2.3 - Other Types of Graphs.notebook
advertisement

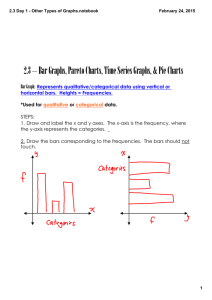
2.3 ­ Other Types of Graphs.notebook 2.3: Other Types of Graphs February 19, 2013 Date: 2/19 Bar Graph: _________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ *Used for _______________ or ________________ data. STEPS: 1. Draw and label the x and y axes. The x­axis is the frequency, where the y­axis represents the categories. 2. Draw the bars corresponding to the frequencies. The bars should not touch. 1 2.3 ­ Other Types of Graphs.notebook February 19, 2013 Pareto Charts: _____________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ *Used for qualitative or categorical data. STEPS: 1. Arrange the data from the largest to the smallest according to frequency. 2. Draw and label the x and y axes. 3. Draw the bars corresponding to the frequencies. 2 2.3 ­ Other Types of Graphs.notebook February 19, 2013 Time Series Graph: __________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ STEPS: 1. Draw and label the x and y axes 2. Label the x­axis for the time and the y­axis for the frequency 3. Plot each point according to the table 4. Draw line segments connecting adjacent points. Do not try to fit a smooth curve through the data points. *A Compound Time Series Graph compares two or more data sets on the same graph. 3 2.3 ­ Other Types of Graphs.notebook February 19, 2013 The Pie Chart: _______________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ STEPS: 1. Since there are 360° in a circle, the frequency of each class must be converted to represent a proportional part of the circle. To convert: Degrees = 2. Each frequency must also be converted to a percentage(%). %= 3. Using a protract and compass, draw the graph using the appropriate degree measures found in Step 1. Label each section with the name and percentages. 4 2.3 ­ Other Types of Graphs.notebook February 19, 2013 Page 84, Example #4: Construct a pie chart: 80 90 100 90 80 110 70 120 60 100 110 50 60 120 140 50 130 40 130 70 40 150 5° 140 30 30 160 150 20 20 160 10 170 0 180 10 0 170 180 5 2.3 ­ Other Types of Graphs.notebook February 19, 2013 Assignment #4 ­ Due (2/21) pg. 84 #1, 3, 6 (time series), 10 pg. 84 #13, 14, 15, 17, 24, 25 iPads ­ Tomorrow & Thursday Media Lab ­ Monday & Wednesday (next week) Chapter 2 Test ­ Tuesday Projects ­ Due next Thursday 6