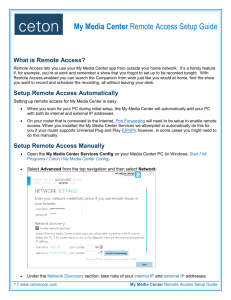
CCNA ICND1 (640-822)
advertisement

CCNA ICND1 (640-822) ! ا آ, ا آ وف ب هردو ها ا و ا ICND1 ال5$! اآة1 ب23ت ها ا20! CCNA 640-802 دة ال$% & .<= ICND 2 ء ا: و ان J و اCBT Nuggets ح ال%1 B ! ب23ت ها ا20! @ ?=و . CBT Nuggets ر ! الKا ." و ا ي#$& د#'( )* + و,أ ا B &0! ??س و$! Senior Technical Support, Manager for VAS Platform. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 1 Did I Miss Anything? I am always interested to hear how my students, and now readers of my books, do on both certification exams and future studies. If you would like to contact me and let me know how this book helped you in your certification goals, please do so. Did I miss anything? Let me know. My e-mail address is waleedmohsen3000@yahoo.com Who Should Read This Book This book is for those people preparing for the CCNA exam, whether through self-study, on-the-job training and practice. There are also some handy hints and tips along the way to hopefully make life a bit easier for you in this endeavor. It is small enough that you will find it easy to carry around with you. Big, heavy textbooks might look impressive on your bookshelf in your office, but can you really carry them all around with you when you are working in some server room or equipment closet somewhere? Dedications This book is dedicated to My MOM, DAD, My Little Brothers, also not to forget my Friends who have Encouraged me and to all my Guests from Arab Hardware and finally to My WIFE, without whom I couldn’t have made it through those long nights of writing and editing. About the Author Waleed Mohsen is graduated at Aug. 2005 from “Higher technological Institute” at 10th of Ramadan City with Graduation Grade Very Good; Major studies were Electronics and Telecommunication Technology. He enjoys Listening and watching “Learning Videos”, and studying the martial art of Taekwon-Do, at the Week End. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 2 THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 3 OSI (Open System Interconnection) Layers It’s a way used to explain Network Communication, and way for Standards to unite them all. Layer 7 Application Layer: Layer Response for the application that is run on the computer and need access to the Internet. Example: 1. 2. 3. 4. HTTP (Hyper Text Transfer Protocol): Browsing Protocol. FTP (File Transfer Protocol): For Downloading Files and Uploading. Telnet: Remote Access Protocol. SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol): For Sending & Receiving Mail. Layer 6 Presentation Layer: Layer that Presents the Data, so its name is Presentation Layer, as following: 1. Format of DATA (MPEG, GIF, HTML, MP3, etc…). 2. Compression or Decompression of DATA. 3. Encoding & Decoding the DATA such as ASCII Code. Layer 5 Session Layer: Set a logical Connection (Session) between different application Say: The Session Layer Ensure that Each Data is in its Own Session or Keep Data Stream Separate by Using Port Number from Layer 4 (Source Port, & Destination Port), Also this Session Establish and Terminate Connection, (SQL, ASP,… etc.), and specify communication Mode (Half Duplex, Full Duplex) NOTE: All the functions in the three layers Above Happens before the Data Leaves the Computer to the Network. All this handles by Windows or Linux …etc. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 4 Layer 4 Transport Layer: 1. Transport Layer Describe how the Data to be send. 2. Well Known Services (Port Numbers) • Transport Layer Describe how the Data to be send. You have the Ability to Send Data Reliable or Un-Reliable, Reliable means when sending a packet it’s acknowledged by the Received Computer and sends back a Packet as OK if it’s received, otherwise the data will be sent Again. • For unreliable its used for Real-Time Application as VOIP or Video over IP or Online-Games, if a packet is lost while you see a streaming video you will see a glitch or some color missing as a tiny Pixel in the Video Who Cares or that, Also if Video Over IP used Reliable Connection it will be a Pain as if the packet is lost while streaming the Screen will Freeze and the Missing Pixel Color will be fixed and appear again and the movie will move over again and that is un-logic. Types of Protocol: 1. TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) – (Connection Oriented Protocol) 2. UDP (User Datagram Protocol) – (Connectionless Datagram protocol) • Port Numbers does designate what type of service need to be accessed, Lets Say we have a client and a Server, the client needs to surf a web, so the internet-explorer has to grab the page from the server, but the server needs to knows what type of data needs to send to the client cause if the server work as (Web-Server & Mail-Server), it will get confused so it need to assure that the client is asking for webpage not requesting email, this is done by the Ports Number Layer 3 Network Layer: 1. Provides Logical Addressing. 2. Finds the Best Path to a Destination. Layer 2 Data Link Layer: 1. Provide Physical Address which is known as MAC Address, this is an address that is burned physically on the NIC. That is used for Communicating just in your Local Network. 2. Ensures DATA ERROR FREE, means if the frame is received on the other side it make sure that the data has not been changed in the Frame from the moment it sent to the moment it get their. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 5 Layer 1 Physical Layer: 1. Provide Access to the Cable, Electrical Signals (Ones & Zero). Live Example: 1. Now Pc want to access www.cisco.com through Internet Explorer, now behind the scenes that computer sends a message to the DNS server (Domain name Service) and what that does is transform the www.cisco.com into IP Address. 2. The Application layer says to the server send me a web Page and that what the Internet Explorer request. 3. The Presentation layer Package that request into a Format HTTP. 4. It passes then the package to the Session layer and the Session layer says ok this is a Specific Request for www.cisco.com and will make it in its own Session, so as not to get Confused from all the Data coming back in, as maybe the local PC may Downloading from ITunes and watching online Video all at the Same Time, so you don’t want that Computer to get Confused by all this Data Coming in so it has to be logically Separated, so that what the Session layer Does. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 6 5. a. Then Passes it Down to the Transport layer, There are two Choices here, the choices for Reliability, in TCP/IP terms that’s the decision Between TCP and UDP, So our Web Browser is hard coded by the people Who made it to use TCP, So that will be the Reliable connection, so what Reliable means ? it means that when I send that request to www.cisco.com the Cisco Servers is Going to receive this and get it and is required by the TCP protocol to send back an Acknowledgement saying “Hey I have Received your Request, Its processing and hang on I will handle you that page” b. The Second Decision is Hard coding of Source and destination port numbers, meaning that the transport layer is partner with the Session layer assisting in keeping everything is Separate, we r using a web-browser and that web browser is sending a message to the web server, but what if that web server is not a just a web-server alone it may be also an email server and database server all in one, so we need to be sure that the message coming from the Internet Explorer get sends to web Server Application and I make sure its send to the web-server and not to the Email Server or database Server, so in order to do that, the Web browser is hard coded that the Destination Port number is Port 80 which is well known Port numbers for HTTP, that’s how I make sure to go to the right Destinations, now about the source port numbers its used to Distinguish that web browser application from everything else running on my Computer, so the Server when it reply back it will use the source port Number from the PC as its Destination and its Source port number will be 80, so as to be assure to reply back to this Web browser Application and not to other browser Application. As you might see in the following Picture: When I open two command prompt and write in it C:\>ftp ftp.cisco.com and in the other window command the same C:\>ftp ftp.cisco.com, then I open a third Window command prompt and write C:\>netstat you will find as in the Picture above all Open Ports on Your Computer, if you watched carefully last Two lines they are the Two Windows we opened and write Ftp Command first Column is the protocol Used which is TCP second is the Local Address and the Source Port, After That the Destination Address and the Destination Port which is written as ftp instead of port 21 (for Ftp port) By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 7 6. Now at IP Layer it will add the Source and Destination IP Address (The Original Source IP Address and the Final Destination IP Address). This IP Address will not Change during Traveling across the entire Network. 7. Moving Down to data Link layer, where the Physical Address is added (Source and Destination MAC Address). This MAC Address will change ALL the Time. So the Source Mac Address is the Computer on the Network and the Destination Mac Address is the Router. So the Switch will route the Frame to the Router cause it Understand Layer 2 and it forward it to Router, now the Router will Get the Frame and look into It and find the Destination Mac Address is him, then it looks up one Layer and find that the Destination IP Address is not for him so it will Package it and send it to the Next Hop (Next router) and So On till it Reaches the Router Destination, then to the Server Cisco www.cisco.com . By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 8 TCP/IP MODEL: AS you can see for TCP/IP model on the right side is what typically used today in Communication, Lot of people Call that DOD the (Department of Defense) Model. Now OSI model describes how network communicate but TCP/IP Describes how it Actually Happens that the Protocol how we use Today, what we need to understand that the TCP/IP is not just One Protocol but it’s a Team of protocol that Makes Network Communication to Happen. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 9 IP Address Format: Defines the Source and Destination of the IP Address, They are 4 Numbers or 4 Octet each number from 0-255, and they are always Combined with Subnet Mask and a typically Default GW. The Subnet Mask Identifies the Network and the Host in the IP Address. Understanding the Two Address Concept: 1. Now you have a Home network with Two Computer at the Left where their address is 10.1.1.10 and 10.1.1.11 connecting to a Router as its Gateway, and the Subnet mask in that Network is 255.255.255.0, where the first three octets is the Network Address and the last Octet is the Host Address. 2. Now 10.1.1.10 need to share some files to 10.1.1.11, now what PC 10.1.1.10 does is that it compares its IP Address with the Destination Address 10.1.1.11 by using the Subnet Mask and find out that the network address for both computer is 10.1.1 and find Out that its on the Same Network Now the computer will Yell by using ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) which is a broadcast message, all computer on the same network will receive this broadcast message, the computer that have this IP address will reply back with his MAC Address. Now the Sending PC 10.1.1.10 will send the File but not by Sending it to IP Address 10.1.1.11 but through the MAC Address of the Destination PC. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 10 1. Another Scenario if PC 10.1.1.10 need to Store the File on the FTP Server which it’s IP is 10.5.5.100. 2. Now the PC looks at its IP Address and on its Subnet Mask and find out that the Destination IP Address is Not on the Same Network, So immediately that means that I cant use my ARP Protocol, cause ARP protocol is a Broadcast Message and one of the Functions offered by the Router that it Doesn’t bypass the Broadcast Message, it block it. 3. Now every computer has a Default GW IP Address, it uses this IP whenever it needs to get outside its own Network. 4. Now the PC 10.1.1.10 will ARP again to know the MAC Address of its Default GW, so the GW will Reply Back by its own MAC Address 5. Now the Sending PC will the Send the Data with Source IP address 10.1.1.10 and Destination IP Address which is for the server 10.5.5.100, also the Source MAC Address will be the PC and the Destination MAC Address will be the Router MAC Address. 6. When the Router Receives the Frame it will notice that the Destination MAC Address is him, and when it look at the Destination IP Address it will realize that its not for him and will realize that this Frame needs to Pass through him to reach some Server on the Road, the Router will see through His Routing Table and find out that its not connected direct to the 10.5.5 Network but I am connected to 10.2.2 Network and my routing table tells me to send it to the next router after me, as they have some way to reach to 10.5.5 Network. 7. When the Next Router Receives the Frame it Tears OFF the entire Data-link Header (Source and Destination MAC Address) and make a New (Source and Destination MAC Address for the Interface on this Line) and so on, NOTICE that the IP Address in the IP header doesn’t Change. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 11 Three usable Classes of Address: CISCO Advice that you shouldn’t go above no more than 500 Host in a Network, so that why we Use Subnet Mask as a Subnetting. Class A: 1 – 126 Class B: 128 – 191 Class C: 192 – 223 Three Ranges for Private Networks: Class A: 10.0.0.0 – 10.255.255.255 Class B: 172.16.0.0 – 172.31.255.255 Class C: 192.168.0.0 – 192.168.255.255 Also 127.x.x.x Loop Back Range used for Testing that the PC has the TCP/IP protocol stack installed correctly. Also 169.254.x.x Auto Configuration Range. That is when a Host can’t get an IP address from a DHCP Server, so it assign it self this IP. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 12 Basic TCP/IP: Difference between TCP & UDP: As we said before when the Data reaches the Transport Layer, it has to choose between TCP or UDP, i.e.: Reliable or Unreliable Connection • TCP: o o o • TCP is a Reliable; it builds the connection, so if a computer wants to communicate to a web server, it would say HELLO Web Server, and I would like to communicate with you, the web server responds and says I see your requests let’s start communicating and that consider building a session. It Uses Sequence Numbers, that means all the packet of data is sent out has tagged on it by a Sequence number, this is useful cause when a PC send a Stream of DATA, the DATA Packets may go on Different Route so as the server to be able to bind them all together it needs the Sequence Number to do the process Reliable, every thing you send is acknowledged back. UDP: UDP is unreliable, meaning it’s a connectionless I never introduce my self to the device I’ am sending too, I just say here is the data and just send them to the Destination address, and the destination address may be not ready to receive that data so it may be drop-it but we never not know about it because UDP is a connectionless. UDP Protocol is used in real Time Application or Real Time Streaming Video cause there is no Delay as VOIP, Online Games. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 13 How TCP and UDP Work: UDP: In UDP PC 10.1.1.1 just sends the Data to the Server and the Server Process the Data with out any Acknowledgment. TCP: 1. Starts a Session with the Device that is going to communicate with by sending a SYN (Synchronization) packet to the Server which means the PC needs to start a Conversation with the Server. 2. The Server Receives that and Reply back with a Packet name SYN-ACK, which Means that the Server is ready to start Conversation with the PC and the ACK is acknowledged for receiving the Previous SYN Packet. 3. PC will send ACK Packet to the Server replying on the SYN-ACK Packet that it was Received. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 14 4. After the Three Way Handshake is Completed the PC will Starts to Send the DATA or Receives the DATA from the Communicating Server. 5. As you see in the Above Picture, the PC will start Counting at Sequence Number 10 (Just a random Number the PC pick it up), and send it to the Server. 6. The Server will reply back with the requested DATA and with Sequence Number 5 (Just a random Number the Server pick it up), and with ACK 11 which means that it acknowledge the PC that the Server has received the DATA of Sequence number 10 and good to go for Receiving the Next Packet 7. Now The PC will reply back with the requested DATA and with Sequence Number 11 (Just a random Number the Server pick it up), and with ACK 6 which means that it acknowledge the Server that the PC has received the DATA of Sequence number 5 and good to go for Receiving the Next Packet NOTE: Now if one of the Packet is Lost and didn’t reach the other Side (The Destination PC or Server), the Destination Host will Resend the Packet Again. Say an Example in the Previous Picture, if PC send the Sequence number 11 but Didn’t Reach the Server, The Server have a time counting down that if the packet didn’t receive before the time goes out it will resend the packet to the PC with the ACK Number 11 and the Sequence number 6 so as the PC resend again the Packet with Sequence number 11 and with ACK 6. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 15 TCP Windowing: As we said before sending some data and getting the ACK, with each data has to be send there is ACK in front of it. This is not Efficient because their will be a lack of time for each packet to be send it have to wait for ACK so as to send the Next One. Its just like when I am talking to you and you have to ACK every Word I said, its bit annoying HUH!! So to resolve that, they just introduce a concept called TCP Windowing, what this does is it increase how much data is Sent based on how reliable the connection is, so here is the idea the First Piece of DATA will be sent and ACK will be Replied Back, so it will increase the Rate of Sending and that is called SLIDING WINDOWS and ACK will be Replied back and So on till a Packet is Dropped and when that happens it will resend that Packet again and at the Same time it will reduce the Window Size a little bit, See Below Picture for Details. In Real World the Sequence Number actually represents how many Bytes the Computer is Sending at Once. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 16 Understanding Port Numbers: In Previous we talked about the first Half of Transport Layer Communication whether the application will choose Reliable or Unreliable, Now in this Second Half we will talk about separating the Data Stream coming in to so as to Distinguish what service we are trying to access or what Windows the Server trying to reply back into. Every time an Application tries to Communicate across the Network, it must not only choose the type of protocol (TCP or UDP) but it also has to generate some port numbers what destination port number it would like to go to and what source port it would like to come from. 1. Lets Say PC on the left would like to communicate with Web Server on the right. It will use HTTP protocol that has a Well Known Port Number which is port 80 and uses TCP Protocol (Reliable). 2. When it sends the message to the WEB Server, that server will receive it on TCP Port 80. Now the way that is Actually Designated and you see it in most of time is the Destination is written as 10.5.1.100:80 by combining the Port Number with the IP Address this TERM are called SOCKET. Meaning you have opened a Socket or a Session over that Web Server, this is the destination Socket you r going to. 3. Now the PC also generates a Source Port Number to allow Traffic to be received on the Host. For Example when I go to Web Site it will goes to Port 80 and will reply back to the Source Port Number that is generated (its Dynamic Port Number Generated by Windows) By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 17 Now Well know Port Numbers Considered Reserved by IANA from (0-1023), and can’t be used by any one, it’s only used for well know Services. So you have to choose from the other ports numbers that are through 65536 Port Numbers. As you observe above in this Picture you will find that TCP has Ports from (0-65535) and UDP has from (0-65535) that means if TCP is working on port 900 that doesn’t means it’s the same service working on UDP at port 900. Also the port numbers written above in the pictures should be memorized. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 18 Well Known TCP Ports: Port Number 21 Name FTP 22 23 SSH Telnet 25 SMTP 53 DNS 80 HTTP 110 POP3 443 HTTPS Description File Transfer Protocol used for Transferring Files or uploading files to the FTP Server. Encrypted Version of Telnet. Clear Text in Telnet no Encryption is Used. Simple mail Transfer Protocol for sending and receiving Emails. That what Email Server Use. Resolves Name to IP Address that what DNS Server do. Web Server. Post Office Protocol, which is used when you want to receive an Email, when you open your Outlook and downloaded it from Email Server. Secure Web Surfing. UDP Well Known PORTS: Port Number 53 69 By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Name DNS Client TFTP Description Resolves Name to IP Address. Trivial File Transfer Protocol, that what we use to send or receive file to or from our Cisco Devices Page 19 The Tale of Two Packets: Now lets Start, BOB is our local Packet, meaning he is a packet originates on a network Segment and stays on that network Segment, this Network is on the Left Side. Now Zooming on the Local Network: • Lets Assume that the Traffic is going from 172.10.1.20 to 172.10.1.30, now BOB Represents a Ping Packet, so we ping to 172.10.1.30 from command prompt opened at 172.10.1.20. • The Host 172.10.1.20 will look at the address you r trying to ping, and compare it with his address and find out it’s the same Network. So I don’t need to access the Router, also I need the MAC Address of that Computer because I ‘am going to send it to a Switch. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 20 • Now the PC will use ARP Protocol to know the Destination Host MAC Address from its IP. It’s a Broad Cast message to every one on the Network to tell to every one that I need the MAC Address for the Host who has an IP 172.10.1.30. • Now every body on that Network will get that Message, even the Router will get it but it will not by pass the Broadcast Message. • Now the Host with IP 172.10.1.30 will receive it and will reply back Directly to 172.10.1.20 his MAC Address • Now the Host 172.10.1.20 knows the Destination MAC Address, it will Generate the Ping Packet as Follow: First the Ping DATA, then the Source and Destination PORT Numbers, then the Source and Destination IP Address, and finally the Source and Destination MAC Address. It will send that Frame to a Switch, the Switch Receives it and reroute the Frame to the Port where the PC 172.10.1.30 is plugged in. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 21 The Story of Sally is different in the way than BOB. Sally is a Ping Packet as a BOB, but it’s from 172.10.1.20 to the Server 192.168.0.100, now we will zoom in on the Local Network for Details: • Assuming the same Subnet Mask in that Network 255.255.255.0 • The PC will compare the Destination IP address with its local address and find out that it’s on another Network, as soon as it realize the both IP is on the Same Network so it will send an ARP Message to the Default GW to know the MAC Address for the Router, because it assume that the Router have a good idea to know were that Destination IP Address is Located, and that what Router do it knows IP Address well and help you out where IP address are. Now the Host 172.10.1.20 knows the Destination MAC Address, it will Generate the Ping Packet as Follow: • By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 22 o o • First the Ping DATA, then the Source and Destination PORT Numbers, then the Source and Destination IP Address, and finally the Source and Destination MAC Address. It will send that Frame to a Switch, the Switch Receives it and reroute the Frame to the Port where the Router is plugged in. Now the Router will access the Frame and tear it off the MAC Address Header after checking the Destination MAC Address and find out the Destination IP Address and Ask himself is he trying to access me or Trying to Pass through me, and figure it out that its trying to pass through me. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 23 Lets look at the Routers Network in Zooming: • The Router on the Left Hand Side represent the Router PC Default GW, now it looks on the Routing Table and find out that its not Plugged in to the Network 192.168.0.0, but my Routing Table Says to me that I must send the Packet to the Router 10.10.1.2, because that Router has the Ability to get me to the network 192.168.0.0 • So what it does here is that the Router 172.10.1.1 bring the Ping Data Packet and put on the Header TCP, and the Same source and destination Port Numbers (its not Changed) and then the Same Source and Destination IP Address (its not Changed), for the MAC Address they are changed as the Source Mac Address will be the Router (3212) (the last 4 Digit) and the Destination MAC Address will be the Router (3DAA) (the last 4 Digit), because that what allows the Packet to travel across the Serial Link between the Two Routers, and so on. • As Soon the Last Router receives this Packet it will looks at the Source and Destination IP Address, and find out that it’s connected to the Network 192.168.0.0. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 24 • Then it will Strip off the Source and Destination MAC Address as the Source MAC Address will be the Router (3211) (the last 4 Digit), and then going to ARP to find out the MAC Address for the IP Address 192.168.0.100. • After knowing the Destination MAC Address it builds the Packet with all the information in it as Protocol TCP and Source, Destination Port Numbers, Source and Destination IP Address and the Source and Destination MAC Address. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 25 Welcome to ETHERNET: • At Data Link its Divided in to two Sub layers: Mac Address & LLC (Logical link Control), what LLC does is Pick what direction it will go to the Network Layer, cause there is Many Network Layer Protocol as (IP Address, IPX/SPX), so what does this field do is to advice the PC or the Host as it De-capsulate up to the Network layer which Protocol it Should get it from the Network Layer. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 26 CSMA/CD (Carrier Sense Multiple Access Collision Detection): Every thing works in the Ethernet Worlds (NIC, Switch) has to comply with some rules (CSMA/CD). Carrier: The Network Signal, (the Signal that is crossed over the Network) Sense: The Ability of All PC connected to the Same Network to detect any Carrier on that Network. Multiple Access: All Devices have an Equal Access, means all Ethernet Network Devices have the Ability to send whenever there is no carrier on the Network, No Priority. Collision: Two Devices Send at the Same time ad Collision happens, means two Devices Sense the Line and find out no Signal and they assumed that no one is Sending so they Send at the both Time. Detection: How the Computer Handles the Collision when its Happens. Three Different Types in Communication in Ethernet: UNICAST: • • • UNICAST Message is One PC sends a Message to Another PC (One to One). Broadcast Message is One PC send a Message to all PCs on the Network means the Message will be out on all the Ports of the Switch except the Port that it received from it the Original Message. Multicast Message is One PC send a Message to A Group of PC on the Network like VLans. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 27 MAC Address: The OFFICAL Explanation: • MAC Address is written in HEX Values from (0 to F) and they are 12 Hexadecimal Characters. • Now every MAC Address is divided in to two half, First 24 Bits identifies the Organization Unique Identifier (OUI), now each Factory registered in the Organization should have a registered range of MAC Address that they can be used by them. • The Second Half is for Vendor Assigned they may use whatever they want must every MAC Address must be Unique. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 28 Cabling Standards: T568-B is the Most Common Type of Cables is used this Day, (Strip Orange, Orange, Strip Green, Blue, Strip Blue, Green, Strip Brown, Brown). Notes: On this Standards we mentioned above it goes for 100 Meters, but you may Create your Own Standards as example (Strip Orange, Orange, Strip Green, Green, Strip Blue, Blue, Strip Brown, Brown), but it will not go Much Longer as the Standards one go because they are arranged inside to Prevent the interference of the Magnetic Field that is moved across the wire, now if you make your own Standards the Interference caused by the magnetic Field will rise and make the Signal to be attenuated much more quicker than the Standard one so that why the Length of the signal want travel to 100 meter. • If you noticed that T568-A when its crimpled on one side and on the other Side T568-A you will have a straight through Cable for 100 Meter. • If you have T568-B when its crimpled on one side and on the other Side T568-B you will have a straight through Cable for 100 Meter. If you have T568-B when its crimpled on one side and on the other Side T568-A you will have a CROSS-OVER Cable for 100 Meter. Now when the Straight through cable is used and when the Cross over Cable is used. • By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 29 By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 30 LAN Switches: The problem with Shared CSMA/CD: • In Hub that is used to connect Networks, it doesn’t matter what type of communication it will be used (Unicast, Multicast, Broadcast) all it does is that it generate the Signal and broadcast it all the other Ports. • Hub has One Collision Domain (How many Devices can send at the Same Time). • Hub has one broadcast Domain. Those mentioned points above are the Problem for the Shared CSMA/CD, as if more than 30 PC is connected to a Hub, more than one device is listening to the line at the same Time, now if a collision happens the PCs that were sending will detect the collision and will send out a signal known as a JAM Signal, this signal what it does is it reaches to all the Devices connected to the HUB and says to all PCs to Stops Sending any data at this moment resend their DATA Again after a Random Time. The more Devices are connected the more chances we may have a Collision again and again and again. As the technologies become more advanced, there is a device called a Bridge or a Transparent Bridge. What the function of the Bridge was is to learn MAC Address. By Adding a Bridge I have Effectively Divide my Network in to two Collision Domain. The Problem with the Bridge that it was Very Slow, it Learns MAC Address and Compare it in its Table and …..Etc. it was Software Based and it was slowing down the Communication. To solve this problem a Switch is Invented, Every Single port in the Switch is a Collision Domain, not only that but also each port has the ability to Communicate in a FULL-Duplex Communication, what that means that it can send and receive at the Same Time, as when you buy NIC 100 Mbps its not 100 Mbps its 200 Mbps cause it receives 100 Mbps and Send at 100 Mbps, so the rate that it says 100 Mbps when you buy a NIC its rated as a Half Duplex. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 31 Switches Learn Much Faster in MAC Address Table than a Bridge does because its not a Software Based any more but its Hardware and its actually know as an ASIC (Application Specific Integrated Circuitry), it was a Chip created by IBM By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 32 How does Switch Switches: 1. When a Switch boots up, it has its CAM (Content Accessible Memory) Table at the beginning is Empty, 2. Traffic has to be sent before the Switch becomes intelligent, lets say PC (A) want to send to PC (B), PC (A) knows IP Address Destination but doesn’t know MAC Address so PC (A) will send ARP. 3. All PC will get the ARP message as it’s a broadcast message and the switch is a 1 broadcast domain, inside the ARP Message is the Source MAC Address of PC A and the switch have learn that PC (A) is on Port 1. 4. When PC (B) gets the ARP Message it will respond back to PC (A) with its MAC Address and the switch have now learned PC (B) MAC Address on Port 2. 5. All other MAC Address will be learned by the Same Concepts in about 15 Seconds for all Network. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 33 Working with Cisco Switch IOS: IOS stands for (Internet work Operating System); it’s the Operating system for Cisco Devices. Connecting to Cisco Devices: 1. Get a Console Cable. 2. Plug the Serial End in to the Back of your PC. 3. Plug the RJ 45 End in to the Console port of the Switch. 4. Get a Terminal Program as a Hyper Terminal which comes with windows but from experienced people says that this Terminal is the Worst as it have a lot of Bugs, the Recommended Programs are as Follows: a) TeraTerm (Download from Google its free) b) Minicom c) SecureCRT 5. After Setup the Program, now you just have to set it up to connect via COM Port with: a) Baud Rate: 9600 b) Data bits: 8 c) Parity: None d) Stop Bits: 1 e) Flow Control: None 6. Now you r Connected. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 34 Understanding IOS Command Mode: • User Mode is Very Basic Monitoring mode (Ping, Telnet to another Switch) • Privilege Mode to enter that mode you should type enable in the User mode, on this mode you can view anything on Cisco Switch view the Packet incoming and outgoing view the passwords, view the Configuration but you cant configure on that mode. • Global Configuration mode is used to make the necessary Configuration on the Switch, by typing conf t in the Privilege mode. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 35 Understanding the Physical Indicator in Switch: No we will talk about the LED’s on the Cisco Switch Devices: 1. System LED: it’s the System Status, when the Power is turned On it will be Blinking Green as its booting up, and become solid green when its booted, if the Light is Amber, then the switch is broken down. 2. RPS (Redundant Power Supply): Most of the Switches have a two power Supply installed inside of them, so if one is failed you have the other working one. Now we have a mode button that is used to switch between different modes, we have four Led's as four Modes as the following (STAT, UTIL, DUPLEX, and SPEED): I. STAT: it’s the Default and it shows the Status of the Port, so if the port is connected to a PC the LED will light Green indicating the Port is connected. II. UTIL: Actually it indicate for utilization of how much traffic is passing through the Switch, it shows in the matter of LED’s as if its an Equalizer of your audio Device, if the Network Utilization is 50 % it may turn the 50% of the LED’s if more or less the LED’s will be the Same. III. DUPLEX: LED will light up on the Port if that port is configured into a Full Duplex, if its not light then its in a Half Duplex. IV. SPEED: LED will light up on the Port if that port is 100Mbps, if its not light then its in a 10Mbps. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 36 Performing Initial Configuration for Switch: When powering up the Switch it will starts loading the IOS from the Flash Memory. See below: After Loading the IOS and checking its Hardware it will ask: As from Experienced People and from Real life World 99% the Answer is always NO. Because once you know how to configure the Switch from the Console you will not need to configure it through a Wizard. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 37 1. First thing you do for configuring a Switch on a New Brand Device is to set a Name. We will change the default name into CBT Switch Of Course the name of the Switch should be named logically which means the Location of the Switch will be its name. 2. Second thing to do is to give the Switch an IP Address in order to Telnet on it. In order to give a Switch an IP Address you must have at least a Basic Understanding on VLAN (Virtual LAN's), what it does is that it divides your local network from one broadcast domain into multiple Broadcast Domains on the same device. So why we are talking on VLAN cause when we assign the Switch with an IP Address we need to go to VLAN Interface, cause the Switch ports is not configured by IP address but the VLAN interface is configured. But we don’t know which VLAN we are on or we don’t know how to create one right now, but by Default the Switches Creates its Default VLAN 1 whether you need it or not, all the Port on the Switch is on VLAN1 by Default, that’s why everything works with out any Configuration on the switch Interfaces, any port can communicate with the other port cause every interfaces is a member on VLAN1 by default. So to configure the IP Address of the VLAN1 do the following. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 38 Now your Switch has an IP Address. Now we need to check what we have done, so we will type the following. As you can see on the Marked Green that Vlan1 interface is administratively is down & Line Protocol is down, • • Administratively is down mean the Physical Layer of Vlan1 is Down Line Protocol is down represents the Data Link State. Note any time you see administratively is down means that the interface is SHUTDOWN, so to enable it type No Shutdown. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 39 Now we need to assign a Default GW to the Switch in order to get out of the Network and be able to communicate with other network. Now Final Step is we need to save the configuration we have made on the Switch. Every thing we have done till now is saved in RAM. To do so we must save the Configuration to NVRAM. To check what we have done type the following. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 40 Configuring Switch Security: • If we don’t set a Telnet Password on Cisco Switch it will not allow us to connect to the Switch through telnet. And gives the following Message. • To secure the Switch we need to setup some Passwords, on the first Use for the Switch there is no password is configured so it needs to be setup. First we will setup a Password to protect the Privilege mode from accessing. But there is a disadvantage in setting this type of password because this password is not encrypted its written in a clear text, as you can see in the following: By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 41 So to make the Password Encrypted and More Secure, we do the Following: Now when we show the running Configuration, the password is written encrypted • Now when we exit from this mode and return to the User Mode and try to enter the privilege Mode again it ill ask for the Password, when you enter the Unencrypted Password it will not accept it but when you enter the Secret Password (Encrypted one) we have entered here which is Cisco1 it will accept it, because the Enable Secret Overwrite the Enable Password. • Why do the enable password exist while the enable secret overwrite it, because a lot of people configure CISCO Devices in a fast Way or on a fly this is done by after making the initial Configuration on the Cisco Device, and then you make the Show run Command after that take a Copy Starting at (! Mark) as shown below in the figure till the End of the Show Run and Paste it in a Notepad Program. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 42 • So now you have a Backup and a Basic Configuration you may use on any Cisco Switch Device, that you may take it and paste it to any device you may want to configure it, by going to the Configuration Mode and just PASTE. • So if you have OLD Version of IOS that only uses enable Password, and not enable Secret, so when you copy the Configuration file and paste it on that old IOS Switch it will accept the enable password. To enable a Password on the Console, on the Global Configuration Mode type the Following: As you can see the Password for the Console Port is Cisco. But the Cisco switch does not know that I need to be asked for that Password, so I should write login to ask me or prompt me to enter a Password. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 43 To enable a Password on the Telnet Note: When you enable Telnet you must type login so as to be prompt for it when you access the Switch. • If you set a password for the telnet but didn’t make the login command you will not be able to enter the Switch. • If haven’t entered a password and type no login in the Line terminal Configuration you will enter with no request of password. • If you type a Password and Login you will be prompt for Entering the Password to enter the Switch. Note: After Configuring the Password for Telnet and Console, when you run the Show run command you will find that they are appeared in clear text and not Encrypted. So to encrypt the entire Password and any Password you have entered on Cisco Device with only one command you type the following: By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 44 Now when you show run you will find the Password for Telnet and Console are Encrypted by level 7 Encryption: But don’t get false Sensitive of Security as this Password is Level 7 that can be decrypted easy by any program lets see how: We will go to Google and Type the following: At the Search result you will choose first link on the Search Page Result: After you enter this Site you will take a copy of the Encrypted Password and Paste it in the Box and Click Crack Password. Now you have seen the Password we have entered for the Telnet is in a Clear Text. The Reason Cisco choose Level 7 Encryption is that it doesn’t add much processor or overhead as type level 5 encryption for the Privilege mode, but at least it doesn’t appear in a clear text, for security who show the running config. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 45 Banner Command: Banner is used to show a Message on the Cisco Devices. First Go to Configuration Mode and type banner and? Mark • You will see a many types of command under Banner, but what we will use is the Login & the motd (Message of the Day). • Login appears when you connect the Cisco Device by VTY Lines even before you type the Username and Password. • Motd appears no matter how you connect to the Cisco Device whether by Console or VTY • If you set both if the mode (login, motd) the message of the motd will appear first and then the login message will appear after. Now to set up the motd message lets do the following: • What it means is that after you enter the command banner motd you should type after that any one character on your Keyboard to start after it type the Message and Ending with the Same character you have Entered. • So we will start with [ Symbol as Example and end the message with [ Symbol too. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 46 When we exit the Cisco Devices and login Again, you will find the Following: By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 47 Securing TELNET by (SSH) (Secure Shell): • Telnet is worst protocol used to telnet, the reason is because the data is transferred in a clear text, as there are many free programs is used to analyze the network data and capture it, lets see how its done. • If we have Program for Capturing the Data as example (Wire Shark network Analyzer) its free by the way, and used it for Capturing, you may get the Password you enter. • After you click on Capture and interface you will see the below Picture, having all the Network Card on your PC, just Click Start on the NIC that is Connected to the Cisco Device to start Capturing By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 48 • After that go to Cisco Device and just type some password Commands as enable secret Cisco and then return to the Program and Select Capture and Stop. • You will find here the Packets that are captured, lets see our Telnet packet, look under Protocol Column and Find out Telnet, as Marked in the Upper Photo, and you will find also the Source and Destination IP Address. Click on this Packet and then click on analyze and choose Follow TCP Stream. You will find the Data you have entered in a Pure Text. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 49 The Words here in the Captured are repeating as you see at the first line ccoonnff tt but that is Conf t command, this is due to one for send and one for received from the Device to PC and Vice Versa, so to filter that out you will choose the IP of your Cisco Device to your PC not the Entire conversation. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 50 Now it will Look like the Following: • In summary Telnet is bad as data is captured easily by any Program used for Capturing Packet and will show it in a Clear Text. The Solution for that is using SSH (Secure Shell), its Telnet protocol but is Encrypted. Note in the following Section their will be no explanation in details for SSH but just how to turn it ON as it’s described in Cisco Security Track not in CCNA. • First we go to Configuration Mode and Setup SSH as Following: • In SSH it needs a Username and a Password as you can see above. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 51 • Second thing you do is to assign a Domain Name it’s like a web address (As Cisco.com) because it generates an encryption certificates, in order to generate a Certificates it just has to know where it is. So we can say this certificates belong to CBTSwitch.cbtnuggets.com, Note you can’t use the Default name as Switch or Router for the hostname. • Now we need to Generate Our KEYS by typing the following on the Global Configuration mode crypto key generate RSA • The more stronger the KEY is the more Secure it will be and the more processing for the Device to perform for encryption, so if one access remotely it will take time to access and more processing will be done. • Experienced people choose 1024 Key as its standard strong Encryption KEY size • After that we need to specify what version of SSH to use, so we will use SSH Version 2 (which it’s standard now). • After that we will return to Telnet line and instead of saying telnet is allowed as a protocol, we will say SSH is the protocol to be allowed on Telnet line, this makes Telnet is denied and SSH is enabled. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 52 • If you need to enable both Telnet and SSH you may write the following. • Don’t forget to do the following Command or the SSH won’t work cause this Command make the Secure Telnet (SSH) be able to login by the Username and Password you have created. • Now what you have to do is to use a program that support SSH like TeraTerm and choose to use SSH instead of telnet. • Now when we capture the Packets while telnet by SSH and analyze it we will find that the DATA is Encrypted as following: By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 53 Setting up PORT Security on Switch: It’s a way to lock down on what devices can plug-in to your Switch or how many devices can plug-in to your Switch. On the following command it shows all the IP Address that is connected to the Switch and on which interface. As we see Status is up which means the physical layer is already connected and the line protocol is up that is the data link layer. Now let’s see the following Command This command gives you all the messages that come from the switch from a telnet session or SSH Session, just a status messages for every action is been taken on the switch. Lets for example connected a laptop on fast Ethernet port 5, and see what happens after activating this code, notice from the previous Picture that show all the interfaces on the Switch the Fast Ethernet port5 is down. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 54 You will find that a message appears that some device is connected to Port 5 and its status is up and protocol is up. After that lets see the MAC address of the device that are connected to the Switch, lets write the following command You will find the following: As you see under the Type Column there are two Types (Static, Dynamic), the static type is the MAC address of the Switch itself because it has many Fast Ethernet Ports so Each port has its own MAC Address, but the Dynamic is what the Switch had learned from the connected PC to each Port. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 55 Now what we will do now that we will configure Port 5 in fast Ethernet switch to work only on the MAC address of the Laptop that is 0015.c5af.ea37 1. The Command Switch port mode access is used to hardcode this interface as an access port, access port means that it tell the switch it is connected to another pc or laptop or server or even a router but not connected to another Switch. 2. After doing that I can now enable port Security, by the following command Once I have done that I enabled the Security feature on this port but the switch still want to know what the action to be done after that if the Security is broken. 3. The first thing I do is to set maximum number of devices that can be connected at this port and access it. The reason for doing this is to keep somebody away from plugging multiple devices at this port by using a HUB, or another Switch. So we will configure this port to accept only one Device at a time and to limit multiple devices from being connected by the following Command. . 4. After that we will configure the Switch to take the Violation Action if this Security setting we configures is breached meaning in our configuration now if some one connects multiple PC on this Port. By default the violation of the switch is configured to be Shutdown, and the only ways to switch the shutdown port back to up is to telnet or console through the Switch and enable the port again. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 56 The other two options which are (Protect & Restrict) virtually they do the same thing, meaning if some one attach more than PC on our secure configure port, it will just listen to only one MAC Address and the others MAC Address will be blocked and can’t access the Network. Protect: Just ignore the rest of PC that is trying to connect to the Network (Block them). Restrict: it will ignore the rest of PC trying to connect to the Network and Log it (Record it) when it happens. It means you will get messages on the switch saying (Hey the Port number 5 is tried to be connected by more than one Device, on the Next Section you will find a Counter that will be incremented whenever someone tries to Violate the Security.) Experienced People Highly Suggest to Use Restrict over Protect. Now if we want to say that a certain MAC Address is the only Address will be able to access this port and no one else can access it, we will do the following. From the Above Picture we find that there are two options for choosing what type of MAC address to be entered whether a certain MAC Address or a Dynamic MAC Address learns by the Switch. If we choose to enter a static MAC address it will be a tired job to do, cause if you have a large network and need a certain type of MAC Address to be entered you will spend a whole day to do so. That does why CISCO offered the Sticky command, what it does is that automatically every PC connected to the Switch right now will assign its MAC Address to the Connected Port. Of course you do this action only if you are sure 100% about the connected devices to the switch that they are allowed to enter that Network. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 57 Now we will choose Sticky Command. And we will show the running Configuration to see if the MAC address is Added automatically to the Switch port number 5 or not. As you see from the Previous Picture the MAC address of the Laptop Connected to port 5 is added automatically. That means that port is assigned only to this Mac Address. Now we need to show the Port Security of Fast Ethernet port 5. Let’s Describe each line: • Port Security is enabled. • Port Status: Secure-up, it’s secured and currently in up Status (the UP Status means that the Lab top is Currently Connected to this Port, if its down means nothing is connected to that port), if I have Disconnect the Laptop from the Port we will see the following. • Violation Mode: The Action Will be Taken is Shutdown the Port, if Someone Violate the Security we have done before as Only one MAC Address can be connected at a time and a Specific MAC Address not any MAC Address, it will take the action according to what you have chosen. • Maximum MAC Address: it’s the Total MAC Address that is Allowed to be accessed through this PORT is ONE. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 58 • STICKY MAC ADDRESS: Its counter for how many Sticky MAC Address it has been learnt till now its ONE. • Last Source Address: Its last Source MAC address has been Entered to this Port also it shows from which VLAN it belongs this MAC Address too. • Security Violation Count: This is the Counter we have mentioned before when we were choosing the action to be taken whether to be Protect or Restrict, if we choose Restrict this Counter will count 1 and the LAST Source MAC Address will be shown the MAC Address of the Laptop that tried to violate the Security, but Protect it doesn’t increment the Counter. Lets for Now Violate the Security by entering on this Port with Another Different MAC Address, and see what happens after showing the port security of this Port interface 5. • As you might see the Port Status is turned to be Shutdown. • Last Source MAC Address is the one that violate the Port and it shows it’s from VLAN 1. Now it’s a challenge for you to find out this MAC Address in your Organization. • Security Violation Count is 1 as we said before it will be incremented whenever any different MAC Address is trying to access this port. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 59 Now if I use the following Command to show all the Security Port that has been configured on the Switch, It will show me all the Status of the Security Ports on the Switch: Now if I need to configure Security on a Group of Ports at once, I will do the following. That will configure all the ports from interface 2 to interface 24 at the Same Time, any configuration you will enter will be applied to all this Interfaces. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 60 Optimizing and Troubleshooting Switches: 1. Configuring Speed & Duplex: By Default Every Port on Cisco Switch has the Speed and Duplex are set on AUTO Detection, the problem for this mechanism is old they were design for network card that were created and Manufactured from a year before, so the problem is that some of the time the Auto detect Mechanism will detect incorrectly the Duplex on the Switch port. For Example on the Switch port it may detect that the Duplex is Half Duplex but on the Other Side of the Cable at the PC Network Card its Full Duplex which make a Duplex Mismatch. By the Way all the time the Switch is Able to detect the Speed Correctly of the Cable; it’s the Duplex that Causes the Problem, and it displays error on the Switch Please look at the Following picture. We have plugged in a router on the FE 0/2 on the Switch and this error message appeared because the Duplex of the both Side are Set to AUTO. Ok here is the question if the Duplex is set to AUTO Detect, why this Error has appeared and why it doesn’t fix it?? The answer of that is because the Switch doesn’t really know whether you need to set the cable to half or full duplex, so it says there is a mismatch please tells me what to do. So if anyone on your organization is complaining about a slow in connection in accessing the Webpage and email and etc…, so one of the reasons for that is the Duplex of the Switch port is set to Half Duplex, and to the PC is set to Full Duplex, so the PC is able to send and Receive at the Same Time, and at the Switch side is will be able to send or receive once at a time, so this May happen a Collision. let’s take an example if PC tries to send a data it will be received by the Switch and the Switch will reply back, but PC is configured on Full Duplex so he won’t stay for the Receiving Data to come so as to send the next packet, because it receives and send at the Same Time, so when the PC send the next packet it will collide with the incoming data from the Switch so Collision Happens, and data will be dropped and that what cause a Slow at the client side. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 61 So what we will do is going to Global Configuration mode and Configure this Port that have a Mismatch in Duplex, ok what Mode of Duplex we will configure is it Half Duplex or Full Duplex, Let’s see the following Message Again and Describe it. 1. It says here Duplex Mismatch discovered on fastethernet0/2 this means the Problem is on FE0/2. 2. Not half Duplex this means that port FE0/2 on this switch is not set on Half Duplex. 3. Access Server Ethernet 0 (Half Duplex) this means that it detected the other Side Router name Access Server and its configured as a Half Duplex. So what we will do now is to set the Interface 0/2 into Half Duplex Also we will configure the Speed too on the same interface. Experience people says that AUTO Detect is Succeed in Detecting correctly the speed and Duplex about 90 %, meaning from every 10 Computer there will be one Computer that will Complain. So what is done in Real life is that Servers and Routers and Switches connected to a Switch, their port should be configured manually, so as to be sure that the services applied for this Device is Correct, but for PC just Make it AUTO Detect. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 62 Note: the following tips are for Practical use in real life but its not present in the Exam, but its better to read ANYWAY, you wont lose your time!! Trust me. FIRST TIP: Now if you noticed that while we are typing our command the message generated by the Switches Appears at any time as in the following Picture, and it’s kind of get annoying cause it interrupt what we are typing. So what we will do is the Following, and what it does is that while you are typing your Command and suddenly a line appears generated by the Switch for informing you for something it will not bother you as the command you were typing will not be split but it will be written in a new line let’s see how it’s done and how it looks like: As you see from above picture we have done line Synchronous on Console Port and on Telnet Port. On the following picture you see that while we are typing Show IP Interface brief on the first line the message appeared interrupting what we are typing but while we continue typing its written in a new clean line without any dizzy to us. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 63 SECOND TIP: If you leave your device without any action or any command is written by you for some interval time it will kick you off, and you will need to re-login again to access the device, but that is good for Security, let’s see how we may enter the Interval time, you may configure for Console Port and VTY Port, here in our example we configure the console Port, also configuring the VTY Port is the same. What we have done is that we have configured the idle time to 30 Minutes and 0 Seconds. THIRD TIP: If for by mistake you typed a wrong command in the privilege mode, you will find the following: Immediately what the switch is trying to do is searching the whole network for a device name Flow, but no one is replying back that what is named DOMAIN LOOKUP, so to avoid mistyping, we will do the following. So when you type accidentally name flow in the privilege mode, it will not translate it: By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 64 FOURTH TIP: We can create Alias for the command what that mean, we can create our shortcut command that is related to a real command in the Cisco Device lets See the following: The following Command is little bit longer and is boring to do it every time: So what we will do is that we will create a shortcut command that is equal in typing this long Command. We enter the global Configuration mode and type Alias after that you choose which mode you will make the ALIAS in, the privilege mode is named exec as just what we typed in the previous picture after that enter the SHORTCUT you need then enter the Command that will be related to that Shortcut. As you see just typing the S Letter in the exec mode it will show me the all the interface of the switch as if I typed the Show IP interface brief Also look at the following picture (More Examples): By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 65 SPANNING TREE PROTOCOL (STP): • • • Switches will forward a Broadcast Traffic to all out ports by Design. Spanning Tree Blocks redundancy Links, till the Main link is down, the Spanning Tree protocol will active the redundant link. How it’s DONE?? This will be explained in ICND2 not in ICND1. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 66 TROUBLESHOOTING USING SHOW COMMANDS: Where do you start when things goes wrong? That’s the question we will answer now!! We have three show Commands that gives you a good scope of what really is happening. 1. Show IP interface brief. 2. Show Interface. 3. Show Run. Let’s start with the first Command. If someone is complaining about his port is not access or he has no internet connection, then you type this command and find out what is the problem? As you may observe the Status of port 4 which is the complaining port is administratively shut down which means someone has shut it down so all you have to do is to open the port up. Second thing you find out in the Show IP interface brief, is the Status and the Protocol, if the Status is Down then the Cable is unplugged or it’s a Bad Cable need to be changed, also for the Protocol if it’s down means that the Protocol type communicating with the Switch is changed, like someone had changed the Encapsulation Type. If everything is looking ok from the First Command we will move on to the second Command. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 67 Let’s start with the Second Command Suppose that you found in the first Command that everything is fine and UP on the Status and the protocol, then we will show the details on that interfaces. • You will find a major and a lot of information in the above Picture, on the second line you will see that the FE 0/2 is UP and the line Protocol is UP, also you will find the MAC address of this Port which is named bia (Built In Address), it’s the Static MAC Address which is assigned for this port while Manufacturing. • At the Fifth Line you will find the Reliability, it means how reliable is this interface, 255/255 means it’s a 100 % Reliable, when you start to get error on this interface as example reconnect it and disconnect it this reliability will goes down, Cisco Decide to use the Scale from (1 to 255) as reference to (0 – 100 %) so if its 1 it will be 0% and if its 255 as in our example and in the above Picture it means the reliability for this Port is 100 %. o Also on the Fifth line you will find TXLoad (Related for Sending Data or Transmitting the Data), and RxLoad (Related for Receiving Data), as you see its 1/255 means there is no much traffic on this port whether in Sending or Receiving the data. o From this Information on this Line you might know if someone is trying to get the PORT Down by sending a lot of data to this Port. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 68 • At the Eighth Line you will find that this port is Configured for Half Duplex and Speed at 10 MB/s, also its says that this Port Supports 10/100 Mbps so you may Change the Speed from 10 Mbps to 100 Mbps for improving the speed of the port but if the other side Handle 100 Mbps Speed. • At this Line 16 & 17 you will find that in summary how many bits or packets are sending and receiving from this port per Second. • The Rest of the lines are shown in the following Picture, it’s all the historical perspective on the Switch when it started ON. The First line shows how Many Total Packets are input and how many Total bytes input (Received). o The second Line indicates the number of Broadcast Packets that is generated by the Switch. o If you have the number of Broadcast is more or at least equal or little bit less than the number of the Packets input, this means you have a lot of Broadcast in that Port which slows down the Network, so to know the Percentage of the Broadcast you will divide (Broadcast Packets) by (Input Packet). 14446/17928 = 80 % of the packets are Broadcast, and that is a large Percentage, in Real Life a high Level of Broad Cast is 20%. o If you find the below Picture for a Real Switch in Industry Region you should normally find the input Packets is Quite larger than the Broadcast Packets. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 69 • The following indicates that they are BAD Links, let's describe each. o o Runts, it describes the Packet that it’s TOO Small, meaning it doesn’t have enough information as a real packet does. Giants, it describes the Packet that is TOO Big, meaning its bigger than the packet should be. Runts and Giants Happens cause of the BAD Connection, meaning some interference effects the Data that is passing in the cable as (Neon Lamp, or MICROWAVE), or after all its just a BAD Cable, and the Packets doesn’t pass the CRC Check (that is present in the Tail of the frame at Layer 2). if you find out that (Input errors, CRC, and Frame) are incremented then there is an Interference and you should trace up the Cable and find out were is the Source of the Interference, if there is no interference so you might test another cable it may be the cable is BAD, or if the Cable is Good and its still incrementing, then the NIC in the PC may be its bad or the Switch Port is starting to get BAD. • The following Picture states for the Output packets and Output Bytes which means packets that are sent. o We will talk about Collision and Late Collision from the following Picture. o A Late Collisions Typically Happens if your cable is too long, meaning you start to go 100 Meter beyond the maximum allowed for the Ethernet Cable, and what happens then is that the Packet is send from the PC and travels a long way and it takes too long to arrive, so the sending PC assumes that the Packets Didn’t Arrive cause there were no reply, and Resend the Packet again, so at the Receiving side when the Receiving PC receives the Packet it will send the ACK Packet and after a while it find another Packet comes from the Sending PC which is the same as the first Packet, that’s name a Late Collision. So if you find late Collision then it means that the Cable is too long or there are too many Switches in between those two PC. o Collision May Happens if there is a Duplex Mismatch between this port and another port. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 70 Let’s start with the Third Command Show Run Command shows you what actually the configuration of your Switches is, so if there is something wrong in the configuration so its you who have types it so its better to fix it, as show run is the easiest way to figure out the problem were it is. We have discussed show run before so it’s not necessary to describe it again!! By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 71 Understanding Wireless Network • Types of Wireless Network: 1. Personal Area Network (PAN) A PAN is typically a small Network for few meters, as Bluetooth Head Set, or Wireless Mouse. 2. Local Area Network (LAN) It supports the LAN in wireless Media. 3. Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) It’s used for Point to point Bridges, with distance 10 Miles Away, it’s very useful for transmitting DATA between Offices and cheaper more than expensive Lines between the offices. 4. Wide Area Network (WAN): Its Technology called Cellular Network, its one of the Technology that has been increasing in usage in daily life, as IPOD Mobile phone that uses the WAP Portals through WAN Technology that supports higher speed. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 72 Wireless LAN Facts: • Wireless Access point communicates like a HUB, which means that all devices connected to the Wireless network have the Same Shared SIGNAL & Half Duplex. Meaning the more devices connected to the wireless network the less Bandwidth will be distributed on those connected Devices. • Wireless network uses un-licensed Band of Radio Frequency, meaning that those frequencies may be used by any one without being judged, on the other side Licensed Band of frequency can’t be used and it’s Illegal to be used, unless you pay for it. • Wireless is a physical and Data link Standard, it’s the same concept we understand before, as wireless network has an IP Address and MAC Address but just the way of connection is a little bit different from a cable to a Wireless. • Wireless network uses CSMA/CA instead of CSMA/CD, meaning Wireless Network uses (Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Avoidance instead of Collision Detection). 1. We said before in Collision Detection the devices on the network wait till the line is free from being used and it sends its DATA, now if you have two devices senses the line at the same time and send their Data at the same time you will have a Collision and they can detect that and resend the DATA. 2. In Collision Avoidance, it doesn’t have any detection mechanism, means that it doesn’t sense for a collision when it happens as the signal collide and vanish in the air. So in Collision Avoidance, what happens is before the device sends its Data, it says first I' am ready to send, and wait the reply from the Access point to say you are ready to send your Data. That what happens in wireless connection and we are sure that no collision is happened. • Wireless Network is Easy to be interfered, by any mean of external factors. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 73 Unlicensed Frequencies: • • • 900 MHZ, Range: 902 - 928 2.4 GHZ, Range: 2.4 – 2.483 5 GHZ, Range: 5.15 – 5.35 Understanding RF (Radio Frequency): • RF Waves are absorbed (Passing through walls) or Reflected (By Metals). • Higher Data Rates have Shorter Ranges, meaning the More Speed you uses the closer you need to be to that wireless Access Point, the Further I move from the Access Point the Lower Speed I get. • Higher Frequencies of RF have Higher Data Rates as we moved to 900 MHZ, to 2.4 GHZ, to 5 GHZ, the Data rates will increases (the more Speed you will get). • Higher Frequencies of RF have Shorter Range means (Shorter distance). Now what that means if I have two access points working on 2.4 GHZ and 5.8 GHZ, the ones that works on 2.4 GHZ has a larger Distance support than 5.8 GHZ it do, also a higher data rate will be high and best if you were close to the access point rather than away from the access point. The 802.11 Lineup: • 802.11 B: • Official as of September 1999 and work at range 2.4 GHZ. Up to 11 Mbps (1, 2, 5.5, 11 Data Rates) MOST POPULAR STANDARDS. Three Clean Channels. 802.11 A: Official as of September 1999 and work at range 5.8 GHZ. Up to 54 Mbps NOT CROSS COMPATIBLE WITH 802.11B/G as it uses 5.8 GHZ 12 TO 23 Clean Channels. Now 802.11B succeeded on 802.11A also they have been officially been used at the same time and 802.11A has More Data Rates and More Clean Channels than 802.11B but the Main Difference is that 802.11A is Not Compatible, means you need a specific Equipment or Specific Network Card to work on this Standard cause it works on 5.8GHZ, also 802.11A Network Card was not available as much as Network Card for 802.11B at that time of Release, so that what makes 802.11B to be succeeded. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 74 • 802.11 G: Official as of June 2003 and work at range 2.4 GHZ. Backward Compatible with 802.11B Up to 54Mbps (12 Data Rates) Three Clean Channels, (cause they are still operating in the range 2.4 GHz) That why 802.11G remain Popular cause it uses the Same Range as 802.11B (2.4GHZ) so you needn’t to buy new Equipment. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 75 Understanding Wireless Channels: Now we will talk about the Channels Concept, 802.11B/G have Three Different Clean Channels that you are able to use, Channels are Ranges of Frequencies. 802.11B/G Operates at 2.4 GHZ that Doesn’t mean it consume all the Frequencies when its Operating but no it just consume a Section of this Range this Section is Called Channel. If you setup the Access Point for the 802.11B/G you will find 11 Channels, and you will say I may use any Channel as I have 11 a channels, but that’s not true cause if you look at the figure below you will find out that the 11 channels all are overlapped means each channel has its own color in the figure below which starts and ends with its own Frequency so as example channel1 (starts at a Frequency and End at another Frequency) is overlapped with Channels 2, 3, 4, 5 as you see from their colors they all intersects. What that means if I have an access point and my neighbor decides to set up an access point and you choose channel1 and he uses channel2 those two access points will end up interfering with each other, and the same goes for Channel3, 4, and 5 all those channels overlap with each other. The Solution is to choose Channels that doesn’t interferes with the other channels and that what we do here, Channel1, Channel6 and Channel11 you see them written in bold and in the Picture they doesn’t interfere with each other, that’s the three clean Channels we can use. In 802.11A you may use up to 23 Different Channels that are considered Clean and that is much better (in the below picture it doesn’t show all the 23 Channels). The main Advantage in 802.11A is that it gives you more flexibility when you have a company or a Department Complex that when all the channels are used in 802.11B/G you convert to 802.11A and definitely you will find free channels to use and away from the interference. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 76 Designing your Wireless Coverage Wireless Access Point has a Range about 300 ft, without any obstacles in the way, cause if there is obstacles the Range will be affected and will be shorter. So to design the wireless coverage in your company you need to not to overlap between channels. Look at the figure below. As you notice each cell with different color represent the Channel, as you might see channel 1, 6, and 11 are being used and well placed. The Power Over Wireless World: The following are the Organizations that manage the Standards for the Wireless Networks. • ITU-R (International Telecommunication Union- Radio Communication Sector), they used to regulate the Radio Frequencies used for wireless Transmission, means they specify the Bands of frequencies and they specify the Unlicensed Frequencies, they are the one who says Wireless networking will uses this Ranges and This Channels. • IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineer), Maintain the 802.11 Wireless Transmission Standards, as 802.11A/B/G/N, just Standards not the Frequencies. • WIFI Alliances, Insures Certified Interoperability between 802.11 Wireless Vendors, what that means is when I buy a NIC of specific Vendor as (Linksys) and connect it with Cisco Wireless Switch, it will connect with no problem and you will finds out a WIFI Alliances Mark on the NIC Card, and that means it works normally with Other Vendors. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 77 Securing and Implementing Wireless Networks: • Wireless Dangers 1. War-Driving: Person trying to search for a connectivity through his wireless NIC and Connect to the internet through your connection cause its opened and no security available and consume resources of Band width of your network. 2. Hackers: A Hackers tries to access your Organization and tried to Destroy or steal any critical Data. 3. Employees: Employees are persons that try to connect through the internet by their wireless Equipment for their own Purposes, in a wired Network with out taking Permission. • Wireless Security Authentication: it asks for Username and Passwords to allow access to the wireless Network. Encryption: Every single data you sent it through wireless across the network is encrypted. Intrusion Preventation System (IPS): it’s a System that detect if there is a wireless access point on your network or not, and verify if this access point should be their or not, and send you a message on pager or cell phone or email that this was detected on this radius and on this area. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 78 • Encryption and Authentication Combination: 1. Pre-Shared Key WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy): WEP was the initial Security method that was considered extremely WEAK, it has many issues, it has a lot known attacks weak point that you could break through those encryption keys. Pre Shared Key is a system of security were you type in a Key on the wireless access point, say the key is CAT as example, and then all of the other clients that join in have to enter the same key entered on the access point which is CAT. Pre-Shared key is great for small organization and home offices, but have a disadvantages, let’s say if an employee leaves the company, and that employee have the Pre-Shared key, so he could be danger on the Network as he may access the wireless network any time he need as he has the access key, so what the Admin do is that he should change the Pre-Shared Key on the access point and after that change individually the key on each laptop needs to access the wireless network, and that is not efficient, also the Pre-Shared key should be changed regularly say every month you should change the key for security purposes. So PreShared key is good for small offices but becomes inefficient as the network growth. 2. Evolution#1 Pre-Shared Key WPA1 (Wi-Fi Protected Access 1): WPA1 is the next Evolution after the WEP, the industry realized that WEP had issues in its Security, so they have invented WPA1, the organizations that came up with this Standards said we need to do a new standard that’s different from the WEP cause of its security issues problem, but the problem is that all the Wireless Equipment that has been already manufactured has a WEP hardware means the chips on that Equipments can’t handle a strong encryption methods, so they said we need a better method that uses the same wireless hardware (without changing the everybody NIC) and that what WPA1 first emerge. WPA1 improved the security and the encryption from WEP without changing out the Hardware, it uses TKIP (Temporal Key Integrity Protocol) it’s the encryption method that is used by WPA1 but also it uses Pre-Shared Key. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 79 3. Evolution#2 WPA1 and 802.1x Authentication: On this Evolution it uses WPA1 as a Security method & 802.1x which is a standard for Authenticating who you are, by username or password or a certificate. We want to have a method that get away from the Pre-Shared key installed, meaning when a laptop or wireless device joins the network and goes to the access point, rather than checking if he has the Pre-Shared Key installed, it will pass a username and password from the laptop to the wireless access point, who will then pass it to some server and ask is this username and password allowed, and the server will say YES, the username and password are allowed. When the access point received the confirmation, the access point and the Laptop will generate an Encryption Key that will be used just for that Session as long as the laptop is connected to that session, and as soon as the laptop end the connection the KEY will be gone, if the laptop tries to reconnect again they will regenerate a new Key and open a new session. Now if some employee has left the company then all you have to do is to go to the server and make his username and password is NOTALLOWED, you don’t need to change the Key on each device, and that is much easy. The Disadvantage is that it still uses WPA1 as encryption system which is weak for now. 4. Evolution#3 WPA2 (802.11I) and 802.1x Authentication: Final Evolution in the Wireless Security is WPA2 that is officially called 802.11I, in order to work on WPA2 you have to buy a new hardware Equipment. WPA2 is Encryption system is actually known as AES (Advanced Encryption Standard), it’s the Best security Standard for Wireless security known till now. 802.1x is Described above (it uses username and password and all the verification happens between access point and server for authentication.) In Evolution#2 and Evolution#3 they both uses a Server to check the Username and password, to check if this account is able or not to consume the resource of the wireless network, but what if you have a small organization or even your home network you don’t want to setup a server for that connecting to a wireless, that’s why Evolution#2 & Evolution#3 Support PSK (Pre-Shared Key) So in Summary you may choose (WPA1 or WPA2) with PSK or with 802.1x. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 80 UNDERSTANDING SSID: We will talk about the design and implementation of wireless. SSID stands for Service Set Identifier, if you have accessed a wireless network before and click on the wireless icon you will find out the Wireless network named by its brand as Linksys or Net gear, or you might change it to any unique name you need to and that identify the Network and separate it, so imagine a one Access Point that can send out multiple SSID. As example Imagine a Company has an access point that has SSID named Public and another SSID named Private, so the people who will access the Public Network may not have any security settings at all, mean they can just join with out requiring an authentication, also the only thing that the Access point can provide for this Public Network is the internet only and cannot access to the Company local network, so to join the Private Network you have to use WPA2 and Encryption to access the local Network of the Company. What happen when a Wireless Client is Enabled: 1. First when you enable the Wireless Card, will send a Probe in to the Network (its just a wireless beacon that search for any Access point). 2. All the Wireless Access point that gets that Probe will respond with a beacon of their own and offering their SSID they have. 3. The Client will start to choose the preferred SSID. 4. The Access Point that is Closest to the Client and has a Strong Signal and offer the SSID that is Chosen by the Client will pickup the Client MAC Address and add it to the Table, and forward its traffic to the internet. • If the Client start walking and the signal start to become weak, the Client wireless NIC will send a beacon searching for another close Access point and if the Access point received that beacon they will re-associate the connection and will pickup the Client MAC Address and add it to the Table, and forward its traffic to the internet. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 81 Correct Design of a WLAN: • So when you design a wireless Network, with on your mind that the clients may roam around, the best way to design it is to have 10-15 % overlap in your RF (Radiofrequency) Area. • Repeater should have 50% Overlap, Wireless Repeater takes the existing wireless Signal and Repeat it and extend it a little bit further. Of Course Each access point should use different Channels as we said before, for example the left Access point will be set at Channel 1, and the Middle Access Point will be set at channel 6 and the repeater will be set at Channel 11. • BSS (Basic Service Set): is a Single Access point. ESS(Extended Service Set): is two or More BSS Connected together through a Switch. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 82 Setting up a Wireless Network: 1. Before you plug in the Access point to the Switch port, just test that Port by plugging a PC or a Laptop to that port, and make sure it gets the Right IP Address, and you can access the internet, make sure every thing works good at that port. 2. Connect the WAP (Wireless Access Point), plug it in the port you have just tested it. 3. Setup and test SSID with no Security, name the SSID anything you need call it Cisco as example. 4. Add and test Security using a PRE-SHARED KEY (PSK), as WEP or WPA1 or WPA2, that’s to make sure that the Laptop supports the Encryption type and every thing is still working. 5. Add and Test Authentication (802.1x) if you want to do that, if you have a server that have the usernames and Password of all the users you have. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 83 Advanced TCP/IP: There are three types of sub netting examples I will show in this document: 1) Subnetting when given a required number of networks 2) Subnetting when given a required number of clients 3) Given an IP address & Subnet Mask, finding original network range (reverse engineering a subnet problem) By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 84 Subnetting, Style 1 - Subnetting when given a required number of networks Example 1: A service provider has given you the Class C network range 209.50.1.0. Your company must break the network into 20 separate subnets. Step 1) Determine the number of subnets and convert to binary - In this example, the binary representation of 20 = 00010100. Step 2) Reserve required bits in subnet mask and find incremental value - The binary value of 20 subnets tells us that we need at least 5 network bits to satisfy this requirement (since you cannot get the number 20 with any less than 5 bits – 10100) - Our original subnet mask is 255.255.255.0 (Class C subnet) - The full binary representation of the subnet mask is as follows: 255.255.255.0 = 11111111.11111111.11111111.00000000 - We must “convert” 5 of the client bits (0) to network bits (1) in order to satisfy the requirements: New Mask = 11111111.11111111.11111111.11111000 - If we convert the mask back to decimal, we now have the subnet mask that will be used on all the new networks – 255.255.255.248 - Our increment bit is the last possible network bit, converted back to a binary number: New Mask = 11111111.11111111.11111111.1111(1)000 – bit with the parenthesis is your increment bit. If you convert this bit to a decimal number, it becomes the number „8 Step 3) Use increment to find network ranges - Start with your given network address and add your increment to the sub netted octet: 209.50.1.0 209.50.1.8 209.50.1.16 …etc - You can now fill in your end ranges, which is the last possible IP address before you start the next range 209.50.1.0 – 209.50.1.7 209.50.1.8 – 209.50.1.15 209.50.1.16 – 209.50.1.23 …etc - You can then assign these ranges to your networks! Remember the first and last addresses from each range (network / broadcast IP) are unusable By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 85 Example 2: Your Company would like to break the Class B private IP address range 172.16.0.0 into 60 different subnets Step 1) Determine the number of subnets and convert to binary - In this example, the binary representation of 60 = 00111100 Step 2) Reserve required bits in subnet mask and find incremental value - The binary value of 60 subnets tells us that we need at least 6 network bits to satisfy this requirement (since you cannot get the number 60 with any less than 6 bits – 111100) - Our original subnet mask is 255.255.0.0 (Class B subnet) - The full binary representation of the subnet mask is as follows: 255.255.0.0 = 11111111.11111111.00000000.00000000 - We must “convert” 6 of the client bits (0) to network bits (1) in order to satisfy the requirements: New Mask = 11111111.11111111.11111100.00000000 - If we convert the mask back to decimal, we now have the subnet mask that will be used on all the new networks – 255.255.252.0 - Our increment bit is the last possible network bit, converted back to a binary number: New Mask = 11111111.11111111.11111(1)00.00000000 – bit with the parenthesis is your increment bit. If you convert this bit to a decimal number, it becomes the number „4 Step 3) Use increment to find network ranges - Start with your given network address and add your increment to the sub netted octet: 172.16.0.0 172.16.4.0 172.16.8.0 …etc - You can now fill in your end ranges, which is the last possible IP address before you start the next range 172.16.0.0 – 172.16.3.255 172.16.4.0 – 172.16.7.255 172.16.8.0 – 172.16.11.255 …etc - You can then assign these ranges to your networks! Remember the first and last addresses from each range (network / broadcast IP) are unusable By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 86 Subnetting, Style 2 - Subnetting when given a required number of clients Example 1: A service provider has given you the Class C network range 209.50.1.0. Your company must break the network into as many subnets as possible as long as there are at least 50 clients per network. Step 1) Determine the number of clients and convert to binary - In this example, the binary representation of 50 = 00110010 Step 2) Reserve required bits in subnet mask and find incremental value - The binary value of 50 clients tells us that we need at least 6 client bits to satisfy this requirement (since you cannot get the number 50 with any less than 6 bits – 110010) - Our original subnet mask is 255.255.255.0 (Class C subnet) - The full binary representation of the subnet mask is as follows: 255.255.255.0 = 11111111.11111111.11111111.00000000 - We must ensure 6 of the client bits (0) remain client bits (save the clients!) in order to satisfy the requirements. All other bits can become network bits: New Mask = 11111111.11111111.11111111.11 000000 note the 6 client bits that we have saved - If we convert the mask back to decimal, we now have the subnet mask that will be used on all the new networks – 255.255.255.192 - Our increment bit is the last possible network bit, converted back to a binary number: New Mask = 11111111.11111111.11111111.1(1)000000 – bit with the parenthesis is your increment bit. If you convert this bit to a decimal number, it becomes the number „64 Step 3) Use increment to find network ranges - Start with your given network address and add your increment to the sub netted octet: 209.50.1.0 209.50.1.64 209.50.1.128 209.50.1.192 - You can now fill in your end ranges, which is the last possible IP address before you start the next range 209.50.1.0 – 209.50.1.63 209.50.1.64 – 209.50.1.127 209.50.1.128 – 209.50.1.191 209.50.1.192 – 209.50.1.255 - You can then assign these ranges to your networks! Remember the first and last addresses from each range (network / broadcast IP) are unusable By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 87 Example 2: Your company would like to break the Class B private IP address range 172.16.0.0 into as many subnets as possible, provided that they can get at least 300 clients per subnet Step 1) Determine the number of clients and convert to binary - Remember, the binary representations of 8 bits (a single octet of an IP address) can only reach 255, but that does not mean we cannot cross octet boundaries when working with Class A or B examples! - In this example, the binary representation of 300 = 100101100 Step 2) Reserve required bits in subnet mask and find incremental value - The binary value of 300 clients tells us that we need at least 9 client bits to satisfy this requirement (since you cannot get the number 300 with any less than 9 bits – 100101100) - Our original subnet mask is 255.255.0.0 (Class B subnet) - The full binary representation of the subnet mask is as follows: 255.255.0.0 = 11111111.11111111.00000000.00000000 - We must ensure 9 of the client bits (0) remain client bits (save the clients!) in order to satisfy the requirements. All other bits can become network bits: New Mask = 11111111.11111111.1111111 0.00000000 note the 9 client bits that we have saved - If we convert the mask back to decimal, we now have the subnet mask that will be used on all the new networks – 255.255.254.0 - Our increment bit is the last possible network bit, converted back to a binary number: New Mask = 11111111.11111111.111111(1)0.0000000 – bit with the parenthesis is your increment bit. If you convert this bit to a decimal number, it becomes the number „2 Step 3) Use increment to find network ranges - Start with your given network address and add your increment to the sub netted octet: 172.16.0.0 172.16.2.0 172.16.4.0 etc… - You can now fill in your end ranges, which is the last possible IP address before you start the next range 172.16.0.0 – 172.16.1.255 172.16.2.0 – 172.16.3.255 172.16.4.0 – 172.16.5.255 etc… By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 88 - You can then assign these ranges to your networks! Remember the first and last addresses from each range (network / broadcast IP) are unusable By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 89 Subnetting, Style 3 - Given an IP address & Subnet Mask, find original network range (reverse engineering a subnet problem) You are given the following IP address and subnet mask: 192.168.1.58 255.255.255.240 Identify the original range of addresses (the subnet) that this IP address belongs to - When reverse engineering a problem, all you need to do is break the subnet mask back into binary and find the increment that was used 255.255.255.240 = 11111111.11111111.11111111.11110000 - As before, the last possible network bit is your increment. In this case, the increment is 16 - Use this increment to find the network ranges until you pass the given IP address: 192.168.1.0 192.168.1.16 192.168.1.32 192.168.1.48 192.168.1.64 (passed given IP address 192.168.1.58) - Now, fill in the end ranges to find the answer to the scenario: 192.168.1.0 – 192.168.1.15 192.168.1.16 – 192.168.1.31 192.168.1.32 – 192.168.1.47 192.168.1.48 – 192.168.1.63 (IP address 192.168.1.58 belongs to this range) By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 90 The Great Exception This sub netting process works by finding the number of bits that are required to meet a given requirement. For example, if I wanted to break a range into 25 networks, I know that I will need to convert 5 bits to network bits to satisfy the requirement. However, because binary numbering counts from zero, there are exceptions to this rule. For example, if I were asked to break a network into 8 subnets, you would assume it would take four bits since 8 in binary are: 00001000 However, you can achieve this requirement with only three bits since 0-7 is really 8 numbers (0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7). If you work out the sub netting problem by reserving only three bits, you will get exactly eight subnets. The same thing happens when breaking into networks for every “precise” binary number: 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, and 128. So how do you avoid this issue? You can always subtract 1 from the number of networks required. For example, if you are asked to break a range into 30 subnets, figure it out for 29. If you are asked to break a range into 16 subnets, figure it out for 15…and so on. There is a similar rule for finding the number of bits to reserve for hosts. For example, if I wanted to break a range into 25 hosts per network, I know that I will need to save 5 bits as host bits to satisfy the requirement. This rule works fine, but does not account for the two hosts that are unusable from every range: the network IP address and the broadcast IP address. The fact that binary counting starts from zero helps us with one of those IP addresses, but we can still come up one short in certain cases. For example, if we were asked to break a network into subnets that can hold up to 31 hosts, you would assume it would take 5 bits since 31 in binary is: 00011111 However, when you work out the problem you will find that you only get 30 hosts per subnet (1 IP address short). The same thing happens with every “full” binary number: 3, 7, 15, 31, 63, and 127. So how do you avoid this issue? You can always add 1 to the number of hosts required. For example, if you are asked to break a range into 25 hosts per subnet, figure it out for 26. If you are asked to break a range into 63 subnets, figure it out for 64…and so on. I realize this exception gets somewhat technical… so to summarize: When sub netting based on the number of networks, SUBTRACT 1 from the number When sub netting based on the number of hosts per network, ADD 1 to the number Follow these rules and you will always be safe. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 91 Router boot and initial Configuration: First Turning ON the Power of the Router Type C850 we will see the Following Boot up Screen. After Loading the IOS and Checking its Hardware it will ask: As from Experienced People and from Real life World 99% the Answer is NO. Cause once you know how to configure the Switch from the Console you will not need to configure it through a Wizard. 1. First thing you do for configuring a Router on a New Brand Device is to set a Name. We will change the default name into CBTRouter. 2. We will configure the Banner Message By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 92 3. Now we will configure the Console Port Password and we will enable the Logging Synchronous. 4. We will set the Time Out at the console port (it’s the time that Kick the Login User if he hasn't make any action for some time), we will set it to 30 Minutes. 5. I will enable now the Password on the Telnet lines, Logging Synchronous, and Time Out. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 93 6. Now we will make a password on the router for accessing the privilege mode. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 94 The following Diagram will be used in our next Sections and we will configure our C850 Router on this Diagram. First of ALL our C580 Router has a Built in Switch with Five Fast Ethernet Switch Port (FE0 – FE4), FE stands for (Fast Ethernet), with a Two Antennas for Wireless Network. So if we do the following Command we will see all the Interface and Ports on that Router. First Interface in the above Picture Is for Wireless Network (Dot11Radio0), and then the Five Fast Ethernet Port, then the Virtual- Dot 11 Radio 0, then VLAN1 (Cause this Series has a Switch Built in so there should be VLAN whenever there is a switch). So if we look closely on the Network Diagram Above at the beginning of the page, we will need to configure Two IP address on the Router Port one for the Internet and one for the LAN, so the Question is Which port will be setup for the WAN as from the Previous Command (Show IP interface brief) it doesn’t shows any Serial Connection for WAN. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 95 In 800 Series Router they have made one of the FE Port to be a WAN Port lets see the following photo of the Router and its Interfaces. On the back of the router you will see a group of four Yellow Interface from (FE0 to FE3), and one Yellow port that is kind of separated from the Rest of the Group which is (FE4 & WAN), so this port can be used as Fast Ethernet or as a WAN Link. So we will write a Description for this Port as it’s a WAN Port and it will be connected on the Internet, cause whoever will use the Router will know that this port is for the Internet. Notice that from FE 0 – FE 3 are all Switch Port, mean they are all Configured as Switch should be as all present in a VLAN1, means any Devices connected at FE0 or FE1, FE2, or FE3, they will be able to communicate with Each other. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 96 Now we will Configure FE4 to the Public IP Address as in above Diagram to the Internet. IP address is 68.110.171.98, with Subnet Mask 255.255.255.224 Let’s Configure the FE4 Port by this IP and Subnet Mask. After that we will make the port to be Administratively UP so we will type no shutdown, so we will do the following. Let’s see what we have done, by showing status of the Ports: As you might see the FE4 is Status UP and Protocol is UP and has a Static IP Address 68.110.171.98 Now in the previous example, the ISP had provided me with Static IP Address, but what if I cant paid for a Static IP address as its much too expensive, so the ISP have another choice which is provide to you a DHCP IP Address which means that the ISP will let you borrow a Real IP whenever the router is online and will take the IP back from you when your is off, DHCP its acronym for (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol), which gives you IP Dynamically. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 97 Now to enable all Fast Ethernet at once you will write the following: After that you will find the entire interface are UP in Physical Layer but in Data Link Layer its not as due to nothing is connected actually to the PORT there is no Electric Signal. Now we will configure the Switch Port IP address, let’s do the following: We will now make sure of the IP Address we have entered for Public and private interface by the following: By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 98 What is Cisco SDM? SDM stands for Security Device Manager; it’s a GUI (Graphic User Interface) that you can use to manage your Router. SDM is a Web based, and need a java Application to be installed on the PC that you would like to manage the router from that PC by SDM. SDM works on all Mainline Cisco Router as 800 Series, 1800, 2600, 2800, 3800, that’s what is mean by Mainline Cisco Routers, what is not Mainline Cisco Routers are the Routers that are Extremely Advanced once that is Used in the ISP (Internet Service Provider) or just Very Old Router as 2500 Series Router. So SDM were designed for allowing IOS Configuration without extensive knowledge of Cisco Commands. Configuring Router to Support SDM: SDM now comes up with every Cisco Routers you buy on the Flash Memory, so if you open the Browser and enter the IP Address of the Router it will automatically open the SDM. But you may download it on your PC from the Following Link: http://www.cisco.com/pcgi-bin/Software/Tablebuild/doftp.pl?ftpfile=pub/web/sdm/SDMV25.zip&swtype=FCS But you must be logged in or create an account on Cisco site, it’s free. Once you download that, and try to install the SDM, it will give you the opportunity to install it on the Computer, or on the Router (Flash memory), or on both. Now if you install the SDM on the Flash of the router, then you can access the router from any PC by just opening a Browser and point that browser to the IP Router. When you try to access the router by Browser, the router will download the SDM on your PC and the SDM will starts running from the Flash of the Router. The Disadvantage of doing that is anything running from the Flash of the Router is Slow so it will take a longer to load up. If you choose to install it only on PC, you will actually run the program locally from the PC, and then you may point it on any Router you want to manage, without need to actually install the SDM on the routers, and it will runs faster. Configuring your router to support SDM 1. 2. 3. 4. Generate Encryption Keys (Used in SSH and Https). Turn ON the HTTP/Https server from your router. Create a Privilege level 15 user accounts. Configure your VTY and HTTP access Ports for privilege level 15 and to use the local user database. 5. Install Java on your pc and access the router using a web browser. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 99 Let’s do it Step by Step: First Step: Generating Encryption Key is important as it encrypts the data between the PC and the router while telnet, before we do that we should first create a domain name that is used to generate an Encryption Key. Then we will generate the Encryption key, as from the following picture you have two choices whether to generate a general key or RSA key that is used for Securing SSH and Https, we will choose RSA Key. Now you have two types of RSA Key (the following description on the General and usage Key is from Security track and not for CCNA Track but to give you some hints.), • General-Keys which is universal Encryption Key it works for anything you don t specifically assigned them for, means you don’t have to say I will use this key for that and this key for another, no its just a universal key for everything. • Usage Keys is used to generate a different Key, each key may be used in whatever you want to. So we will choose the General-Keys, In the above picture it says the name for the Keys will be CBTRouter.nuggetslab.com, so that means when somebody connects in to the router it will say this is my encrypted key for this router, by the way if you change the Router name or the domain name, you should regenerate the Key from the beginning for the new domain name, or of the new router name. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 100 Now we will choose the modulus of the key, experienced people says its better to choose 1024 encryption rather than 512 or 2048, as its good encryption key and it want take processing too long. Second Step: In this step we will turn ON the HTTP, and Https on the router to enable the router to use HTTP or Https, which allow you to access into privilege mode upon connection. Third Step: In this Step we will Create a Privilege Level 15 User account, privilege level 15 is the highest level you may get from Cisco devices which let the user after accessing by his username and password to enter to the Privilege mode direct and do whatever he wants, whenever the level decreases than level 15 the command in the privilege mode will also decrease, as an example in level 6 you might not be able to use the SHOW RUN command or even you can not enter the Configuration mode. So to create a user account with privilege level 15. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 101 So we will choose Privilege and then hit the ? Mark. As you might see above there are many options in the privilege mode, what we will do is to create a password for the user, so we have password (which specify the password for the user) or you may type secret which is better cause secret is encrypted than the password that its not encrypted as we said before, in this scenario we will choose password. As you might see in the above picture the 0 means unencrypted password, 7 means an encrypted password level 7, remember when we crack level 7 password that’s level 7, last one is LINE written in capital letters means you may write whatever you want so we will write Cisco as a password. So now we have created a privilege level 15 user account that will be used to access web page interface. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 102 Fourth Step: What we have done in the above picture is tell the HTTP Server how you want to authenticate or ask people for their password when they come to the router, whether by the enable password only, or by the local user database (username and password) we created in the third step, so we done here to ask for the username and password. Now we will secure the VTY Port, observe the following picture. In previous sections, we used to secure the VTY lines by the command login and then the password, and the router will prompted you for the password only when you try to access it terminal and when you enter the password it will enter you to the user mode. But here its different in the previous picture we make a condition which is when you connect to the router by telnet it will prompt you for username and password to access the privilege mode rather than user mode. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 103 As you might see it ask for Username and password rather than Password only, also it enters you direct to Privilege mode rather than user mode. So login Local override login command Fifth Step: Install Java and you are ready to go. Now Run the SDM Program after you have download it and install it, it will appear the following windows. You will mark on the (This Device has HTTPS enabled and I want to use It.) so as to connect to the router in a secured connection. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 104 After that it will ask you for the username and password level 15. As you might see from the below picture it’s the capture for the router that I work with in GNS3, that’s the SDM in GUI, you have many buttons, we will discuss later on it. You may try it by your self and investigate the menus and the buttons around. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 105 Using SDM to Configure DHCP: Understanding DHCP DHCP is the acronym for (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol), it’s an automated way to give the PC an IP addresses in the local area network. There are two ways to give an IP address to the pc on the network. 1. Manually, means assign each pc with an IP address. 2. Automatic by using DHCP. • DHCP have the option to give IP address to the PC for a limited time, means you may setup the DHCP settings to give an IP address to the PC for 8 Days as an example, unless the PC ask for another IP again before this period finishes the DHCP will then provide him the requested IP address. • DHCP can be “Manually Allocated” means the DHCP can provide a specific IP address to a Specific PC when it comes online, so when this PC comes online and ask for IP address from the DHCP Server it gives it a Specific IP address you assign for it, and that could be benefit if you don’t want to change the IP address of your Servers when they comes Online. • DHCP can be Server based which means you can have a windows server that can be used as DHCP Server, or Router Based which means you can handle a DHCP by router. • The Advantage of DHCP Router-Based is its more stable than windows based; also the Advantage of DHCP Windows-based is you can deal with it much more easily than router as it has a GUI (Graphical User Interface). By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 106 DHCP Process: Let’s see the process how the client may go to get his IP address from DHCP. 1. When you set the PC to get an IP Address Automatically what it will do is send out a DHCP Broadcast on the Network to find out a DHCP Server. 2. When DHCP Server receives the DHCP Broadcast message, it will send a Unicast message to the PC (DHCP offer) and will introduce the IP address needed to the requested PC. 3. Now after the PC accepts the new IP address it will send a Unicast message to the DHCP server saying I accept that IP thank you for that. 4. Now DHCP will send a Unicast Acknowledge message to the PC, confirming that this IP is in use now and working and will be added to the DHCP database so as no one use this IP address in that network so as no duplicate happens. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 107 Let’s use the SDM to configure our Router to be a DHCP Server. 1. Before we start Configuring in the SDM windows we will click on EDIT menu then point to Preference, then mark on preview command before delivering to router, this option will show you what commands will be written to the router before its send to it. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 108 2. First thing we will do is to click on the Configure Button, and it will open the Configuration Windows, at the left there is a row of buttons which you may use for configuring router what we will click on is the Additional Task button which is located at the bottom. The Additional Task Button By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 109 3. The Additional task will open a windows with more task you may do on the router, we will choose the DHCP Icon, and it will open a sub list under DHCP, one is name DHCP Pools, which is the range of IP address the DHCP can assign from it to the Requested PC, and the DHCP Bindings which is to assign a Specific IP address that I want to assign to a Specific PC by (MAC Address) By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 110 Now when I select DHCP Pools and click ADD the following windows will appear, this windows has many details that will be used for the client whoever connects to the router and their NIC Configuration is set to obtain Automatic IP and Obtain DNS Automatic as following. • DHCP Pool Name, any name you might enter for the DHCP Pool name. DHCP Pool means the range of the IP that the DHCP Server may choose from. • DHCP Pool Network, it’s the Network address for the Pool. • Subnet Mask will be the Subnet Mask of the Network. • Starting IP, first IP the DHCP will choose from, (its better to leave the first 20 IP Address in the network for the Servers.) • Ending IP, Last IP in the range • In lease length sector, there are two choices in choosing whether the IP that will be provided by the DHCP Expires by providing a period or choosing never expires. When you choose the User defined and specify as example 3 Days the DHCP will check after 3 Days if the provided IP address to the PC is Online and using it, if yes it will renew the period for another 3 days, but if the PC is offline, it will take that IP from that PC and return it to the Pool. • In DHCP Options, you may specify the DNS Server IP which is used to resolve the Domain name into an IP address. Also the most important thing is the default router which is the default Gateway, where the client will use it to access the internet. • By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 111 • The last option is the (import all DHCP options into the DHCP server Databases). This is used if you don’t want to write all the DHCP Option Section and make the router to forward automatically the ISP Configuration and pass it to the Client PC direct. The Following Picture is after completing all the required information. After that when you press OK, it will deliver the Command for Configuring the DHCP Server to your router, as from the following picture if you configure the SDM to show you the command before it delivers to the router you will see the following picture as a confirmation. After you review the command you may click on Deliver button for delivering the command to the router. You may click on the (save running config. to startup config.) if you want to save after delivering those commands. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 112 Now at the SDM Interface, when we create our DHCP Server it will appear in the windows as following. When you press DHCP Pool Status it will show you all the IP address that is assigned. Now when we access the router and type the following command: Now you can see the IP address that is assigned to the PC with the PC MAC Address and the Expiration date for that IP. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 113 Understanding The Purpose of the Router: A PC is connected to the Network 192.168.1.0 with IP address 192.168.1.20 and connected to the Gateway (Router IP) 192.168.1.1, with a connection between the two Routers at Network 192.168.2.0, were R1 IP address is 192.168.2.1 and R2 IP Address is 192.168.2.2, and finally R2 is connected to the other Network 192.168.3.0 with IP Address 192.168.3.1 and the PC at the right is connected at IP address 192.168.3.20 Now if I were logging console at R1, I would be able to ping on Network 192.168.2.0, and on Network 192.168.1.0 because R1 is Directly Connected to those Networks, now if R1 Pings on Network 192.168.3.0, he will not get any Replies cause R1 does not know that this Network Exist, although R1 is connected to R2 that is Connected to Network 192.168.3.0 but R1 is not Smart enough to understand that R2 has the ability to get to that Network, likewise R2 knows how to reach Network 192.168.3.0 & 192.168.2.0, but doesn’t know Network 192.168.1.0 exist, the Result is that PC at the Left can’t Communicate to the PC at the right, because the routers are not yet Routing. How Static Routing Can Help. Static Routing is were you as an administrator get on the routers and start telling them were to go (Manual). Now we will access Router1 and see what Interfaces is connected too, as from the following its connected to two Interfaces as in the above Picture, FE0/0 for IP address 192.168.1.2 & to the Serial Interface 192.168.2.1 By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 114 Now we will access Router2 and see what Interfaces is Connected too, as from the following its connected to two Interfaces as in the above Picture, FE0/0 for IP address 192.168.3.1 & to the Serial Interface 192.168.2.2 & and to the PC 192.168.3.20 After we seen the two Routers with their Connection, we will move back to Router 1 and see what Network Address it knows. Let’s do the Following: From the Above Picture we see R1 had learned that network 192.168.1.0 & 192.168.2.0 are connected to its interfaces, the Codes in the above picture tells you how the Router learned that Network address by which Method, in our Picture it says it has Learned the Two Network Address cause they are directly connected to Router interfaces which is method C which is written at the Beginning of the line which refers to Connected means (those Networks are Directly Connected to the Router). As we said before R1 can’t connect to Network 192.168.3.0 & R2 can’t connect to Network 192.168.1.0, so let’s solve that as following: Ok as you see above we will write down the Command IP route where this is the Syntax for Static Route, and hit the ? Mark, you will find many options but we will choose the Highlighted one, which tells you write down the Destination network address you want to go to, so I will write network 192.168.3.0 By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 115 But that’s not all we will hit the ? Mark again and see the rest of the command as following, It will ask you, What the Subnet Mask is for that Network, so we will write down class c mask: After that we will hit the ? Mark again and see the following: In the above picture we have several of choices but we will choose the first line, which states for what is the Next HOP (Router) IPAddress that will let you reach to network 192.168.3.0 with subnet mask 255.255.255.0, so we will type the following: The above command says to get to 192.168.3.0 with subnet mask 255.255.255.0 I need to use 192.168.2.2. OR I will use IP address that I' am able to reach (192.168.2.2) to reach a network that I previously don’t know about it which is (192.168.3.0). By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 116 Let’s See after the executing the previous Command if R1 has the information for reaching network 192.168.3.0 or not: As you might see above it has the Method S which means Static which refers to Manual route that the Administrator tells the Router to reach 192.168.3.0 you have to go to 192.168.2.2 The same will be done for Router2 as the following: Lets See after the executing the previous Command if R2 has the information for reaching network 192.168.1.0 or not: As you might see above it has the Method S which means Static which refers to Manual route that the Administrator tells the Router to reach 192.168.1.0 you have to go to 192.168.2.1 By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 117 Let’s see, For R1 pinging on IP 192.168.3.1, will it Reach after the Configuration we done previously or not: As you might see its Success Rate is 100% meaning all the Pinging Packet had reached successfully. Let’s see also, For R2 pinging on IP 192.168.1.2, will it Reach after the Configuration we done previously or not: As you might see its Success Rate is 100% meaning all the Pinging Packet had reached successfully. The Disadvantage in using Static Routing is when you have a Large Network you will have to Configure Each router one by one Static Routing, and that will take a long time. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 118 Now another Scenario: Here in the following Picture we see that the Router is able to ping on the PC and to the ISP IP address (68.110.171.97) because they are directly connected, the problem here is when the Router Ping to any internet site it won’t ping although we can ping on the IP address of the ISP (Internet Service Provider) I will ping on the ISP IP address and we will see from the following it will reply back: But if I ping on IP address for Google Web site, it will not ping and the success rate is 0, because it doesn’t know about the internet route: By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 119 This is due to the Router hasn’t learned yet how to access the internet, if we do the following command it will show you what Network the Router knows which is the ISP IP address, and the Local area IP address, so if you search for the Google IP address [72.14.207.99] you will not find it in the below picture. Now the Question is how I can get all the route of the entire Internet on the whole Planet??!! , Well Thanks to Cisco as they have a simpler way which is called a Default route, were you tells the router any network you want to reach and you don’t know how to reach it, please send it over this IP, it’s the Same Example as the PC when the PC need to send a Packet to another Network it will send it to the Default GW IP, let’s see the following how we can do that: What this command Says is Send any IP address with any Subnet Mask to that ISP IP address if you don’t have a specific route in your routing table. Now if we do the following to check whether the Router learned and added the Previous Command in its IP route table or not. Now you notice the S Symbol which refers to the Static Method and the * means the Router realize this is his default IP address to the outer World which send anything to the ISP IP address. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 120 Now let’s Test by Ping on Google IP address and See what happens: As you might see its pinging now and Google IP is Replying back to the router with Success 100% means the Router is able to find the unknown route that it doesn’t present in the routing table through sending it to the ISP IP address. Remember when we said before how the PC knows the IP address of the Internet Site, by sending the name of the site to the DNS server and find out what it is IP address, in router we may do the same by the following: As you might see above in the picture we configured the router to look for the DNS server (4.2.2.2) whenever there is Translating from internet site name to IP address, and as you might see we have ping on google.com after that and it says Translating it through 4.2.2.2, and it gives reply back with 100 % success. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 121 Now let’s see our picture AGAIN and see what we have done: From the above picture we have Successfully make the router to be able to access the internet, but does the PC in the local Network will be able to access the internet too, lets see the following: Lets ping from PC the DNS Server 4.2.2.2 As you might see the packets are DYING the packets cant get to the DNS Server 4.2.2.2, lets see why in the following picture, and investigate were the packets stops. The first thing the PC done is it go to the Router interface 192.168.1.1 to ask it to route him to 4.2.2.2, so the PC have done the first step which is to go to the router when it doesn’t know were to go, after that there is no reply the packets are dying, Why is that ? Because the Router is trying to send that IP address of the PC which is from a Private network to the ISP IP address, and what does the ISP do is BLOCK that Packets from traveling cause it’s a Private IP address which Is not allowed to use the Internet, the solution for that is the Router require a Feature known as NAT (Network Address Translator) it will be described later. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 122 Now we will combine the two pieces now, lets Make CBT Router be able to reach to R1 and R2 Networks. First we will check the Routing Table in the CBT Router: As you might see it does know how to reach the internet and to the Local Area Network 192.168.1.0, but it doesn’t know how to reach 192.168.2.0 & 192.168.3.0, so if we ping on Network 192.168.2.0 it won’t ping lets see the following: By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 123 So to make CBT Router to be capable to reach the Network 192.168.2.0, we will do the following: Now we will make sure the route is added in the route table: As you see above its added now as Static Route, were network 192.168.2.0/24 will be able to reach it through interface 192.168.1.2. Now we will ping on this network to be sure that it reaches it: It reaches, and that is OK!! Now read the following carefully!! Now if we ping from CBT Router on IP address 192.168.2.2, what will happen!! Well the packets that travels from the CBT Router knows how to reach to the network 192.168.2.0 because we have added this route in the routing Table that it will reach this network via interface 192.168.1.2, Now when the Packets reach the Network 192.168.2.0 and Enters the Interface of Router R2 192.168.2.2, R2 Should Reply back the Ping by Sending the Reply Packet from Network 192.168.2.0 to the Network 192.168.1.0, and because we have Configured before R2 in the routing Table to reach network 192.168.1.0 via the interface of R1 192.168.2.1, the Ping will Successfully reach CBT Router, but if R2 weren’t configured in the routing table to be able to reach to network 192.168.1.0, the Ping from CBT Router would Fail. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 124 Now lets Ping from CBT Router to the PC with IP 192.168.3.20 The Success is 0% and the Reason is CBT Router doesn’t know how to reach to Network 192.168.3.0, because it doesn’t have this network Present ion the routing Table. So we will fix that by adding this network in the route Table of CBT Router, so to add this Network we will type the Following Command: The Reason why we choose the Next HOP IP Address 192.168.1.2 to get to the Network 192.168.3.0, because the Next Hop (Next Router) Interface IP address to CBT Router is 192.168.1.2, that’s why we choose it, and because R1 is Capable of route my Data to R2 and R2 is capable to route me to 192.168.3.20 we will reach it. Now I will do the Ping from CBT Router to 192.168.3.20 and it will success in Traveling 100%: The Disadvantage of Static Routing as we Said it take a lot of effort to Configure each router for Learning them the Network , so imaging a hundreds of Router in a Network that will be Hard, that what we will discuss in the Following Sections Dynamic Routing. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 125 Dynamic Routing Now in the Upper Diagram we have removed all the Static Routing from all the Routers, so every router knows only the Network that is directly connected to. • Routing Protocols: Routing Protocols tells what you know present in the Routing table to other Routers. So if R3 as example is configured Dynamic Routing, what it does is it send on all its interfaces its connected to that it knows how to reach to Network 192.168.3.0 & 192.168.2.0, Now R2 will receive that message and says you know 192.168.2.0 as I do so that is no use for me, but I don’t know you are connected to 192.168.3.0 Network and I will add that information to my database (Routing table), and I will make the Interface that I received from it that Update Message will be my Next HOP interface to reach that Network, (the interface which come the message from 192.168.2.2). Also R2 will send on all the Interfaces its connected to that it knows how to reach to network 192.168.2.0 & 192.168.1.0 & 192.168.3.0 (because someone told me how to reach to this Network), R1 gets that Message and says you know 192.168.1.0 as I do so that is no use for me, , but I don’t know there is 192.168.2.0 & 192.168.3.0 Network so I will add them in my routing Table and I will make you my Next HOP (the interface which come the message from 192.168.1.2) So all the Routers in the Network now will build all the Path Automatically. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 126 Type of Routing Protocols: There are Three Classes Type: 1. Distance Vector: o o o Easy to Configure Not many Features (means if there is a problem in the Network, Distant Vector is Slow in detecting that) Protocols Example: RIP & IGRP, (RIP Protocol works well in smaller environment & IGRP too.) 2. Link State: o o o Difficult to Configure (More Knowledge Required). Feature-Riffic (means they support every Feature in the Network they need). Protocols Example: OSPF & IS – IS 3. Hybrid: o o o “The best of Both Classes above”, means Easy to Configure as Distance vector with all the Feature of Link State. Proprietary (means only for Cisco Devices). Protocols Example: EIGRP. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 127 Understanding RIP: • • Algorithm first Developed at 1969 Rip comes in two Versions: RIP V1 & RIP V2, but Today we only use RIP V2, but we will know just the Difference between the two version RIPV1: • Class full version (Doesn’t support VLSM “Variable Link Subnet Mask”) let’s take an Example ,Router R1 sends a Message to all its Interface that it know a Network IP address but it doesn’t tell what its Subnet Mask it is. So let’s say from the following picture that R1 is connected to the Network at its left 172.16.1.0/24, now that IP address is a Sub netted Network because by default this IP starts with 172 which is a class B but it has a Subnet Mask of Class C. So when R1 starts Telling everyone connected to its Interface that it know Network 172.16.1.0, R2 will receive the Message that R1 knows Network 172.16.1.0, Only without the Subnet Mask Information, so R2 will say I have Two Options for the Subnet mask Issue, First I will look at my Interfaces I connect to and see if there is a Similar Network ID and see its Subnet Mask and take it, Or if no I will assume that the Subnet Mask will be by default Class B because it’s Class B IP address. • No Authentication: Means if there is another Additional new Router is Added to the Network, and this new Router is connected to a Small Network, as a result the Routers in the Network will be updated from the new Router that there is a New Network connected to it, also the other Router will start sharing the Information about their Network to the New Router and all the Data will get out to this Unsecured new Network, and that is Bad. • Uses Broadcast: Routers will start to send Broadcast once every 30 Seconds telling Everybody its Routing Table, and that will be a lot of Network Traffic. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 128 Rip V2: • Classless Version: It Support VLSM, means when the Router Advertise on its Network to the other Routers connected to it, it will advertise the Network ID and the Subnet Mask information. • Authenticated: It Support Authentication now means when the Router Starts to Update the Table with the other Router they will send the data with a password attached within it, and every router has to use the same passwords to accept that updates. • Multicast: Now it uses Multicast (One Message is Send to a Specific Group, not to everyone), so the only ones will receive the Multicast is the RIP Routers only. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 129 Configuring RIP Now we will start Configuring the Router with RIP V2: We will start with R2; first of all we will check our Routing Table to be sure there is no Previous Configuration still exists. We will configure the RIP Protocol on the router so let’s do the following: As you see form the above we have enabled the RIP Protocol in the first line, & specified version. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 130 Now the last step is to enter the Network Statement means: 1. Tell Rip what Network to Advertise. Let’s do the Following: What we have done is the first point which is telling RIP protocol on R2 to advertise for Network 192.168.1.0 & to advertise for Network 192.168.2.0 Now RIP will send from R2 both out of its interface, information about network 192.68.1.0 & 192.168.2.0, So R1 will now hear RIP coming from R2 with the information about the two Networks (192.168.1.0 & 192.168.2.0), & R3 will hear RIP coming from R2 with the information about the two Networks (192.168.1.0 & 192.168.2.0) Now we will access R3 and find out in the Routing Table if it has been updated by RIP from R2 or not. As you might see from the Highlighted line the Network 192.168.1.0 is added by the RIP protocol, were R Symbol refers to RIP Protocol. Let’s describe this line in details: • As we said before Network 192.168.1.0 with Subnet Mask 255.255.255.0 is added by RIP Protocol. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 131 • [120/1], 120 is the Administrative Distance, mean how believable the routing protocol is, essentially the lower the number the more believable the routing protocol become, let’s take an example, Assume if we connect between R3 and R1 a Direct Cable and configure the Routing Protocol as OSPF, now in this Case R3 will hear about Network 192.168.1.0 from R1 via OSPF & from R2 via RIP, now R3 should take a decision which route it should believe, actually OSPF will be chosen cause it has a lower administratively Distance which means its more believable than RIP & a Symbol will be replaced from R to O, so R3 will choose the lowest Administrative distance which is OSPF Protocol, by the way the Administratively Distance for OSPF is 110. The second number in [120/1], represent the Metric, this numbers refer to how far away is that Network, so in this Example it says that network 192.168.1.0 is far away by one HOP which in this case by one Router . Now let’s get this line again and describe it in summary what it means: R3 will get out from Serial0/0 to go through 192.168.2.1 interface because that interface Router will get me to the network 192.168.1.0 Now we will advertise for network 192.168.3.0, to be published by RIP all over the router on the whole network Now we will return to Router 2 and check that Network 192.168.3.0 is added in the Routing table and you will find it that it’s added. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 132 Now we will return to router CBT Nuggets, and we will see the Routing Table: As you can see the Router CBTRouter has learned Two Network through the RIP Protocol, one of them 192.168.2.0 & the other one 192.168.3.0 with [120/2] which indicates that this Network is away by Two HOP. So when we ping from Router CBTRouter to network 192.168.3.0, it will reach and the device 192.168.3.1 will reply back. Now the final Step, we need the rest of the Network to be able to access the Internet Link from the Router CBTRouter, meaning I need to make R2 and R3 to be able to access the Network between CBTRouter and ISP. Now what we always do is we enter the Global Configuration mode and type router rip then we type the Network that need to be advertised and known by all other Routers, now here is the Trick, at the Router CBTRouter!! RIP Protocol is a very old Protocol were once you type-in the Network IP that need to be known by all other routers, RIP treat that Network IP as a Class-full, mean this IP 68.110.171.96 is the Network IP for (68.110.171.98/27),and RIP will treat it as a CLASS-A Network cause CLASS-A Start from (1-126) and the Sub-netted Mask of Class A will be 255.0.0.0, that’s why RIP will see it as 68.0.0.0 instead of 68.110.171.96, it doesn’t care if its sub-netted or not, even if you typed in the Network ID 68.110.171.96, RIP will take it as 68.0.0.0, that’s all. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 133 So take care while you configure your Router with RIP Protocol, when you type the Network ID, type it in the Default Subnet Class without any sub-netting. So we will do the following: Now we will see how it’s been added to the other Routing Table in the other Routers: As you might see above in R2 Routing Table 68.0.0.0/8 is added as Class A with subnet Mask 255.0.0.0, so the Disadvantage of the RIP is by default looks at it as a Class-full Network without sub-netting. Ok look at the following Command, Trick!! The following Command will be done on all the Routers on the Networks. Now what that Command does is Keep RIP from automatically summarizing the Network ID back to class-A Address by default, lets take an example CBTRouter has an IP address 68.110.171.98/27 on one of its interface, if you reverse Engineer this IP address to find out the Network ID it will be 68.110.171.96, and RIP by default convert that Network ID to Class-A address 68.0.0.0, So what this command do is write the Network ID as it is on the Routing Table, without turning it in to a Class A IP address. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 134 So if we access now R2 and see its Routing Table, you will find that its been updated by the following: As you might see R2 has been updated its table by that Network 68.110.171.96/27 with also the Network ID above it 68.0.0.0/8, so as you noticed now there is Two RIP address for Network 68.0.0.0 & for 68.110.171.96, but the one that will be deleted after a while when the routing table will be updated is 68.0.0.0/8, and the other Network ID 68.110.171.96 will exist only. • But Notice when you configure RIP, make sure that network you types in for advertising it is a CLASSFULL Version as we said before, even if you have enabled the auto summary command. In Real World if you typed by Mistake the Network ID rather than the Class-full Network ID, the Router will fix it and make it a class-full Network ID, let’s see the following: If I typed in the Network ID 68.110.171.96 rather than 68.0.0.0: The Route will Auto Correct it, and will add it as 68.0.0.0 in the routing Table, when we make Show Run Command, we will find at the router Rip protocol the following: But in Exam the Simulator won’t fix it for you, so Please Take care, to type it in Class-full version only. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 135 Understanding the Need for NAT (Network Address Translator) Internet is just a Big Networks, which are connected to each other, so there are too many Devices on that Large Network and each device need an IP address, so after a while all the Real IP address will Ran Out. So the what NAT do is allow multiple devices to share an Internet IP address. How NAT Works Now let’s see, Two PC on the same Network on the left need to access the internet, but all we have is a single Internet IP address (200.1.1.1), ok now how NAT works is as following. If one of the PC need to access the internet it will go to the Router, and the Router will realize that it has a Private IP address (192.168.1.50), so what router will do is to translate this Private IP to a Public IP to access the internet. Lets say this pc wants to access cisco.com, as we said before on the TCP/IP layer (Transport Layer), each window you open it locally on your computer has a Source port and a Destination port, so if this PC want to access cisco.com it will access it by HTTP protocol so the Destination Port will be 80, and the Source port is Generated Randomly by Windows System lets say the source port will be 6751, so when the request reach cisco.com the Server will reply back as a Destination port 6751 and Source port is 80. So what NAT does is using the Unique Source Port number of PC 6751 to make the Translation of the IP address Unique, so when I enter the Router it will enter by the source IP 192.168.1.50 with Source port number 6751, and as we said before this is called Socket a combination of IP address and Port number is called Socket. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 136 So when I enter the router as 192.168.1.50:6751 it will come out as 200.1.1.1:6751, the Same Source Port number is used at the Internet IP address. Inside the Router a Table is created called a NAT Table, were all the information is recorded in that table, so when the Server cisco.com replies back and the router receives it, it will look for the Port Number and find it 6751, and it will forward that Data to the IP 192.168.1.50 Ok what if both of those PC 192.168.1.50 & 192.168.1.51 choose the same Source Port Number as 6751, what will happen?? Well, whoever reach first to the Router, will be served first and it will get out of the router with port number 6751, the Second one that will reach later the router will take the action to change the outside address Port number from 6751 to 6752, and will go out, so when the Server replies come back the Router, the Router will compare it with the data in the outside address table and find out that this port number is been changed to 6752 so it will change it back to the original port number 6751 and forward it to the IP address 192.168.1.51 That’s why this Form of NAT is called PAT (Port Address Translation). By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 137 Hosting Server Using Static NAT NAT also works with Static Entries, meaning let’s say we had a server on our network 192.168.1.51, well that server needs to be accessed from the internet meaning if it’s an email server, and someone send you an email from the internet, the email will come into the router, and then into your email server, so how do you set NAT up a way that allows it to go the opposite direction, well that is using Static NAT, Static NAT has no problem at all, as you might see in the below Picture we say to the router if someone send a Request to the IP 200.1.1.2, I need you to forward that request to the IP 192.168.1.51 which is the email server as shown in the below picture. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 138 Configuring NAT using SDM: In CCENT or ICND1 Exam Cisco expects that you able to configure NAT through SDM, but in CCNA Exam CISCO expect that you know how to configure it in a command line interface (CLI). Now we present on PC with IP 192.168.1.20, and we ping on our GW it will ping, but if we ping the other side of the router 68.110.171.98, it will reply too, now if I ping to the ISP 68.110.171.97 my ping will be dead an no reply back, the reason is I am coming through the router with private address, and the ISP will block it cause they are not allowed to pass on the internet. So what NAT does is translate the Private IP address to a Public address to allow the traffic to go through. So let’s access the SDM Interface in the Configuration part and choose the NAT Tab As you might see there are two type of NAT, Basic NAT and Advanced NAT, Basic NAT is the PAT (Port Address Translator), and Advance NAT allows you to create Static Mapping, to allow people on the internet to access to your server on your local network. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 139 For now we will configure Basic NAT, we click on the launch the Selected Task Button, we will see a welcome screen so we press Next, and it will move you to the below page: First there is a drop down list that ask you what interface is connected to the Internet from the Service provider. If you look down below you will see the interfaces and what networks are connected to, FE4 is connected to the Internet, and VLAN1 is connected to my internal Network. So we will choose FE4 from the Drop down list, as it’s the interface that is connected to the internet, and we will check the Box in front of the Range of the IP that need to access the internet, we will check on VLAN1. Now the interface will look like the following, after the choices we have done. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 140 That’s it we have finished Configuring NAT on the Router. As you might see below a summary of the IP address range that will share the Internet Connection. Now when we jump back to our PC and start to ping to the ISP address we will find the following: Success Rate in Pinging 100% to the ISP IP address. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 141 If we type in the Following Command in Router you will see the following: As what appears in the above is the translation that happens between the local IP address on the PC and to the router, let’s describe the first Line: • • • • First Column is showing the type of protocol if it’s TCP or UDP. Third Column (inside local) is the Local IP address of the PC as 192.168.1.20 with source port number 62357. Second Column (inside global) it’s the Public IP address 68.110.171.98 with the Same Source port number 62357, where the local IP PC address is translated to the Public IP address with the same Port number. The Fourth and Fifth Column are the Destination IP address with the Destination Port number. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 142 Categories of Wan Connectivity: In WAN technology their is a new Different Technology present in the Physical Layer and DataLink Layer, as you might see in the following Picture at Physical layer they are not just Ethernet cable or RJ-45 no but it’s a Serial cable with many different types and Prices, also in the Second Layer the Data Link Layer, there is no MAC address cause MAC address are in Ethernet, we moved in to things like Frame-Relay, ATM, PPP. Styles of WAN Connection: There are Three Styles of Wan Connection: • Leased Lines (Dedicated Bandwidth Between Locations): o • T1 CAS, its speed is 1.544 Mbps; you may have T1 or E1 cable modem connection, or T1 DSL or T1 Frame Relay. The benefit of leased lines is that the BW (Band Width) is all yours and at any time also if you don’t use the Line no one else can use it or share the Speed with you. The Disadvantage is its COST is High. Circuit Switched: o it’s on demand Band Width between Locations, means when you need the BW you have to dial it through a Modem, the benefit of Circuit Switch is their Price is cheap and available anywhere in the world, the Disadvantage is the BW it’s too low, it uses the Telephone company Band Width which is never designed for high speed. Types: DIAL-Up Modem ISDN • Packet Switch: o Shared but Guaranteed BW between Locations. Types: o Frame Relay. o ATM. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 143 The Physical Connection for WAN Interface in Routers: There are two ways of connection to the Internet: 1. First way is to install WIC-1t or WIC-2T, which is a Card installed in the Router for Serial Interface the difference between the Two of them is WIC-1T provide one Serial interface, & WIC-2T provide two Serial interface at the Same Card, after that a Serial Cable is Plugged in to the Card and the Other end will be installed in the CSU/DSU unit, which is used for providing a Clock Rate for the line, and Convert from a Serial Cable to a RJ-48 Cable, after that an RJ-48 Cable is connected to the wall connector at a point called DEMARC, were at this point the ISP Responsibilities Start. 2. Second Way Is to connect the router to the Card WIC-T1-DSU, as this card has a built in the unit DSU/CSU, and just connect it to the RJ-48 to the DEMARC Point. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 144 Configuring Leased Line Connection: As you see below in the picture we will configure the Routers for working on Leased Line Connection. Now we will access Router 2, and see the interfaces connected to the Router. As you might notice that Serial Interface 0/1/0 is up and configured by IP address 192.168.2.1 By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 145 Now we will see in details the Serial Interface 0/1/0 As you might see below, in the interface 0/1/0 details its up and line protocol is up, also its IP address is mentioned, and MTU 1500 bytes (MTU = Maximum Transmission Unit) it’s the maximum size of the packets can be send, also the reliability and TXLOAD and RXLOAD, those lines were described before. What I need you to observe is LINE 6, were Encapsulation is HDLC, HDLC is a Layer 2 Protocol, that is running between Router 2 and Router 3, HDLC stands for (High Level Data Link Control), this protocol only works on Cisco Devices, the benefit of HDLC is its Simplicity, meaning you just connect the serial cable between the routers and they just work without any configuration. The alternative for HDLC protocol is PPP protocol which stands for (Point to Point Protocol), its industry Standard layer 2 Protocol, were I can use it on any Routers vendors. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 146 So now I will configure R3 to work on PPP protocol, first we will telnet to R3 from R2 to check our serial interface 0/0 in R3 and see its Encapsulation first before we configure anything. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 147 As you might see the Encapsulation is HDLC, so we will do the following to configure the Router to work on PPP protocol. As you might see we entered the Configuration mode and then to the serial interface, then you will see the various type of Encapsulation in WAN, for now we will choose PPP. After a while the Telnet Connection now is DOWN, because I have configured R3 to talk PPP protocol while on R2 it Talk HDLC, so the Connection between the Two Routers is down. I will go back to R2 by hitting the combination Key (SHIFT + CTRL + 6 + X), to terminate the Telnet Connection and go to back to R2, now I will check the Line Protocol of Serial interface on R2 if it’s up or down. As you might see the Serial interface in R2 the Physical connection is UP, but the Protocol is down (Data Link Layer is Down) due to Encapsulation Mismatch between the two Routers. So we will configure the Serial interface to PPP. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 148 Now if I make the following command to check the Line Protocol if it’s up or not. As you might see its up and Working Now, so we will reconnect to R3 and see the Serial Interface status. As you might see the encapsulation is changed from HDLC to PPP. In a LAB Environment you may connect two Routers as if one of them is ISP and the other will work as a router, so to connect this two end by a cable you have to buy a Cross-Over Serial Cable, and the Router which act as ISP will provide the Clock Rate and the other Router that acts normally will take that clock to function on it. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 149 The Cross over Serial cable is labeled at one end as DCE (Data Communication Equipment), and the other end is labeled as DTE (Data Terminal Equipment). The DCE side will be connected to the Router that act as ISP because it’s the router that will gives the Clock signal, and the other End of the Cable for the other Router, you might See below the picture for the Cross Over Cable DCE/DTE. To Check what type the Serial interface in the router will be whether its DCE or DTE we will do the following: By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 150 As you might see above the Highlighted word is DTE for the Serial interface 0/0 for Router 3, also at the same line you will find written Clock detected!! So that’s mean that Router 2 is giving that Clock signal, so we will Check the Serial interface of Router 2 that is connected through Serial Cable to Router 3, to see the Clock Signal were it comes form. As you have noticed its DCE and the clock rate is 2000000 bps (bits per second) or 2Mbps. So in order to get those Serial connections works between Router 2 and Router 3, what we have done and how we have configured it is as the following: There are many clock speed supported by that interface but I didn’t appear that in the picture here. Then we will choose what speed we will use it for. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 151 MANAGING TELNET AND SSH SESSION: We have been using Telnet and SSH, in whole this Description before, here we are not showing how to setup the SSH or the Telnet because that was in the foundation of the router, what we will get into is how to manage SSH and Telnet Session, and how to effectively move around the Network Quickly, so we will use our existing Network, and we are sitting now on the same computer we used to work from which is the one at the left at the network 192.168.1.20. There are a Variety of Ways we can manage our Telnet and SSH Sessions: • First one is <CTRL + SHIFT + 6> then X, that Combination Suspend the Telnet Session or the SSH Session, it doesn’t STOP the Session it just Pause it, lets see the following: we are on Router 2 and we have Telnet to Router 3, now when we hit the Combination Key we have mentioned above it will Suspend the Session and return to Router 2, if we make the Combination Key Again it will Return to the place were you have left it in Router 3. • Second one is <Show Sessions>, it shows all the Opened Telnet session FROM your Router. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 152 As you might see there is one opened Telnet Session to the host 192.168.2.2 which is Router 3 IP address, but you might find as many as Telnet Session on your router and you might choose any one of those Session, by just typing the Command Resume & the Number of the Conn which refers to Connection, lets see the following how its does. As you might see the First line is the Show Session that we previously described it, and then the Command Resume and the number of the connection you want to resume to which we have only one session so we have choose number 1, and now we are in R3. Also there is a shortcut command were you type in the connection number, only and the router will resume it. Let’s see the following: As you might see I have just typed number 1 in the privilege mode in Router 2 and it resumed the connection to router 3 as the Router 3 is the connection number 1. Now if I opened a Session to Router 1 which is CBTRouter, and then returned back to Router 2, and make the Command Show Session: Now we have Two Sessions opened now on Router 2, one for Router 3 and the other to CBTRouter, if you notice the Sign Asterisk (*), that referred to the most recent Telnet Session that I have been using. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 153 If I hit the Enter Key on the Keyboard in the privilege mode it will resume the Most recent Telnet I have entered which is the one that has the Asterisk Key on it, also if I just type the number of the connection it will resume that Connection. As shown in the following Picture: • Third one is <Show Users>, it shows all the Opened session TO your Router. Now we are on Router 2 and we will use that command to show who is opening telnet Sessions on Router 2. As you might see only one Telnet Session is opened to Router 2 which is VTY 194, and it’s coming from IP address 192.168.1.50 Now if I switched to Router 3 and we typed this command again, we will see the following: As you might see only one Telnet Session is opened at the Location 192.168.2.1 which is (Router2) to Router 3. • Fourth one is <Disconnect>, which Kills one of your own Telnet Session FROM your router. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 154 Now we are on Router 2, and type in the command that shows the Sessions, and as you might see it has two Opened Session labels by number 1 & 2. if I typed the command disconnect and the number of the session it will close it for me, as following we have disconnect the Session number 2, and only one session is left. • Fifth one and the last one is <Clear line>, which Kills the Telnet session Opened TO your Router As you might notice we will clear line number 67 means we will disconnect that telnet session, which is from user 192.168.2.1, and then it will ask you to confirm and just hit Enter Key to confirm that. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 155 Ok lets look at the following TRICK!! We are now on Router 2. If you have noticed above there is no number for the Telnet Lines is showed, it just showing VTY 194, & VTY 195 without the VTY Line Number. So we will do the following Command to show the lines number. The highlighted number is the number of the VTY line which is by Coincidence the same Number of VTY 195. Ok we will kill that Opened Session to my router. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 156 Understanding the Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP): This protocol is very helpful, when you have a diagram like the following, with no information on it or IP address. There is a lot of times when you walk into a company and want to do some work, and the company may don’t have the Network Diagram, or their diagram is outdated or it just doesn’t have an IP address on it. So what CDP does is allows you to see Directly Connected, so if I write the CDP Command on Router 2 it will show me R3 and That Cisco Switch, so CDP works only and ONLY for CISCO Devices that’s what you have to know for exam, but in real world 3com and HP have license for CDP protocol from CISCO, so they will show up as well if they present in the network, but for the test and exam CCNA its only for CISCO Devices, TAKE CARE!!. CDP Protocol sends Broadcast to the Network every 60 Seconds for Updating the other Devices. Now we will access Router 2 by a Laptop through a Console Cable, because we don’t know any IP address for any Cisco devices on the Network, so we can’t Telnet. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 157 First of all I will do the following Command before starting the CDP: Were from this command we have defined the Interfaces of our Router and which one is Active with their Local IP address. Now we will write the following, but before that you will notice that you may write the CDP Commands on USER MODE OR PRIVILEGE MODE it doesn’t matter. Now as you might notice there are two devices one is named (CBTSwitch.cbtnuggets.com) and the other router is R3, so we are connected to R3 through Serial Interface 0/1/0, and the other through the FE 0/0. Let’s describe the line of R3 in the above Picture. • • • • • Local Interface: it’s the interface that I am connecting from R2 to R3. Hold Time: its how long since you have heard from that neighbor. Capability: R means it’s a Router. Platform: it’s the 2610 Model Router. Port ID: it’s the Remote interface that I am connected to them. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 158 Now lets move to the next Command: As you might see the Command Show CDP entry R3, shows information for R3 only, but you may write it as Show CDP entry *, which shows you all the Devices information connected. Now this shows more benefit Information, here we have the Device ID, and the Entry Address (192.168.2.2), which is the Remote IP address I connect to, also it tells the Platform 2610, and the capabilities is ROUTER, also it tells the Serial interface I am plugged and the Serial interface, I am going to, also the Hold Time which tells you the Time for our Router to wait the other Remote Router to hear from, were if this Time is over it will consider the Remote router is Down, and finally down you will see the IOS Version. Ok now you know the IP address of Router 3, so you may Telnet it. Now we will write the following Command in R3, after accessing it Telnet: As you might See Router 2 is shown in the table with the Interfaces info, which means that Router 3 doesn’t see any more Cisco Devices after it. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 159 We will do the following to show all the Interfaces on Router 3 with its IP address. Also we will see the neighbors of the Switch as following: As you might see its connected to a Access Server, Cat3550, and East which is Windows 2000 Server in the platform column, BUT we mentioned before that CDP only works on Cisco Devices so does that means it can see windows Server, the Answer is NO, cause what is here is a Cisco Server that runs on it a Windows 2000 Server, which is installed on it a CDP protocol. Now let’s see the following command which is equal to the command show cdp entry By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 160 You will see below in the picture, the highlighted line is windows 2000 server, but as that’s now a Windows Server it’s a Cisco Server that runs on it Windows Server, as we said before. As you have noticed the CDP protocol Send a lot of Sensitive information to whom request it, as it sends the Interfaces IP address and the IOS version and all the Connected Devices beside it, so to prevent that information from leaking out from some interfaces, or prevent it from provided it totally to any requested devices, we may use some specific Command for doing that. Let’s give an Example, R1 is connected to the ISP, and R1 is running CDP, and its running CDP to the internet, meaning that’s once every 60 Seconds it send out a broadcast to the internet giving its all Sensitive information, so you don’t want that information to get out to the internet, and you make sure it runs only inside your company. Ok let’s access CBTRouter which is R1, and the first thing we do is to disable CDP on the FE4: Soon as I have done that, its disabled on that interface. To Disable CDP on all the interfaces of the Router, we will do the Following in the Global Configuration mode: By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 161 Management and Security: File management It’s good to take a backup of your configuration and your IOS File, in this section we will see how we may make a Backup files, Copying to and from your Router. Understanding the Copy Command: Before we start on the copy command, let’s see the memory components of the Router, and the TFTP Server. The first one is RAM, the RAM present in the Cisco Switch or Cisco Router, is just as the RAM on your PC, the benefit of RAM, is its Extremely Fast, it’s able to read and write to it fast, however the Disadvantage of RAM is that when the power goes out everything is lost. Also the benefit of RAM is that it stores the Running Config and the Packets coming into the Router its stores permanently in the Ram till it look at the Table and decide which interface to get it out. The Second Memory we will talk about is NVRAM (Non Volatile RAM) and that is what we store in it the Running Config, were when you type <copy run config start config> its stored in the NVRAM, NVRAM is very small because it only store the Startup Config If I typed the following command: By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 162 We will see how much memory I have in my Router and other useful information, but we will concentrate in the Memory: As you might see, the first line is our RAM memory, which is written as 238592/23552K this is the RAM memory were CISCO devices Partition the RAM some times in to two partition, so if we add (238592 + 23552 = 262144K, which if I divide it by 1024 it will give the Result in Mega Byte, so 262144/1024= 256 MB of RAM). If you noticed also that the NVRAM size is too small (191K) cause it just stores the Startup Configuration File. Also if you noticed that the Flash memory has 62592K Total in size, Flash memory is used for storing the IOS, if you have noticed that when starting up the Switch or the Router, you will notice the ###### symbols all over the screen and that is due to its Decompressing and copying the IOS from the Flash to the RAM, cause as we said RAM is fast in running things on it, but FLASH and NVRAM are used for Storing the data only. Ok now the only last memory that is not present in our router is the TFTP (Trivial File Transfer Protocol), which is a Server that stores in it the files, the protocol that is used to transfer the file to the TFTP is UDP port 69, that in case you have a firewall and need to pass it. So TFTP is used to copy to and from the IOS image file to the Router. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 163 Ok how we may setup a TFTP, well its Free if you go to Google and type in the Search box TFTP32, and choose the first Result. So if you entered that site you just go down the page and find out the Download Link, so you download the program and install it, and now you have a TFTP server. So when you run the program you will find the following Screen By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 164 What we will do is we want to make a backup for our Configuration to the TFTP server, so we will do the following: Now it ask what is the IP of the TFTP server So from the TFTP program we setup its server interface is 192.168.1.50, see the above TFTP picture on the IP server Interface. After we write down the IP address of the TFTP server it , the Router will ask for what Name should the file will be, usually it’s better to save it with extension .txt or .doc so as to be able to open it on windows, if you want to review the file later. After that the file will be copied successfully as you see above in the picture, and you find it on your computer, according to the Current Directory in the TFTP program. Now we will back up the IOS File, but before that we need to know first the name of the IOS file. By using the following command it shows the IOS name: So by taking this File name Copy the IOS Name and Paste it in the following lets see how: This command above is described as follow, first copy the IOS File that is named (flash:c2801adventerprisek9-mz.124-4.XC.bin) into TFTP that its address is 192.168.1.50, and the file name to be saved in the TFTP is the same file name with the same extension on the flash which is (c2801-adventerprisek9-mz.124-4.XC.bin). By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 165 If you press ENTER it will ask you if you are sure of the information you have entered as following: You just keep pressing Enter, till it starts transferring the IOS file to the TFTP server, now if you see the TFTP program we have setup you will find that is copying the IOS file from the Router to your PC: Notice: When you copy anything to RAM, the IOS MERGE them, meaning if you have a backup Config file on the TFTP server, and you copied the Config file from TFTP to the RAM, what happens is that the Config file from the TFTP will not replace the Config file on RAM but it will merge them mean the two of them will be in one Config file with both features and configuration. As example if you have setup your FE0/0 in RAM by IP address 192.168.2.1, and in the Config File in TFTP its configured as 192.168.3.1, in here the one that is in the TFTP will replace that in the RAM by 192.168.3.1, cause when there is a conflict between the Configuration in RAM and TFTP Config file, the Config which comes from the TFTP file Replace the one in RAM if they both exist. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 166 The Disadvantage thing is if you configured a NAT on the Router and you don’t need it anymore and the NAT Config is not present in the Configuration file at TFTP, and you copied the Config TFTP file to RAM, the NAT Configuration will still exist in RAM, cause there is no conflict or nothing overwrite it or replace it from the TFTP File Config to RAM file Config. So what you do if you want the TFTP config file only works on RAM and no previous Config exist in RAM, just the New Config needed, well this Is done by copying the TFTP Running Config to the NVRAM (Startup Config.), cause in this Case the Configuration file is replaced in NVRAM by the one comes from the TFTP rather than Merging it. Ok now we need to copy the Configuration file from NVRAM to RAM, what we will do, is to REBOOT the Router, because copying the Config file from NVRAM to RAM will merge it and it will not be replaced. So we will copy the Config file from TFTP to NVRAM as following: As you might see in the fourth line it asks for the Destination Filename what should be its name, so by Default you should leave the name Startup-Config cause that the file name the router is looking at it when it reboots, so don’t rename it. If you want to upgrade your IOS, a lot of times people delete their IOS from the Flash Memory and download a new IOS from Cisco sites and place it in the Flash memory. But the safe way to do this is actually to allow your router to boot-up from the TFTP server rather than boot-up from Flash Memory, and keep the old IOS in the flash memory as it is. So we download the New version of IOS in to the TFTP server, and make the router to boot up and take the IOS file from TFTP server rather than Flash, so we will do the following: By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 167 As you might see it says where do you want to boot from, so we will boot from the TFTP server with the IOS Filename as following: At that point the next time the router boot it will boot from the TFTP server, with the mentioned IOS File name, but if it didn’t find that file on TFTP server it will revert by default to the Flash memory and load the IOS in the Flash Memory. By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 168 n اl( m By Eng. Waleed Mohsen Page 169