Phylum Chordata
advertisement

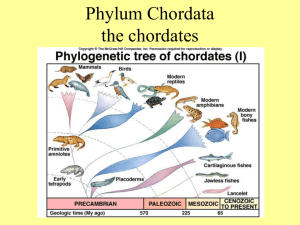
Phylum Chordata Tunicates Amphioxus 1 Phylum Chordata Taxonomic Summary z Phylum Chordata – – – 3 Subphylum Urochordata Subphylum Cephalochordata Subphylum Vertebrata Phylum Chordata Subphylum Urochordata z z 4 Defining characteristics – Notochord and nerve cord are found only in the larval stage Most of the urochordates are filter feeders Phylum Chordata Colonial Species 5 Phylum Chordata Nice Tunic z z 6 Soft exoskeleton made of cellulose with 2 external openings Some species have spicules and toxins in the tunicate Spicules Phylum Chordata Filter Feeding Sexual Reproduction z z 8 Most colonial species retain eggs and fertilization is internal with development The larvae are microscopic, short-lived, non-feeding, pelagic tadpoles Phylum Chordata Subphylum Cephalochordata z Defining characteristics – – 9 The notochord extends beyond the nerve cord to the anterior end of the animal The notochord is contractile, formed as a longitudinal series of flattened discs Phylum Chordata A Little Ditty It’s a long way from amphioxus, It’s a long way to us It’s a long way from amphioxus To the meanest human cuss Goodbye to tails and gill slits, Hello: nails and hair! It’s a long way from amphioxus But we came from there 10 Phillip H. Pope sing to the tune of “It’s a long way to Tipperary” Phylum Chordata Anatomy 12 Phylum Chordata Filter Feeders z z 13 Filter feed using a special pharynx similar to tunicates Slotted pharynx supported by skeletal bars similar to acorn worms Phylum Chordata Reproduction z 14 Separate sexes with gonads located in the atrial region – Fertilization occurs in the water – Developing young are free swimming propelled by cilia Phylum Chordata