African Music
advertisement

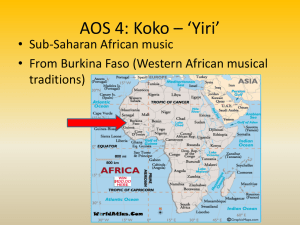
African Music Music has important role in society. Important in terms of religion and festivals / celebrations. Often combined with dance and speech. Rich, diverse traditions throughout Sub-Saharan tradition (south of the Sahara). Repetition Improvisation Polyphony Call and response Types of music: drumming, choral song, instrumental music. Drumming Most common: Djembe – frequently used in groups Dundun – double headed, hit with sticks Donno – talking drum. No notation Use of call and response Solos. Steady beat – timeline. Highly complex rhythms Polyrhythms created from cross rhythms. Choral singing Call and response Short, simple melodies Improvisation Rounds Harmony Strong link between singing and speech. African languages are tonal. This means that the pitch level of the speaking voice helps to determine the meaning of the words. Isicathamaya – quite, harmonious style that originated in mines of South Africa. Choral music often includes portamento (sliding between notes). Instrumental music Instrument classification Idiophones – percussion but not drums. Mbira (thumb piano quite important) Membranophones – drums made from wood, gourds, metal, earthenware. Aerophones – wind Chordophones – strings Repetition Improvisation Cyclic structures Polyphonic textures Interweaving melodies Minimalist music shares some characteristics with African music – polyrhythms, linear texture.