EXAMPLE EXAM QUESTIONS - MULTIPLE CHOICE
advertisement

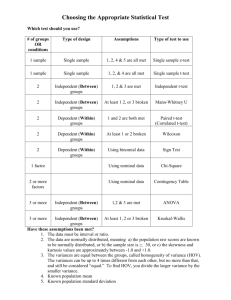
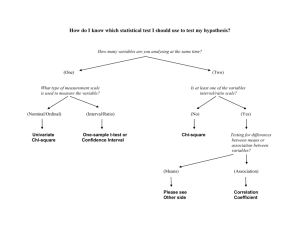
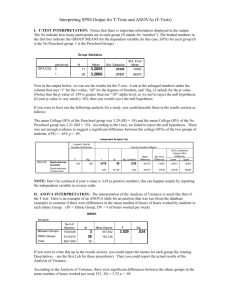
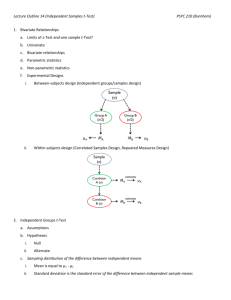
EXAMPLE EXAM QUESTIONS - MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Lisa is appointed as a research assistant of the marketing department at K.U.Leuven. She was hired to investigate whether perceptions regarding the educational system differ between students of different nationalities. Before collecting primary data, Lisa inspects secondary data. Which of the following sources could she have consulted to collect secondary data? A. Reports about the advantages and disadvantages of different learning systems from the Belgian Ministry of Education (publicly available via Google). B. Reports about studying abroad from private research organizations (publicly available via Google). C. Previous results from course evaluations (available via the intranet). D. All of the above. 2. All of the following techniques are commonly used in exploratory research EXCEPT A. In-depth interviews with key informant survey. B. Examination of purchase behavior through observation. C. Experiments. D. Qualitative research through focus groups. 3. What are the advantages associated with secondary data A. Variation in definition of terms. B. Stronger than primary data. C. Faster than primary data. D. All of the above. 4. Which of the following is a non-probability sampling plan? A. Convenience sampling. B. Judgment sampling. C. Quota sampling. D. All of the above. (5.) H0: Intentions to buy computers via the Internet do not depend on nationality Ha: Intentions to buy computers via the Internet do depend on nationality 5. Assume that ‘intentions to buy computers via the Internet’ has been measured using a 5-point Likert interval scale, which of the following tests is appropriate? A. Independent samples t-test. B. One sample t-test. C. Simple regression analysis of intentions to buy computers via the Internet on nationality. D. Chi-square test for goodness-of-fit. (6.) Assume that researchers want to find out whether the satisfaction with life is dependent on gender for which they created the following hypotheses: H0: Women are equally or less satisfied with life than men. Ha: Women are more satisfied with life than men. Respondents had to answer the following questionnaire question: how satisfied are you with the life you are currently living? They could answer on a scale from 1 (very dissatisfied) to 7 (very satisfied). Group Statistics SatisfactionwithLife sex 1 2 N 185 251 Mean 4,3341 4,5801 Std. Deviation 1,30491 1,38220 Std. Error Mean ,09594 ,08724 Independent Samples Test Levene's Test for Equality of Variances F SatisfactionwithLife Equal variances assumed Equal variances not assumed Sig. ,706 ,401 t-test for Equality of Means t df Sig. (2-tailed) Mean Difference Std. Error Difference 95% Confidence Interval of the Difference Lower Upper -1,881 434 ,061 -,24603 ,13081 -,50313 ,01108 -1,897 408,528 ,059 -,24603 ,12968 -,50094 ,00889 6. Looking at the output above, what would you conclude if you coded 1 = male and 2 = female (at a significance level of 5%)? A. One cannot reject H0 because the observed level of significance is 0.061. B. One can reject H0 because the observed level of significance is 0.0295. C. One can reject H0 because the observed level of significance is 0.0305. D. One cannot reject H0 because the observed level of significance is 0.059. (7.) Do you also think patriotic French people should buy imported cars when that would put French workers out of employment? O Yes O No O Don’t know 7. This is an example of: A. A double-barreled question. B. A leading question. C. A screening question. D. A sensitive question. (8.) Statement I: A question that is asked to disguise the purpose or sponsorship of a project is called a context question. Statement II: Sometimes several questions are needed instead of one. If the researcher ignores this, s/he is likely to formulate a double-edged question. 8. Which of the following statements is true? A. Statement I is true, statement II is false. B. Statement II is true, statement I is false. C. Statement I and II are true. D. Statement I and II are false. (9.) A marketing manager wants to know whether loyal customers would buy their toothpaste if the price would rise with 10%. He formulates the following hypotheses: H0: Loyal customers are neutral or positively inclined to buy our toothpaste in case of a price increase of 10%. Ha: Loyal customers are negatively inclined to buy our toothpaste in case of a price increase of 10%. He asked 100 people the following question: If the price of the toothpaste you are currently using would increase with 10%, how likely would it be that you would buy it next time you need toothpaste? Very likely Neutral Very unlikely 1 2 3 4 5 9. What kind of test would you use to test the following hypothesis? A. A Chi-square test for goodness-of-fit. B. A Chi-square test for independence. C. An independent samples t-test. D. A one-sample t-test. (10.) Consider the following 2 questions from a questionnaire: * Question 1: How secure do you feel about using online banking services (one answer possible) Very secure Secure Indifferent Insecure Very insecure 1 2 3 4 5 * Question 2: What have you bought on the Internet during the past 6 months? (more than one answer possible) 1. DVDs 2. CDs 3. Books 10. If you would enter the data you gathered with these two questions in SPSS, how many columns would be used? A. 2 columns. B. 4 columns. C. 6 columns. D. 8 columns. (11.) Consider the following screenshot: Which of the following set of null and alternative hypotheses could be tested if you know that the variable ‘Appreciate’ measures ‘how much do you appreciate the current course scheduling procedure’ on a 5-point Likert scale (1=dislike a lot, 2=dislike, 3=neutral, 4=like, 5= like a lot)? A. H0: Students have a neutral appreciation regarding the course scheduling procedure. Ha: Students do not have a neutral appreciation regarding the course scheduling procedure. B. H0: Students have a neutral or negative appreciation regarding the course scheduling procedure. Ha: Students have a positive appreciation regarding the course scheduling procedure. C. H0: Students have a neutral or positive appreciation regarding the course scheduling procedure. Ha: Students have a negative appreciation regarding the course scheduling procedure. D. All of the above. (12.) Emma wants to find out if the time that someone spends in the first round of registration differs between males and females. She has the following set of hypotheses: H0: There is no difference in the time that males spend in the first round of registration compared to the time that females spend. Ha: There is a difference in the time that males spend in the first round of registration compared to the time that females spend. She measures the time that someone spends with an open question where respondents could indicate the number of minutes spent in the registration, and asks respondents whether they are male or female. 12. Which is the most appropriate test to do with these variables (no recoding)? A. Chi-square for independence. B. ANOVA. C. Independent samples t-test. D. Regression. (13.) Consider the set of hypotheses in question 12. If the questionnaire question that was used to measure the time spent would have been a closed question with the following answer options: < 10 minutes, 10-19 minutes, 20-40 minutes, > 40 minutes, which is the most appropriate test? A. Chi-square for independence. B. ANOVA. C. Independent samples t-test. D. Regression. (14.) Emma tests the following set of hypotheses with an independent samples t-test: H0: Students that spend more than 15 minutes in the first round of registration give the same or a higher evaluation for the current course scheduling procedure than students that spend 15 minutes or less. Ha: Students that spend more than 15 minutes in the first round of registration give a lower evaluation for the current course scheduling procedure than students that spend 15 minutes or less. She gets the following output: 14. Which of the following statements is true? A. One cannot assume equal variances because the p-value of the Levene’s Test for Equality of Variances is .786. B. One cannot assume equal variances because the p-value of the Levene’s Test for Equality of Variances is .393. C. One can assume equal variances because the p-value of the Levene’s Test for Equality of Variances is .786. D. One can assume equal variances because the p-value of the Levene’s Test for Equality of Variances is .393. (15.) Which of the following statements is true? A. The evaluation of students that spend > 15 minutes is not significantly different from the evaluation of students that spend <= 15 minutes because the p-value of the t-test is .450. B. The evaluation of students that spend > 15 minutes is not significantly different from the evaluation of students that spend <= 15 minutes because the p-value of the t-test is .225. C. The evaluation of students that spend > 15 minutes is not significantly different from the evaluation of students that spend <= 15 minutes because the p-value of the t-test is .449. D. The evaluation of students that spend > 15 minutes is not significantly different from the evaluation of students that spend <= 15 minutes because the p-value of the t-test is .2245.