Prelab4_solutions
advertisement

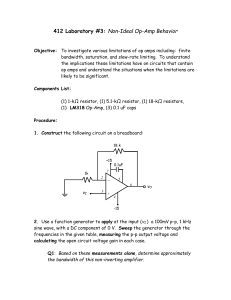
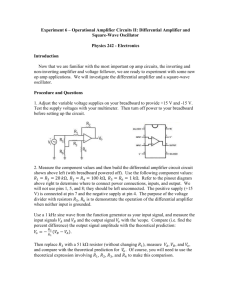
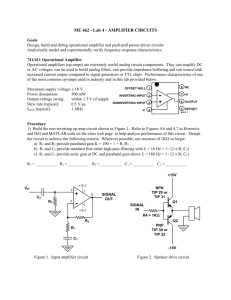
Physics 3330 Solutions Pre-lab 4 Spring 2013 Pre-lab4 Problems 1. Data for the LF356 op-amp (same as LF156) are given at the National Semiconductor Web Site: http://www.national.com/ds/LF/LF155.pdf (there is a link from the 3330 web page and a copy in the lab). Verify that the following values are reasonable approximations to use in solving the problems. Identify your source of each item by quoting the graph or table number and page number. DC voltage gain Unity gain frequency Maximum output voltage Maximum slew rate Maximum output current Input resistance Output resistance Input offset voltage Input bias current 2. A0 = 2·105 (same as AVOL in tables) fT = 5 MHz (same as GBW in tables) Vsat = ± 13 V (same as VO in tables) SR=(dVout/dt)max = 12 Volts/µsec (IO)max = 25 mA Ri = 1012 (RIN in tables) Ro = 40 (See the theory section for help with Ro.) VOS = 3 mV IB = 30pA Calculate the values of low frequency gain G0 and the bandwidth fB for the non-inverting amplifier in Fig. 4.2. for: (a) RF = 50 and R = 50 Gain: 2 Bandwidth: 2.5MHz (b) RF = 50 k and R = 50 k Gain: 2 Bandwidth: 2.5MHz (c) RF = 50 k and R = 5 k Gain: 11 Bandwidth: 450kHz (d) RF = 0 and R = infinity (the voltage follower)Gain:1 BW: 5MHz Be careful about which equations you use here. Make sure you justify when you can use an approximate equation i.e., what you get from the golden rules for an ideal op-amp, and when you need to do some extra work. The point of the comment above is mostly regarding the concern that the Gain=2 amplifier of part (a) might push the op-amp to produce its max current near the rail. (e) Draw Bode plots (log-log; use the voltage gain instead of ‘dB’ for the y-axes for this time) for the open loop gain and the closed loop gains from 2b, 2c, 2d above on the same graph. What is the exponential rise-time for square waves in each case (see page 4.5)? Make a table of your results. 3. Estimate the input and output impedances of the amplifier with RF = 20 k and R = 150 for 1 kHz sine waves. 4. What is the maximum output amplitude for 5 MHz sine waves if they are not to be Physics 3330 Solutions 4.1 Physics 3330 Solutions Pre-lab 4 Spring 2013 distorted by the slew rate of the LF356 op-amp? (See H&H p. 192.) Draw a voltage vs. time plot showing a sine wave input and a typical slew rate limited output on the same plot. (Note that an amplifier limited by slew rate will change a curved line to a straight line if the slope of the curved line would exceed the slew-rate.) 5. Design an inverting amplifier (Fig. 4.3) with a closed-loop gain of 20. Select appropriate values for R and RF to avoid the potential problems you found in question 2 above. Choose RF large enough so that the maximum output current of the op-amp is not exceeded when the output is near the saturation voltage (~13V). Predict the bandwidth and the input impedance at the signal input. How would you measure the input impedance in the lab? [The DMM is not going to properly read the input or output impedance when connected to a circuit because of all the other resistors and bias voltages present. Here is a hint: Recall that when the signal generator with a 50 output impedance has a 50 load the signal into the load drops by a factor of two. Physics 3330 Solutions 4.2