed a leadership role at the Versailles Peace Conference. As a result of its role in World War I, the United States emerged as a dominant global power. Essential Questions Essential Knowledge How were American and European views of a lasting peace different? Differing views of a lasting peace Wilsons leadership through the Fourteen Points at the Versailles Conference Essential Skills Wilsons concept of self-determination of nations The student will develop skills for historical analysis, inlcuding the ability to communicate findings orally, in brief analytical essays, and in a comprehensive paper. (11.17e) (M) Wilsons proposal for the League of Nations Gather, classify, and interpret information. (MC) European reaction to the Fourteen Points, self-determination, and the League of Nations Explain cause and effect relationships. (MC) Strengths and weaknesses of the Versailles Treaty Draw conclusions and make generalizations about data. (MC) Debate over the League of Nations reflected the tradition of isolationism (George Washington: . . . avoid foreign entanglements) vs. a growing belief in a global role for the U.S. I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 60 STANDARD 11.9c GRADE LEVEL 11 The student will analyze and explain the importance of World War I, in terms of political, social, and economic change in Europe and the United States. Essential Understandings Essential Questions Fear of radicals, foreigners, and anarchists produce harsh government actions. How did fear of change manifest itself in the political and social events of the 1920s? Overproduction in wartime often leads to recession in peacetime. How do wartime economies affect postwar economics? During wartime, wages do not keep up with prices, leading to post-war strikes. Migration from farms to cities led to a clash between old rural policies and new urban policies. African-American migration to northern cities triggered discrimination as well as a rebirth of African-American culture. Essential Knowledge 1920s events Red scare Palmer Raids Sacco-Vanzetti Agricultural overproduction and price supports Steel workers strike, 1919-20 Coal miners strike, John L. Lewis, 1919 Scopes Trial Prohibition Roaring Twenties Harlem Renaissance (Langston Hughes) Role of women and the 19th Amendment Essential Skills Gather, classify, and interpret information. (MC) Explain cause and effect relationships. (MC) Draw conclusions and make generalizations about data. (MC) War produces unpredictable results. I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 61 GRADE LEVEL 11 STANDARD 11.9d The student will analyze and explain the importance of World War I, in terms of causes of World War II. Essential Understandings The treaty ending World War I planted the seeds for World War II. Essential Questions Why did WWI pave the way for WWII? Essential Knowledge Causes of WWII related to WWI Treaty of Versailles made harsh demands on Germany. War guilt (WWI) and reparations Failure of U.S. to join the League of Nations Economic instability in postwar Europe I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material Essential Skills Gather, classify, and interpret information. (MC) Explain cause and effect relationships. (MC) Draw conclusions and make generalizations about data. (MC) 62 STANDARD 11.10a GRADE LEVEL 11 The student will analyze and explain the Great Depression, with emphasis on causes and effects of changes in business cycles. Essential Understandings The business cycle fluctuates from peaks of prosperity to troughs of depression. Many Americans enjoyed the prosperity of a booming economy without recognizing its volatility. Essential Questions Essential Knowledge What is the business cycle? Definition of business cycle What were the characteristics of the business cycle in the 1920s? Causes Easy credit for consumers Easy availability of capital for business Installment buying Unbalanced foreign trade Mechanization of American industry Essential Skills Gather, classify, and interpret information. (MC) Explain cause and effect relationships. (MC) Draw conclusions and make generalizations about data. (MC) Effects Overproduction of goods Overspeculation in stock market Increases in personal debt Lack of foreign markets for American goods Fluctuations in employment and wages I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 63 GRADE LEVEL 11 STANDARD 11.10b The student will analyze and explain the Great Depression, with emphasis on weaknesses in key sectors of the economy in the late 1920s. Essential Understandings All Americans did not share in the prosperity of the 1920s. Changes in technology and consumer trends led some businesses to prosper and others to decline. Essential Questions How did the weaknesses in key sectors of the U.S. economy contribute to the Great Depression? Essential Knowledge Key sectors of the U.S. economy Farmers suffered from the depressed agricultural economy: overproduction low prices high debts. Textile mills faced competition from foreign countries. Many mills relocated from the Northeast to the South. Essential Skills Gather, classify, and interpret information. (MC) Explain cause and effect relationships. (MC) Draw conclusions and make generalizations about data. (MC) Weak American exports contributed to the decline of the economy. I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 64 STANDARD 11.10c GRADE LEVEL 11 The student will analyze and explain the Great Depression, with emphasis on United States government economic policies in the late 1920s. Essential Understandings The U.S. government economic policies did not adequately address the complex economic problems of the 1920s. The failure of the Federal Reserve Bank to prevent collapse of the banking system was a primary cause of the Great Depression. Retaliatory tariffs cut world trade and contributed to unemployment. Essential Questions Essential Knowledge Were federal government economic policies helpful or harmful in the late 1920s? Economic philosophies and policies Federal Reserve failed to prevent widespread collapse of the nations banking system in the late 1920s and early 1930s, leading to severe contraction in the nations supply of money in circulation. High protective tariffs produced retaliatory tariffs in other countries, strangling world trade (Smoot-Hawley Tariff). I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material Essential Skills Gather, classify, and interpret information. (MC) Explain cause and effect relationships. (MC) Draw conclusions and make generalizations about data. (MC) 65 GRADE LEVEL 11 STANDARD 11.10d The student will analyze and explain the Great Depression, with emphasis on causes and effects of the Stock Market Crash. Essential Understandings A pervasive attitude of overconfidence in the American economy encouraged reckless business and consumer practices. The Stock Market Crash contributed to a severe decline in the overall U.S. economy whose effects spread worldwide. Essential Questions What were the causes of the Stock Market Crash? What were the effects of the Stock Market Crash? Essential Knowledge Causes Overspeculating in stocks Buying stocks on margin Increasing the number of small investors in the stock market Speculating and panic selling of stocks Essential Skills Gather, classify, and interpret information. (MC) Explain cause and effect relationships. (MC) Draw conclusions and make generalizations about data. (MC) The Crash October 29, 1929 Effects Bankruptcies Bank closing Factory closings Massive unemployment Deepening agricultural depression Further weakening of European economies I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 66 GRADE LEVEL 11 STANDARD 11.10e The student will analyze and explain the Great Depression, with emphasis on the impact of the Depression on the American people. Essential Understandings Wage cuts, growing unemployment, and lower farm prices brought widespread suffering to many Americans. Essential Questions How did the Depression affect the everyday lives of Americans? How did Herbert Hoover respond to the Depression? Essential Knowledge Homeless Americans Hoovervilles Hobos Bread lines/soup kitchens Farmers Foreclosures and bankruptcies Dust Bowl Veterans Bonus army Women Married women had difficulty finding employment Children Child welfare and womens services cut by the states Many school closings Bread lines/soup kitchens Essential Skills The student will develop skills for historical analysis, inlcuding the ability to analyze documents, records, and data (such as artifacts, diaries, letters, photographs, journals, newspapers, historical accounts, etc.). (11.17a) (M) Gather, classify, and interpret information. (MC) Explain cause and effect relationships. (MC) Draw conclusions and make generalizations about data. (MC) Workers Unemployment Business failures I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 67 GRADE LEVEL 11 STANDARD 11.10e (continued) The student will analyze and explain the Great Depression, with emphasis on the impact of the Depression on the American people. Essential Understandings Essential Questions Essential Knowledge Essential Skills African-Americans Increase in discrimination *When teaching the above essential knowledge, the teacher should include the following standards: understand the settlement patterns and migration routes of various racial and ethnic groups. (11.15d) I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 68 STANDARD 11.10f GRADE LEVEL 11 The student will analyze and explain the Great Depression, with emphasis on the impact of New Deal economic policies. Essential Understandings Essential Questions The federal government began to play a more active role in the economy. What should be the role of government in times of economic distress? People looked to the government for support. While increasing the role of the government in the economy, New Deal policies also preserved democracy and the free enterprise system. How did Franklin Roosevelt respond to the Great Depression? Essential Knowledge Policies of Franklin Roosevelts Administration Farm relief and rural development Agricultural Adjustment Act (AAA) Tennessee Valley Authority (TVA) Business assistance and reform Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) National Recovery Administration (NRA) Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) Employment projects Works Progress Administration (WPA) Civilian Conservation Corps (CCC) Essential Skills Gather, classify, and interpret information. (MC) Explain cause and effect relationships. (MC) Draw conclusions and make generalizations about data. (MC) The student will develop skills in discussion, debate, and persuasive writing with respect to enduring issues and determine how divergent viewpoints have been addressed and reconciled. Such issues include the relationship of government to the individual in economic planning and social programs. (11.18c) (M) Housing and Social Security Home Owners Loan Corporation (HOLC) Social Security Act I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 69 GRADE LEVEL 11 STANDARD 11.10f (continued) The student will analyze and explain the Great Depression, with emphasis on the impact of New Deal economic policies. Essential Understandings Essential Questions Essential Knowledge Essential Skills Labor relations National Labor Relations Act Fair Labor Standards Act Effects Some federal agencies still active today: TVA, Social Security, FDIC, and SEC Increase in the income of farmers and workers Preservation of natural resources Provision of security for the sick and the aged Organization of unions Increase in the infrastructure of the nation National debt raised Federal bureaucracy doubled Failure to bring an end to the Depression Continued high unemployment until World War II. I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 70 STANDARD 11.10g GRADE LEVEL 11 The student will analyze and explain the Great Depression, with emphasis on the impact of the expanded role of government in the economy since the 1930s. Essential Understandings The New Deal dramatically changed the relationship between the federal government and the American people. Essential Questions How does the philosophy of government during the New Period continue today? Has government grown too large and assumed too many responsibilities? Essential Knowledge New Deal philosophy today Extension of the power of the federal government and the power of the President Deficit spending The welfare state established Greater concern for workers Conservation gains Renewal in faith of democracy and the free enterprise system Regulation of business I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material Essential Skills The student will develop skills for historical analysis, including the ability to formulate historical questions and defend findings based on inquiry and interpretation. (11.17c) (M) The student will develop skills in discussion, debate, and persuasive writing with respect to enduring issues and determine how divergent viewpoints have been addressed and reconciled. Such issues include the relationship of government to the individual in economic planning and social programs. (11.17c, 11.18c) (M) 71 GRADE LEVEL 11 STANDARD 11.11a The student will demonstrate an understanding of the origins and effects of World War II, with emphasis on the rise and aggression of totalitarian regimes in Germany, Italy, and Japan. Essential Understandings Certain economic and political conditions may lead to totalitarian governments. Aggression and intolerance are characteristics of totalitarian governments. Essential Questions What explains the rise of totalitarian regimes? Essential Knowledge Essential Skills Totalitarian leaders Hitler Mussolini Tojo Interpret map and globes. Roles played by Nazi Party Anti-Semitism Treaty of Versailles Fascism Militarism Economic depression Sequence events in chronological order. (MC) Important topics Germanys annexation of the Rhineland, Austria, and the Sudetenland Germanys invasions of Poland, France, and the Soviet Union Italys invasion of Ethiopia Japans occupation of Manchria and invasion of China I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material Locate areas (regions) of conflict on maps and globes. (MC) Differentiate between historical facts and historical interpretations. (MC) The student will develop skills for historical analysis, including the ability to develop perspectives of time and place, including the construction of various time lines of events, periods, and personalities in American history. (11.17d) (M) 72 STANDARD 11.11b GRADE LEVEL 11 The student will demonstrate an understanding of the origins and effects of World War II, with emphasis on the role of the Soviet Union. Essential Understandings The Soviet Union began the war as a neutral and entered a nonaggression pact with Nazi Germany. It became an ally of the United States after it was invaded by Hitlers Army. Essential Questions How did the war affect the Soviet Union? Essential Knowledge Essential Skills Stalin was the totalitarian leader of the Soviet Union. Gather, classify, and interpret information. (MC) The Non-Aggression Pact between Hitler and Stalin Locate areas (regions) on maps and globes. (MC) The Eastern Front Draw conclusions and make generalizations about data. (MC) The Siege of Leningrad and Stalingrad The Yalta Agreement I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 73 GRADE LEVEL 11 STANDARD 11.11c The student will demonstrate an understanding of the origins and effects of World War II, with emphasis on appeasement, isolationism, and the war debates in Europe and the United States prior to the outbreak of war. Essential Understandings Initial response of the West to Hitler was to seek agreements to preserve peace. The U.S. slowly moved from neutrality to active support of the Allies. Essential Questions How do we stop the aggressive actions of another country? When does a country abandon neutrality? Essential Knowledge Munich Conference Neutrality Acts in U.S. Lend-Lease Act Why did the U.S. pursue isolationism in the 1930s? Essential Skills Gather, classify, and interpret information. (MC) Locate areas (regions) on maps and globes. (MC) Draw conclusions and make generalizations about data. (MC) Appeasement did not stop Hitlers aggressive actions. I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 74 STANDARD 11.11d GRADE LEVEL 11 The student will demonstrate an understanding of the origins and effects of World War II, with emphasis on the impact of mobilization for war, at home and abroad. Essential Understandings The impact of war mobilization changed the U.S. economy. War mobilization altered the role of women in the work force. War accentuated existing racial and ethnic divisions. The war expanded the role of government in American life. Essential Questions How does war change the economic and social fabric of a society? Essential Knowledge Draft and enlistment Wage and price controls Shortagesrationing Women called to work War bonds Segregated units in military Relocation of Japanese-Americans Race riots of the 1940s in American cities Zoot Suit riots in Los Angeles I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material Essential Skills Gather, classify, and interpret information. (MC) Locate areas (regions) on maps and globes. (MC) Draw conclusions and make generalizations about data. (MC) The student will develop skills in discussion, debate, and persuasive writing with respect to enduring issues and to determine how divergent viewpoints have been addressed and reconciled. Such issues include problems of intolerance toward racial and ethnic groups in American Society. (11.18f) (M) 75 STANDARD 11.11e GRADE LEVEL 11 The student will demonstrate an understanding of the origins and effects of World War II, with emphasis on major battles, military turning points, and key strategic decisions. Essential Understandings WWII changed the nature of warfare. Essential Questions How did WWII change the way wars were fought? Why did the Allies win the war? Essential Knowledge Major military battles/turning points Invasion of Poland by Germany and the Soviet Union German invasion of France Battle of Britain German defeat at Stalingrade turning point on the Russian Front Pearl Harbor Battle of Midwayturning point in the Pacific Invasion of Normandy (D-Day) Battle of the Bulgeopened the way to the Allied invasion of Germany Stalingrad Iwo Jima Okinawa Essential Skills Gather, classify, and interpret information. (MC) Locate areas (regions) on maps and globes. (MC) Draw conclusions and make generalizations about data. (MC) Strategic decisions Blitzkrieg U-Boats in the Atlantic Island hopping Manhattan Project Dropping of the atomic bomb I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 76 STANDARD 11.11e (continued) GRADE LEVEL 11 The student will demonstrate an understanding of the origins and effects of World War II, with emphasis on major battles, military turning points, and key strategic decisions. Essential Understandings Essential Questions Essential Knowledge Essential Skills Leaders Franklin D. Roosevelt Winston Churchill I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 77 GRADE LEVEL 11 STANDARD 11.11f The student will demonstrate an understanding of the origins and effects of World War II, with emphasis on the Holocaust and its impact. Essential Understandings Essential Questions Wars demonstrate mans inhumanity to man. What is a war crime? Not all acts are justified during wartime. How could a modern state with achievements in art, literature, and science engage in mass murder of a people? The Holocaust was a systematic effort by a modern state (Germany) to exterminate an entire people (Jews). Essential Knowledge Nazis imprisoned and exterminated millions of Jews, Slavs, gypsies, political enemies, homosexuals, and the physical and mentally disabled in concentration camps. (Auschwitz) Allies liberated the concentration camps. Essential Skills Gather, classify, and interpret information. (MC) Locate areas (regions) on maps and globes. (MC) Draw conclusions and make generalizations about data. (MC) Nuremberg trials Many Jewish survivors of the Holocaust founded the state of Israel. I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 78 STANDARD 11.11g GRADE LEVEL 11 The student will demonstrate an understanding of the origins and effects of World War II, with emphasis on the reshaping of the United States role in world affairs after the war. Essential Understandings The U.S. could no longer endorse an isolationist foreign policy. The U.S. became the worlds leading superpower after World War II which brought burdens and responsibilities. Essential Questions How did WWII change the world order? Essential Knowledge The United States and the USSR emerged as the two superpowers at the end of WWII. United States had the atomic bomb. USSR had the largest military force. I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material Essential Skills Draw conclusions and generalizations about data. (MC) Gather, classify, and interpret information. (MC) 79 GRADE LEVEL 11 STANDARD 11.12a The student will analyze and explain United States foreign policy since World War II, with emphasis on the origins and both foreign and domestic consequences of the Cold War. Essential Understandings Essential Questions Diplomatic relations between the U.S. and the Soviet Union quickly broke down after the war. Why did relations between the U.S. and Soviet Union deteriorate during this period? The ideological beliefs and concerns created different goals for the two superpowers. Why were Americans so suspicious during the 1950s? Was the Cold War inevitable? Essential Knowledge Origins (1943-1954) Define Cold War. Wartime conference Yalta Leadership FDR Churchill Stalin Truman Essential Skills Compare and contrast differing sets of ideas, values, personalities, behaviors, and institutions. Draw conclusions and generalizations about data. (MC) Gather, classify, and interpret information. (MC) American/Soviet differences Ideology Communism vs. Democracy Security Soviet Invasion of Eastern Europe and creation of satellites (Iron Curtain) Domestic consequences Loyalty oaths House Un-American Activities Committee (HUAC) I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 80 STANDARD 11.12a (continued) GRADE LEVEL 11 The student will analyze and explain United States foreign policy since World War II, with emphasis on the origins and both foreign and domestic consequences of the Cold War. Essential Understandings Essential Questions Essential Knowledge Essential Skills Spy cases Alger Hiss Ethel and Julius Rosenberg McCarthyism Senator Joseph McCarthy Foreign Consequences Policy of containment Nuclear arms raceH-bomb Space race Defense spending increased I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 81 GRADE LEVEL 11 STANDARD 11.12b The student will analyze and explain United States foreign policy since World War II, with emphasis on communist containment policies in Europe, Latin America, and Asia. Essential Understandings American foreign policy in the postwar years was based on containment of Communism. Aimed at Europe, the policy of containment was extended to include Latin America and Asia. The Cold War often exploded and created hot spots. Wars such as those in Korea and Vietnam were a result of American Cold War policy of containment (resisting the expansion of Communism). Essential Questions Why did the U.S. pursue a policy of containment? Did the U.S. policy of containment work? Essential Knowledge Define containment. Europe Truman Doctrine Marshall Plan Berlin blockade and airlift Formation of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) Berlin Wall Essential Skills Draw conclusions and generalizations about data. (MC) Gather, classify, and interpret information. (MC) Latin America Economic Aid Alliance for Progress Guatamala Cuba Fidel Castro Bay of Pigs Cuban Missile Crisis Nicaragua Sandinistas vs. Contras Reagan policy toward Sandinistas and Contras I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 82 STANDARD 11.12b (continued) GRADE LEVEL 11 The student will analyze and explain United States foreign policy since World War II, with emphasis on communist containment policies in Europe, Latin America, and Asia. Essential Understandings Essential Questions Essential Knowledge Essential Skills Asia China Defeat of Chiang Kai-shek by Mao Zedong Creation of Peoples Republic of China Flight of Chiang Kai-shek to the island of Formosa (Taiwan) Nixons visit to China opening of diplomatic relations with China. Korea Temporary division at 38th parallel North Korea invades South Korea. UN Police Action Cease-fire agreement and stalemate Firing of General Douglas MacArthur I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 83 GRADE LEVEL 11 STANDARD 11.12b (continued) The student will analyze and explain United States foreign policy since World War II, with emphasis on communist containment policies in Europe, Latin America, and Asia. Essential Understandings Essential Questions Essential Knowledge Essential Skills Vietnam Division of Vietnam into North and South Vietnam Domino Theory leads to U.S. involvement to prevent Northern (Communist) takeover of South Vietnam Escalation of U.S. involvement, including the Gulf of Tonkin Resolution, and the Tet offensive Vietnamization and the withdrawal of American troops, followed by defeat of South Vietnam and reunification under Northern control Conflict at home Hawks vs. Doves Antiwar movement Detente Nuclear Test-Ban Treaty SALT Nixons visit to Chinaopens diplomatic relations with China I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 84 STANDARD 11.12c GRADE LEVEL 11 The student will analyze and explain United States foreign policy since World War II, with emphasis on the strategic and economic factors in Middle East policy. Essential Understandings U.S. policy in the Middle East has been guided since the end of World War II by containment, support for Israel, and the need for oil. Essential Questions What factors determined U.S. foreign policy in the Middle East? Essential Knowledge Essential Skills Creation of OPEC and the oil embargo Locate areas (regions) of conflict on maps and globes. (MC) U.S. involvement in Arab-Israeli disputes Military monitoring of conflicts between Israelis and the PLO army U.S. troops attacked in Lebanon Interpret ideas/concepts and events. (MC) Peacekeeping attempts by U.S. Camp David Accords Rabin/Arafat Peace Agreement Gather, classify, and interpret information. (MC) Draw conclusions and generalizations about data. (MC) Relations with Iran Support for Shah related to policy of containment and oil The hostage crisis Persian Gulf War Invasion of Kuwait by Iraq Operation Desert Storm Creation of the State of Israel I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 85 GRADE LEVEL 11 STANDARD 11.12d The student will analyze and explain United States foreign policy since World War II, with emphasis on relations with South Africa and other African nations. Essential Understandings U.S. policy toward Africa reflected competition between the U.S. and the Soviet Union. Essential Skills Essential Questions Essential Knowledge What attitudes guided our foreign policy in Africa? U.S. policy toward Africa The end of World War II triggered independence movements throughout the African continent. Research content materials from computer programs. U.S. foreign policy was characterized by support for proWestern governments and the free enterprise system. Gather, classify, and interpret information. (MC) Draw conclusions and generalizations about data. (MC) U.S. foreign policy supported humanitarian issues, including relief efforts during famines. U.S. foreign policy slowly changed from one of support for the white South African government to a call for an end to its apartheid policies. I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 86 STANDARD 11.12e GRADE LEVEL 11 The student will analyze and explain United States foreign policy since World War II, with emphasis on the collapse of communism and the end of the Cold War. Essential Understandings Essential Questions Essential Knowledge The collapse of the Soviet Union brought an end to the Cold War that had dominated American policy for forty years. How is the world different because of the collapse of communism? Reasons for the collapse of the Soviet Union Reagans defense policies including the Strategic Defense Initiative (SDI) and encouragement of internal dissidents in Communist countries (Solidarity movement in Poland) Soviet government mismanagement, economic inefficiency, and corruption Nationalist sentiment in the Soviet republics Communism as an economic policy failed. Reagans defense buildup forced the Soviet Union to try to compete, hastening its internal collapse and the end of the Cold War. Trends and events in Soviet Union and the newly independent states Policies of Mikhail Gorbachev Free elections Establishment of independent states Efforts toward market economy I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material Essential Skills Gather, classify, and interpret information. (MC) Explain cause and effect relationships. (MC) The student will develop skills in discussion, debate, and persuasive writing with respect to enduring issues and determine how divergent viewpoints have been addressed and reconciled. Such issues include problems of intolerance toward racial and ethnic groups in American society. (11.18f) (M) 87 GRADE LEVEL 11 STANDARD 11.12e (continued) The student will analyze and explain United States foreign policy since World War II, with emphasis on the collapse of communism and the end of the Cold War. Essential Understandings Essential Questions Essential Knowledge Essential Skills Parallel events and trends in Eastern Europe Collapse of Soviet influence in Eastern Europe Establishment of non-totalitarian governments Fall of Berlin Wall and reunification of Germany I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 88 STANDARD 11.12f GRADE LEVEL 11 The student will analyze and explain United States foreign policy since World War II, with emphasis on new challenges to Americas leadership role in the new world. Essential Understandings As the sole superpower, the U.S. struggles to establish a consistent policy in a rapidly changing and an increasingly interdependent world. Essential Questions How does the United States, as the remaining superpower, respond to the global forces of unity and disunity? Essential Knowledge Forces for global unity Economic interdependence Communications explosion Role of international agencies Essential Skills Draw conclusions and generalizations about data. (MC) Gather, classify, and interpret information. (MC) Forces for global disunity Ethnic and religious factionalism Economic disparity Nuclear proliferation Terrorism I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 89 GRADE LEVEL 11 STANDARD 11.13a The student will evaluate federal civil rights and voting rights developments since the 1950s in terms of the Brown v. Board of Education decision and its impact on education. Essential Understandings Essential Questions Essential Knowledge Essential Skills The student will develop skills in discussion, debate, and persuasive writing with respect to enduring issues and to determine how divergent viewpoints have been addressed and reconciled. Such issues include the tension between majority rule and minority rights problems of intolerance toward racial groups in American society the evolution of rights, freedoms, and protection throughout political and social movements. (11.18e, f, g) (M) Separate but equal is inherently unequal. How did integration of U.S. schools take place? Meaning of the equal protection clause of the 14th Amendment U.S. Supreme Court decisions can promote social change. How do we balance majority rule with minority rights? Change in the separate but equal interpretation in Plessy v. Ferguson (1896) to mandate integration of schools in Brown v. Board of Education (1954) State actions must comply with federal mandates. Resistance to school integration Little Rock, Arkansas VirginiaMassive Resistance Revival of the Ku Klux Klan Efforts to achieve school integration Busing I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 90 STANDARD 11.13b GRADE LEVEL 11 The student will evaluate federal civil rights and voting rights developments since the 1950s in terms of civil rights demonstrations and related activity leading to desegregation of public accommodations, transportation, housing, and employment. Essential Understandings Nonviolent demonstrations and protests produced changes. The Federal government responded to calls for change. Essential Questions How do people change the political, social, and economic order? Essential Knowledge Events Montgomery bus boycott March on Washington Civil Rights Act, 1964 Watts riot Letter from a Birmingham Jail (11.16) (M) Sit-ins and Freedom Rides Essential Skills Definitions Civil disobedience Black Power The student will develop skills for historical analysis, including the ability to analyze documents, records, and data (such as artifacts, diaries, letters, photographs, journals, newspapers, historical accounts, etc.) formulate historical questions and defend findings based on inquiry and interpretation. (11.17a, c) (M) Organizations NAACPNational Association for the Advancement of Colored People SCLCSouthern Christian Leadership Conference SNCCStudent Nonviolent Coordinating Committee Black Panthers The student will develop skills in discussion, debate, and persuasive writing with respect to enduring issues and determine how divergent viewpoints have been addressed and reconciled. Such issues include Civil disobedience vs. the rule of law (11.18a) (M) I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 91 GRADE LEVEL 11 STANDARD 11.13b (continued) The student will evaluate federal civil rights and voting rights developments since the 1950s in terms of civil rights demonstrations and related activity leading to desegregation of public accommodations, transportation, housing, and employment. Essential Understandings Essential Questions Essential Knowledge Leaders Martin Luther King, Jr. Malcolm X I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material Essential Skills Freedom of the press vs. the right to a fair trial Problems of intolerance toward racial groups in American society The evolution of rights, freedoms, and protections through political and social movements. (11.18 d, f, g) (M) 92 STANDARD 11.13c GRADE LEVEL 11 The student will evaluate federal civil rights and voting rights developments since the 1950s in terms of reapportionment cases and voting rights legislation and their impact on political participation and representation. Essential Understandings Legislation and court cases have led to increased minority participation in government and office holdings. Gerrymandering continues to be controversial. Essential Questions How have changes affected the political participation and representation of minority groups? Essential Knowledge Definition of gerrymandering Selma to Montgomery March Voting Rights Act, 1965 24th Amendment Wesberry v. Sanders (concept of one person/one vote) I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material Essential Skills Interpret ideas and concepts as expressed in print and non-print sources. (MC) Gather, classify, and interpret information. (MC) Draw conclusions and make generalizations about information. (MC) 93 GRADE LEVEL 11 STANDARD 11.13d The student will evaluate federal civil rights and voting rights developments since the 1950s in terms of affirmative action. Essential Understandings Affirmative action is a policy for correcting the effects of discrimination in employment or education based on race, ethnicity, or gender. Affirmative action has become a divisive issue in American politics. Essential Questions What is affirmative action? Essential Knowledge Definition of affirmative action Regents of the University of California v. Bakke (1978) Proposed equal rights amendment Essential Skills Interpret ideas and concepts as expressed in print and non-print sources. (MC) Gather, classify, and interpret information. (MC) Draw conclusions and make generalizations about information. (MC) I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 94 STANDARD 11.14a GRADE LEVEL 11 The student will demonstrate an understanding of domestic policy issues in contemporary American society by comparing conservative and liberal economic strategies. Essential Understandings Essential Questions Essential Knowledge Contemporary America refers to the time period from 1970 to the present. How do liberals and conservatives differ in economic strategies? Conservative economic strategies Reduced government spending on social programs Reduced government regulation of business Reduced taxation There are philosophical differences about the role of government in managing the economy. Liberal economic strategies Increased government spending on social programs Increased government regulation of business I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material Essential Skills Compare and contrast differing sets of ideas, values, personalities, behaviors, and institutions. (MC) Select and defend positions. (MC) Differentiate between points of view of self and others. (MC) 95 GRADE LEVEL 11 STANDARD 11.14b The student will demonstrate an understanding of domestic policy issues in contemporary American society by explaining current patterns of Supreme Court decisions and evaluating their impact. Essential Understandings Essential Questions Essential Knowledge Essential Skills Contemporary America refers to the time period since 1970. Do Supreme Court decisions since 1970 reflect a more liberal or conservative philosophy? Supreme Court issues Since 1970, patterns in legal questions heard by the U.S. Supreme Court include Right to abortion vs. the right to life Roe v. Wade, 1973, has been upheld consistently while parental notification has also been upheld. Discrimination against women Reed v. Reed, 1971 expands prohibition of discrimination into gender issues. Religion The wall of separation between church and state has been upheld (school sanctioned prayer is prohibited), yet allowing for exceptions (studentinitiated prayer and moments of silence are constitutionally permissable). Evaluate information from various forms of multimedia materials. (MC) The trend of the Supreme Court has been toward conservativebased decisions, with a few exceptions that reflect a more liberal philosophy. Why does the Supreme Court shift philosophies? I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material Evaluate information for accuracy and separate fact from opinion. (MC) Use computers to research content materials from computer programs. (M) The student will develop skills in discussion, debate, and persuasive writing with respect to enduring issues and determine how divergent viewpoints have been addressed and reconciled. Such issues include The relationship of government to the individual in economic planning and social programs Freedom of press vs. the right to a fair trial 96 STANDARD 11.14b (continued) GRADE LEVEL 11 The student will demonstrate an understanding of domestic policy issues in contemporary American society by explaining current patterns of Supreme Court decisions and evaluating their impact. Essential Understandings Essential Questions Essential Knowledge Student speech Court decisions have greatly narrowed students free speech rights while expanding the authority of school officials. Rights of the accused The trend is toward limiting the rights of accused in the areas of searches and seizures and the death penalty. Freedom of the press vs. the right to a fair trial I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material Essential Skills The evolution of rights, freedoms, and protections through political and social movements. (11.18c, d, g) (M) 97 GRADE LEVEL 11 STANDARD 11.14c The student will demonstrate an understanding of domestic policy issues in contemporary American society by comparing the positions of the political parties and interest groups on major issues. Essential Understandings Essential Questions Essential Knowledge Contemporary America refers to the time period 1970 to the present. What has distinguished the positions of major political parties and interest groups since 1970? Political parties Democratic Republican The primary difference between the two parties is on the role of government, whether governments role in addressing social problems should be greater or lesser. Why has public trust in government and politicians declined? Interest groups AFL-CIO (American Federation of Labor - Congress of Industrial Organizations) National Association of Manufacturers Sierra Club AARP (American Association for Retired Persons) AMA (American Medical Association) Essential Skills Identify and explain symbols expressed in cartoons/pictures. Compare and contrast differing sets of ideas, values, personalities, behaviors, and institutions. (MC) Draw conclusions and generalizations about data. (MC) Gather, classify, and interpret information. (MC) Some issues that divide Democrats, Republican, and interest groups Democrats generally favor greater role for government in addressing social problems. Republicans generally favor private sector or individual action to address social problems. I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 98 STANDARD 11.14c (continued) GRADE LEVEL 11 The student will demonstrate an understanding of domestic policy issues in contemporary American society by comparing the positions of the political parties and interest groups on major issues. Essential Understandings Essential Questions Essential Knowledge Essential Skills Democrats are generally more willing while Republicans are generally less willing to regulate business activity. I=Initial Instruction R=Reinforcement of the Skill M=Mastery of the Skill MC=Mastery of Complex New Material 99