Science 10 Exam Review
advertisement

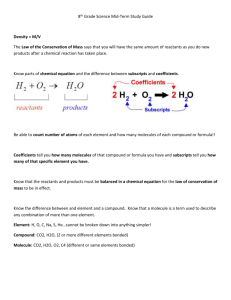
Science 10 Exam Review Biology 1. What is an ecosystem? 2. How does sunlight enter the food chain? 3. Explain how changes in one part of a food web affect populations in other parts of the web. 4. Why are there rarely more than four links in a food chain? 5. Draw a pyramid of numbers, biomass, and energy for an ecosystem. 6. Write the formula for photosynthesis. 7. Write the formula for cellular respiration. 8. What produces more energy per unit of land area? Plants or animals? 9. What are carnivores? 10. What are herbivores? 11. What are omnivores? 12. What do detritivores eat? 13. Give an example of a producer. 14. Give an example of a primary consumer. 15. Give an example of a secondary consumer. 16. Give an example of a tertiary consumer. 17. How can DDT spread through a food chain? 18. What is biological magnification? 19. What is the relationship between DDT concentration and trophic level? 20. What is carrying capacity? 21. List four factors that determine carrying capacity. 22. One of the main ingredients in fertilizer is 23. Nitrogen is an essential part of _____________________, ___________, and _____________________________. 24. Carbon dioxide only makes up _______________ of Earth’s atmosphere. 25. Photosynthesis is one stage if the___________________________. During photosynthesis, plants capture ____________________ and combine it with ___________________ to make carbohydrates. Some carbon is used by plants to build other carbon-containing compounds, such as ______________________________. 26. What three things does a tree need to make carbohydrates? 27. Earth is a ____________________system. What is a closed system? 28. What are nutrients? 29. Over the years, carbon dioxide produced by cellular respiration has tended to __________________ the amount of carbon dioxide absorbed by photosynthesis. However, the balance can be changed if ________________________ of carbon are _____________________ or _____________________ parts of the carbon cycle. 30. Be able to draw a simple carbon cycle and explain what is happening. 31. Be able to draw and explain the nitrogen cycle. Be able to explain nitrification, denitrification and nitrogen fixation. Chemistry 1. Describe how the elements are organized on the periodic table (Groups, periods, metals, .non-metals, metalloids) 2. Know how many shells in Periods (1,2,3,4) 3. Know how many valance electrons in Groups 1, 2, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18 4. Know how to find the # of protons, electrons, and neutrons. 5. Be able to draw electron shell diagrams for any of the first 20 elements and show the corresponding electron dot diagrams. 6. Be able to draw electron dot diagrams for individua l elements, binary ionic compounds, and binary molecular compounds 7. State which type of element tends to form cations and which type tend to form anions. Give an example for each. 8. Know how to find cations and anions with the same number of electrons as noble gases. 9. Know the definitions for atom, proton, electron, neutron and nucleus 10. Know the physical properties that are the same and different for oxygen and hydrogen. 11. Distinguish between an ionic compound and a molecule. Give an example of each. 12. Be able to use the X rule to make formulas for binary ionic compounds 13. Name two atoms that would combine to form a covalent bond. 14. Be able to name binary ionic compounds and molecules. 15. Name two atoms that would combine to form an ionic compound. 16. Know what a noble gas is. 17. Know the properties of a metal, non-metal and metalloid. 18. Define the term “binary compound”. Give the name and formula of a binary compound and a binary molecular compound. 19. Give at least 3 examples of compounds of transition metals. Name 3 compounds with the classical system and Stock system. 20. Write the name and formula for 2 polyatomic ions. 21. State the Law of conservation of Mass. Explain how it is related to writing a balanced equation. 22. Tell the difference between an acid and a base. Know who Svante Arrhenius is. Be able to give examples of acids and bases. 23. Know the difference between endothermic and exothermic reactions. 24. Be able to balance equations and classify reactions as: combustion, single displacement, double displacement, synthesis, decomposition. 25. Know what the pH scale is and what acids and bases are on the pH scale. Physics 1. Be able to convert between (milli, centi, deci, (g, m, l) decka, hecto, kilo 2. Be able to change m/s to km/hr and km/hr to m/s 3. Know significant digits (how to find out how many are significant). Know how to multiply and divide using significant digits and how to add and subtract using significant digits. 4. Be able to put numbers in scientific notation and be able to put scientific notation into numeric notation. 5. Know the difference between a scalar and a vector. 6. List some machines that measure motion 7. Know the two conclusions that scientists have agreed upon about motion. 8. Know distance, displacement, time, position, velocity, speed acceleration (we had notes on these that you have to know) 9. Know the formulas for the vectors/scalars listed above and how to rearrange them 10. Know how to do questions on distance/displacement, velocity, acceleration 11. Know what + and – mean in physics Questions ____ 1. Atom ____ 2. Proton ____ 3. Neutron ____ 4. Electron ____ 5. Nucleus ____ 6. outer shell ____ 7. valence electrons ____ 8. Ca+2 ____ 9. O-2 ____ 10. Al+3 a. neutral b. protons and neutrons c. valence shell d. electrons in the outer shell e. aluminum cation f. negative charge g. oxygen anion h. calcium cation i. positive charge j. smallest possible particle of a chemical element that retains its chemical properties . True or False ______ 1. Periods on the periodic table tell how many valence electrons an element has. ______ 2. Groups on the periodic table tell how many shells an element has. ______ 3. The element in Group 2, Period 3 is Beryllium ______ 4. The element in Group 18, Period 2 is Neon ______ 5. The element in Group 5, Period 4 is Tin. ______ 6. Hydrogen is a non-metal. ______ 7. Lithium is a non-metal. ______ 8. Gold is a metalloid. ______ 9. Helium is a noble gas. ______ 10. Fluorine has 7 valence electrons. Multiple Choice (10 points): 1. The first shell or energy level of an element can hold _______ electrons. a. 1 c. 2 b. 4 d. 8 2. The second shell or energy level of an element can hold _____ electrons. a. 1 c. 2 b. 4 d. 8 3. Elements in Period 3 have _______ energy levels or shells. a. 1 c. 3 b. 2 d. 4 4. Hydrogen has _______ protons. a. 1 b. 2 c. 3 d. 4 5. Carbon has _______ protons. a. 2 b. 6 c. 4 d. 8 6. Fluorine has _______ neutrons. (Round to the nearest whole number) a. 9 c. 10 b. 11 d. 19 7. Copper has ______ neutrons. a. 29 b. 35 c. 30 d. 64 8. Neutral sodium has ________ electrons. a. 11 c. 1 b. 3 d. 23 9. When a neutral atom gives up an electron, it becomes a positively charged ion known as a: a. anion c. electron b. protons d. cation 10. When a neutral atom gains electrons, it becomes a negatively charged ion known as a: a. anion c. electron b. protons d. cation Diagrams: Draw electron dot diagrams to represent the following elements. (10 points) a. Be b. S c. O d. Cl e. H Diagrams: Using electron dot diagrams, show how these ionic compounds form. (10 points) Remember to use brackets in the final answer. a. CaO b. KF c. LiCl d. MgCl2 e. Na2 O Diagrams: Using electron dot diagrams, show how these molecules form. (10 points) 1. F2 2. H2 O 3. O2 4. N2 5. CO2 6. Think of two cations and two anions that have the same number of electrons as an atom of Krypton. Use chemical symbols to represent these cations and anions. (4 points) Cations Anions ________ _________ ________ __________ Matching (10 Points) ____ 1. Endothermic a. substance that produces hydrogen ions in a solution ____ 2. Exothermic b. defined acids and bases ____ 3. Acid c. containing 2 elements ____ 4. Base d. 2 non-metals ____ 5. Ionic Compound e. a metal and a non-metal (cation + anion) ____ 6. Molecule f. metals that have more than one charge ____ 7. Binary Compound g. require the addition of energy ____ 8. Polyatomic Ionic h. substance that produces hydroxide Compounds ions (OH-) in a solution ____ 9. Transition Metals i. energy releasing reactions ____ 10. Svante Arrhenius j. have more than one non-metal + a metal (e.g. CaCO3 ) . True or False (10 points): ______ 1. Elements in Period 3 have 3 shells. ______ 2. Elements in Group 2 have 2 valence electrons. ______ 3. Acids are 7 and above on the pH scale ______ 4. Bases are 7 and below on the pH scale ______ 5. 7 is neutral on the pH scale ______ 6. Some acids and bases can be used as medications ______ 7. In a synthesis reaction, a compound falls apart. ______ 8. In a single displacement reaction, two elements switch places. ______ 9. In a double displacement reaction, one element gets left alone. ______ 10. Combustion occurs when you add hydrogen. Fill in the blank (10 points) 1. Two examples of acids are ________________________ and _______________________________. 2. Two examples of bases are ______________________________ and _______________________________. 3. Reactants are on the ______________________ side of the arrow in an equation. 4. Products are on ten ______________________ side of the arrow in an equation. 5. Combustion occurs when you add _______________________. 6. An example of an ionic compound is ______________________. 7. An example of a molecular compound is _____________________________. 8. An example of a transition metal (just the transition metal) is _____________________________. 1. Look at the following equation. KOH + HBr => KBr + H2 O a. Balance the equation. ______ KOH +_____ HBr => _____ KBr + _______ H2 O b. Classify the type of reaction. Circle one of the following: synthesis, decomposition, single displacement, double displacement, combustion. c. Name all of the chemicals in the formula to make a word equation. _______________________ + ______________________ => ________________________ + ______________________ 2. Look at the following equation. aluminum hydroxide + hydrogen bromide => aluminum bromide + dihydrogen monoxide a. Make formulas for the equation. _________ + ___________ => _________________ + _________________ b. Balance the equation. ___ ______ + ___ _____ => ____ ________ + ___ __________ c. Classify the type of reaction. Circle one of the following: synthesis, decomposition, single displacement, double displacement, combustion. True or False (10 points): ______ 1. The symbol ∆ is pronounced “delta” and means “change in”. ______ 2. Distance is a vector quantity, so it has a magnitude (size) but no direction. ______ 3. Position describes how much an object’s position has changed. ______ 4. Displacement is a vector. ______ 5. Speed describes how far something has moved. ______ 6. Acceleration describes how much an object’s velocity changes in a certain time. ______ 7. Acceleration results from any change in speed. ______ 8. Earth’s gravity makes objects accelerate at 9.8 m/s2 downward. ______ 9. Speed is a scalar and does not indicate direction. ______ 10. Because of the language of physics, observations made in one place, by one scientist, can be understood correctly by other scientists working in other places. Scalars or Vectors: Tell whether the following are scalars or vectors (5 points): 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Distance Time Velocity Acceleration Displacement _____________ _____________ _____________ _____________ _____________ Convert the following (10 points): 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 1 m = _________ mm 250 g = ________ kg 1000 kg = __________ mg 90 cm = _______ m 95 m = _______ km 6. 678 mg = ________ g 7. 10000 kl = ________ L 8. 52 g = _______ mg 9. 50 cl = ________ ml 10. 6500 cg = _________ hg Convert the following. Show your work. (10 points) 1. 10 m/s = _________ km/hr 2. 25 km/hr = ___________ m/s 3. 650 m/s = _____________ km/hr 4. 45 m/s = ___________ km/hr 5. 65 km/hr = ______________ m/s Significant Figures: Tell how many significant digits are in the following. (5 points) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 0.0092 100 1.0 x 105 1030 1.0650 _________ _________ _________ _________ _________ Add/Subtract or Multiply/Divide the following. Write your answer using the significant digits rules (10 points) 1. 45 – 10.0 = 2. 100 + 12 = 3. 50 / 2 = 4. 3 x 52 = 5. 100 x 12 = _________ _________ _________ _________ _________ 6. 32.65 + 31. 3 = 7. 0.0045 – 0.0032 = 8. 150 x 325 = 9. 4.0 / 5.2 = 10. 25.657 – 22.78 = _________ _________ _________ _________ _________ Write the following in scientific notation. (5 points) 1. 23 000 000 ______________ 2. 65 289 000 ______________ 3. 7 890 ______________ 4. 6 785 ______________ 5. 0.00050080 ______________ Write the following in numeric notation. (5 points) 5.01 x105 1. ______________ 6.78 x 10 - 9 ______________ 3. 8.90 x 10 -4 ______________ 4. 5.0 x 104 2. 5. 4.6578 x 10 ______________ 5 ______________ 1. In 1999, a racecar driver was in the Daytona 500. He completed 500 laps at 1000 m a lap. He finished where he started. What was his total displacement? (For this question you do not have to show your work. Answer in sentence format.) (5 points) 2. A person started watching a movie at 5.10 s. They finished watching the movie at 801 s. How long did they watch the movie? (Show your work with a formula. Put your final answer into a sentence at the end.). (5 points) 3. A car traveled 501 m in 23 seconds. What was the average velocity? (Show your work with a formula. Put your final answer into a sentence at the end.). (5 points) 4. How long would it take for a car to accelerate from 10m/s to 25 m/s with an acceleration of 25 m/s 2 ? (Show your work with a formula. Put your final answ er into a sentence at the end.). (5 points) 5. What is the acceleration of a train that has a change in velocity of 110 m/s and a change in time of 25 s? (Show your work with a formula. Put your final answer into a sentence at the end.). (5 points) 6. If a person left their house and started running at 5 km/hr. They ran for 15 minutes with an acceleration of 2 km/hr 2 . What was the final velocity? (Show your work with a formula. Put your final answer into a sentence at the end.). (5 points) * hint – start by changing minutes to hours. Formulas Time: ∆t = tf - ti Distance: ∆d = df - di Velocity: ∆v = vf - vi Vav = ∆d ∆t Acceleration: a = ∆v ∆t