Tutorial 2 - web page for staff
advertisement

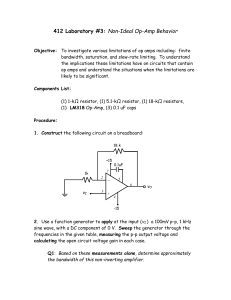
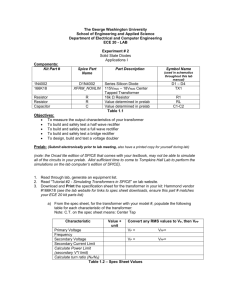
1 Asst.Prof.Rardchawadee Silapunt Transformer Full wave rectifier Operational Amplifier (Op-Amp) Digital logic gate 2 2 1 1. Select components from Get New Part. 2. Use wiring tool for drawing the line between components. 3 Transformer is an electrical device that transfer energy from one circuit to another through electromagnetic induction. Transformer can convert both current and voltage. 4 Draw a transformer circuit and modify the values of components. 2. Add K_Linear element in order to create mutually coupled inductors. 1. In this schematic, transformer has a ratio of 1:1. 5 Set up parameters in transient analysis. 6 Put the voltage markers on input and output of the transformer to compare input and output waveforms. 7 You can vary output waveform by using N1 = L1 N2 L2 N1 20 = = 2. So, the output N2 5 From the schematic, there is waveform has amplitude 50% less than input waveform 8 Voltage at the primary inductor is 10V and at secondary inductor is 5 V. 9 Full wave Rectifier : Center Tap Transformer Full wave Rectifier : Bridge Rectifier 10 http://www.electronics-tutorials.ws/diode/diode_6.html A shape of the waveform before and after entering full wave rectifier. 11 http://www.docstoc.com/docs/15562456/Full-Wave-Bridge-Rectifier http://www.sptc.ac.th/prapruet/devicesweb/books/book_4.htm 12 How does the center tap transformer create full wave? 13 http://www.sptc.ac.th/prapruet/devicesweb/books/book_3.htm During a positive cycle, half of the voltage occurs between the center tab and the top of the secondary transformer. D1 is the conducted current and current flows through load. During a negative cycle, half of the voltage occurs between the center tab and the bottom of the secondary transformer. D2 is the conducted current and current flows through load. Currents in both cycles flow in the same direction. Thus, the output waveform is a full wave. 14 15 Select Analysis ->setup -> Transient 2. Set up Transient Analysis 3. Measure waveform by voltage marker 1. 16 Output waveform is the full wave. 17 Add capacitor C1 to lower the voltage ripple. 18 Set up values in Transient and Fourier Analysis. 19 Compare voltages between input and output. 20 Plot -> Add plot to window Trace -> Add trace -> I(Rinput) 21 Change to the FFT function to observe harmonics. 22 Delete step ceiling in order to see harmonic’s response clearly. 23 Plot -> Add plot to window Trace -> Add trace -> I(Rinput) 24 Full wave Rectifier : Center Tap Transformer Select the FFT function and use cursor to measure peaks of waveform. 25 FFT function displays each harmonic in different amplitude. We use this FFT to measure a distortion of waveforms. Typically, Total Harmonic Distortion(THD) can be determined from ∑ (I n ) THD = n=2 (I1) 2 2 ×100 In practice, we can calculate from 2nd to only 25th harmonic but the ideal standard is from 2nd to 50th harmonic. 26 During the positive circle, D1 and D2 conduct current. Current flows in full cycle. The potential occurs at load. Similar to positive, during the negative circle, D3 and D4 conduct current. Current flows through load. Potential occurs. The result of this operation is the full wave. 27 http://www.sptc.ac.th/prapruet/devicesweb/books/book_4.htm Operation Amplifier Operational Amplifier or Op-Amp is an electronic device containing a transistor inside to increase the signal amplitude. Symbol of Op-Amp http://www.markallen.com/teaching/ucsd/147a/lectures/lecture5/2.php 28 Op-Amps are widely used in electronic circuits such as • Amplifier • Integrator • Differentiator • Voltage follower • Oscillator 29 Symbol of Op-Amp : The Triangle is the symbol for amplifier and displays the direction of a current flow. Symbol of Op-Amp Package :TO-5 and DIP Package of Op-Amp – Usually found either in TO-5 or DIP. 30 http://silp.elec-cm.com/opamp/book/lesson1.pdf Code number– The first two letters indicate manufacturer. Three numbers are type of Op-Amp. The follower letter informs the temperature range. The last letter explains the package. Manufacturer code 31 http://silp.elec-cm.com/opamp/book/lesson1.pdf Code number– The first two letters indicate manufacturer. Three numbers are type of Op-Amp. The follower letter inform the temperature range. The last letter explain the package. Latter Meaning Latter C commercial 0 to70 degree Celcius D I Industrial -25 to 85 degree Celsius J M Military -55 to 125 degree Celsius N,P Temperature code Meaning Plastic dual in line for surface mounting on PC board Ceramic dual in line Plastic dual in line for insertion into sockets Package code 32 http://www.scribd.com/doc/19017130/Characteristics-of-Opamp The usual way to classify amplifier is the phase relationship of input and output signals which can be divided in to Inverting Amplifier and Non-Inverting Amplifier. http://www.elexp.com/t_gain.htm 33 Inverting Amplifier 1. Draw a schematic and change values of components. 2. Use the voltage marker to measure input and output voltage. 34 The feedback is negative. So, the output waveform inverts 180 degree compared to the input waveform and the amplifying gain of this circuit can be calculated ோ from య . ோమ 35 Non-Inverting Amplifier 1. 2. Draw a schematic and change values of components. Use the voltage marker to measure input and output voltage. 36 The output waveform is in-phase with the input waveform. Gain can be calculated from 1 + R3 . R6 37 Half-bit adder Half bit adder has a circuit and truth table as shown. 38 http://www.eng.warwick.ac.uk/eng/staff/elh/es153/00/pspice/students_model_solution_pspiceassignment_report.pdf Draw a circuit and select components as the following. http://www.eng.warwick.ac.uk/eng/staff/elh/es153/00/pspice/students_model_solution_pspiceassignment_report.pdf 39 Double click at DigCLK DigCLK1 and DigCLK2 have different ON-TIME and OFF-TIME’s values. The result shows the difference of digits over time. 40 Select Analysis -> Setup ->Transient 41 Select Digital Setup and set up parameters. 42 Result of the simulated waveforms. 43 To produce digital signal you can also use STIM1 STM1 can be found in Get New Part. COMMAND in STIM1 can be used to set up CLK STMI1, STMI4, STMI16 are programmed for 1,4,and 16 parallel and independent digital signals. 44 Use DSTM instead of DigCLK at point B 45 Another method to set up CLK by users is to use a command Doubleclick DigCLK for setting parameter. 46 Set the values at lines ‘COMMAND’ in DSTM. 47 Run the simulation After a user inputs values by COMMAND, the rest of the input bit is set default at ‘0’. 48 Full wave Rectifier 49 Harmonic’s result 50 51 52