Photosynthesis and Elodea
advertisement

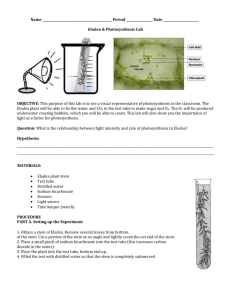
Photosynthesis and Elodea By Matthew Abolafia Abstract Abstract This lab is about Elodea and photosynthesis, and how the distance of a light source affects the rate of photosynthesis. The lab may influence plant growers to place their plants closer to a light source, to increase the rate of photosynthesis. The experiment proved that if the light source was too far away, photosynthesis would be slower and less productive. The procedure was to place Elodea under heat lamps and count the bubbles of photosynthesis in test tubes. A higher count of bubbles showed a higher rate of photosynthesis. The variables were photosynthesis and the distance of the light source. The results were recorded for 1 trial. When the lamp was closest to the Elodea, the amount of bubbles of photosynthesis was 39, a fast rate of photosynthesis. As the lamp rose in height, the number of bubbles dropped, showing slower rates of photosynthesis This experiment could influence botanists who produce Elodea by helping to increase their harvest rates. Research: Part 1: Photosynthesis Photosynthesis is a cycle gone through by plants to convert light into chemical energy for later use. Photosynthesis starts in chloroplasts, which are a part of the plant. The chloroplasts capture chlorophyll, an important chemical needed for photosynthesis. Chloroplasts also capture water, carbon dioxide, oxygen and glucose. The chlorophyll is taken to the stroma, another part of the plant. In the stroma the carbon dioxide and water blend together to make oxygen and glucose. The oxygen keeps all species on earth alive because animal cells need an aerobic environment, or air filled environment to survive. The glucose produced by the chloroplasts is used in many ways by different animals. Glucose is absorbed into the animals’ bloodstream where it is used as a nutrient. Photosynthesis does not happen all at one time, photosynthesis is divided into two important sections. The first is light-independent reactions. These reactions happen when light energy is captured and made into a chemical known as Adenosine triphosphate, or ATP. ATP is an enzyme used for reproduction, in a more modern term ATP is the molecular unit of currency for reproduction. The second step of the process occurs when ATP is used to create glucose, this is the light dependent reaction (Rader, 1997). Photosynthesis takes electrons from water to energy-lacking carbon dioxide molecules, forming energetic sugar molecules. This movement of electrons is an example of an oxidation reduction process. “The water loses electrons and becomes oxidized,” (Pearson, 2014). Then, the oxidized water is taken to a different species. Photosynthesis uses light energy to transfer electrons from water to more energetic states in sugar molecules, therefore changing solar energy to chemical energy (Pearson, 2014). Research: Part 2: Elodea Elodea is also called: American elodea, common elodea, anacharis and Canada waterweed (Aquatic Biologists, 2014). Elodea can grow in heights between 4 inches to 3 feet, depending on the depth of the body of water. Elodea is an underwater marine plant with oval shaped leaves grouped into clusters of 3 or 4 around the stem that provides shelter for fish and other sea organisms, and is an excellent producer of much needed oxygen. Elodea is a food for geese and ducks, who feed on the fruit produced by Elodea. Elodea reproduces by growing large buds in the springtime, relying very little on seed reproduction. Because Elodea relies on a fragmenting process of breaking off stem particles that sink to the ground and grow a new plant. But along with its advantages, Elodea has some disadvantages. If populations of Elodea become overly crowded, Elodea can reduce water temperatures, which can disturb sea life and possibly kill them. Dense growth can become a poorer habitat for fish. Elodea is a common aquarium plant, but even though it is very common, most people don’t know its name. Its common name is “that aquarium plant.”(Rader, 1997; Swistock 2014). Elodea grows in pond habitats and prospers in the fine sediment at the bottom of cool, spring-fed ponds. Elodea is one of the few pond plants that can remain green throughout the cold winter season.” (Swistock, 2014). Question and Hypothesis Question \ Hypothesis Does the distance of a light source from an Elodea plant affect the rate of photosynthesis? If the light source is closer to the plant, then the rate of photosynthesis will be faster, because the light is closer and more intense. Variables and Materials Variables Materials The independent variable was the distance of the light source from the plant. The dependent variable was the rate of photosynthesis of the Elodea plant. Elodea (15.24 cm stem) 3 stems Distilled Water 50 ml 500 ml Beaker 1 Heat Lamp 3 Test Tubes and Rack 1 Rack, 3 Test Tubes Tape and Marker 1 of each Goggles 1 Ruler (30.44 cm) 1 Scissors 1 Procedures 1. Put on necessary safety items (apron and goggles) 2. Obtain materials and label test tubes T1, T2, T3, and Ctrl Procedures 3. Pour 50 ml of water in a single test tube 4. Place 15.24 cm Elodea in a single test tube and place test tube on rack 5. Adjust heat lamps to heights of 25 cm, 31 cm, and 45 cm. 6. Place test tube rack under heat lamp of height indicated for that trial 7. Turn lamp on and carefully count bubbles on Elodea stem for 5 minutes 8. Repeat steps 3-8 for trials 2 and 3 9. For Ctrl, time for five minutes outdoors in the sun 10. Record results in journal Results 50 45 40 Lamp Height (cm) Bubbles counted 35 25 39 30 31 21 25 45 19 20 15 10 5 0 1 2 Lamp Height (cm) 3 Bubbles counted Conclusion: Part 1 The purpose of this lab was to find how the distance of a light source from a plant would affect the rate of photosynthesis. In the lab, the independent variable, or the distance of the light source, affected the dependent variable, or the rate of photosynthesis; when the light source was farther, the photosynthesis would decrease due to the decreased intensity of heat and light. Whereas if the light source was closer, the intensity would increase, thus increasing photosynthesis (refer to graph for reference). The hypothesis of the lab was if the Elodea is placed farther from the light source, then it would lower the rate of photosynthesis. The hypothesis was supported because when the light was closest (25 cm above the plant), the bubble count was 39. When the light source was raised to 31 cm from the plant, the rate went down to 21. When the lamp was raised to 45 cm, a count of 19 bubbles was recorded. Conclusion: Part 2 The control recorded outside in the sun offered a count of 28 bubbles. The bubble count indicated the rate of photosynthesis; if there was a higher count that meant that there was a higher rate of photosynthesis. As the results showed, when the light source was the closest the count was the highest. That proved the hypothesis correct. In the experiment, there were some procedural errors that may have affected the data. One of those errors was the possibility of recounting the same bubble. In the 3rd run of the first trial, the lamp was crooked and may have not focused the full beam intensity. If the lamp had not been crooked, the results may have changed. The largest error was the fact that not all of the trials were finished. Only trial 1 was recorded due to the fact that there wasn’t enough time to do a total of 15 minutes of counting for 3 trials. Conclusion: Part 3 This lab may change if the light source is more natural, like the sun at different times of day. It would most likely extend to only 1 trial a day, as you would have to count at sunrise, noon and sunset. But the results may be more reliable. This lab would affect the real world for plant growers and harvesters. If farmers put their plants closer to the light, photosynthesis would increase, as the experiment results show. Bibliography Aquatic Biologists (2014) Weed Info-Elodea (Canadian Water Weed) Rader, Andrew (2014) Photosynthesis Retrieved from http://www.biology4kids.com/files/plants_photosynthesis.html Pearson (2014) An Overview of Photosynthesis Retrieved from https://www.aquaticbiologists.com/algae--weed-id-guide/submergedweeds/elodea-(canadian-water-weed) Retrieved from http://www.phschool.com/science/biology_place/biocoach/photosynth/overview.html Swistock, Bryan (2014) Elodea (Common Waterweed) Retrieved from http://extension.psu.edu/natural-resources/water/ponds/pondmanagement/aquatic-plants/elodea-common-waterweed Photosynthesis and Elodea By Matthew Abolafia Abstract Abstract This lab is about Elodea and photosynthesis, and how the distance of a light source affects the rate of photosynthesis. The lab may influence plant growers to place their plants closer to a light source, to increase the rate of photosynthesis. The experiment proved that if the light source was too far away, photosynthesis would be slower and less productive. The procedure was to place Elodea under heat lamps and count the bubbles of photosynthesis in test tubes. A higher count of bubbles showed a higher rate of photosynthesis. The variables were photosynthesis and the distance of the light source. The results were recorded for 1 trial. When the lamp was closest to the Elodea, the amount of bubbles of photosynthesis was 39, a fast rate of photosynthesis. As the lamp rose in height, the number of bubbles dropped, showing slower rates of photosynthesis This experiment could influence botanists who produce Elodea by helping to increase their harvest rates. Research: Part 1: Photosynthesis Photosynthesis is a cycle gone through by plants to convert light into chemical energy for later use. Photosynthesis starts in chloroplasts, which are a part of the plant. The chloroplasts capture chlorophyll, an important chemical needed for photosynthesis. Chloroplasts also capture water, carbon dioxide, oxygen and glucose. The chlorophyll is taken to the stroma, another part of the plant. In the stroma the carbon dioxide and water blend together to make oxygen and glucose. The oxygen keeps all species on earth alive because animal cells need an aerobic environment, or air filled environment to survive. The glucose produced by the chloroplasts is used in many ways by different animals. Glucose is absorbed into the animals’ bloodstream where it is used as a nutrient. Photosynthesis does not happen all at one time, photosynthesis is divided into two important sections. The first is light-independent reactions. These reactions happen when light energy is captured and made into a chemical known as Adenosine triphosphate, or ATP. ATP is an enzyme used for reproduction, in a more modern term ATP is the molecular unit of currency for reproduction. The second step of the process occurs when ATP is used to create glucose, this is the light dependent reaction (Rader, 1997). Photosynthesis takes electrons from water to energy-lacking carbon dioxide molecules, forming energetic sugar molecules. This movement of electrons is an example of an oxidation reduction process. “The water loses electrons and becomes oxidized,” (Pearson, 2014). Then, the oxidized water is taken to a different species. Photosynthesis uses light energy to transfer electrons from water to more energetic states in sugar molecules, therefore changing solar energy to chemical energy (Pearson, 2014). Research: Part 2: Elodea Elodea is also called: American elodea, common elodea, anacharis and Canada waterweed (Aquatic Biologists, 2014). Elodea can grow in heights between 4 inches to 3 feet, depending on the depth of the body of water. Elodea is an underwater marine plant with oval shaped leaves grouped into clusters of 3 or 4 around the stem that provides shelter for fish and other sea organisms, and is an excellent producer of much needed oxygen. Elodea is a food for geese and ducks, who feed on the fruit produced by Elodea. Elodea reproduces by growing large buds in the springtime, relying very little on seed reproduction. Because Elodea relies on a fragmenting process of breaking off stem particles that sink to the ground and grow a new plant. But along with its advantages, Elodea has some disadvantages. If populations of Elodea become overly crowded, Elodea can reduce water temperatures, which can disturb sea life and possibly kill them. Dense growth can become a poorer habitat for fish. Elodea is a common aquarium plant, but even though it is very common, most people don’t know its name. Its common name is “that aquarium plant.”(Rader, 1997; Swistock 2014). Elodea grows in pond habitats and prospers in the fine sediment at the bottom of cool, spring-fed ponds. Elodea is one of the few pond plants that can remain green throughout the cold winter season.” (Swistock, 2014). Question and Hypothesis Question \ Hypothesis Does the distance of a light source from an Elodea plant affect the rate of photosynthesis? If the light source is closer to the plant, then the rate of photosynthesis will be faster, because the light is closer and more intense. Variables and Materials Variables Materials The independent variable was the distance of the light source from the plant. The dependent variable was the rate of photosynthesis of the Elodea plant. Elodea (15.24 cm stem) 3 stems Distilled Water 50 ml 500 ml Beaker 1 Heat Lamp 3 Test Tubes and Rack 1 Rack, 3 Test Tubes Tape and Marker 1 of each Goggles 1 Ruler (30.44 cm) 1 Scissors 1 Procedures 1. Put on necessary safety items (apron and goggles) 2. Obtain materials and label test tubes T1, T2, T3, and Ctrl Procedures 3. Pour 50 ml of water in a single test tube 4. Place 15.24 cm Elodea in a single test tube and place test tube on rack 5. Adjust heat lamps to heights of 25 cm, 31 cm, and 45 cm. 6. Place test tube rack under heat lamp of height indicated for that trial 7. Turn lamp on and carefully count bubbles on Elodea stem for 5 minutes 8. Repeat steps 3-8 for trials 2 and 3 9. For Ctrl, time for five minutes outdoors in the sun 10. Record results in journal Results 50 45 40 Lamp Height (cm) Bubbles counted 35 25 39 30 31 21 25 45 19 20 15 10 5 0 1 2 Lamp Height (cm) 3 Bubbles counted Conclusion: Part 1 The purpose of this lab was to find how the distance of a light source from a plant would affect the rate of photosynthesis. In the lab, the independent variable, or the distance of the light source, affected the dependent variable, or the rate of photosynthesis; when the light source was farther, the photosynthesis would decrease due to the decreased intensity of heat and light. Whereas if the light source was closer, the intensity would increase, thus increasing photosynthesis (refer to graph for reference). The hypothesis of the lab was if the Elodea is placed farther from the light source, then it would lower the rate of photosynthesis. The hypothesis was supported because when the light was closest (25 cm above the plant), the bubble count was 39. When the light source was raised to 31 cm from the plant, the rate went down to 21. When the lamp was raised to 45 cm, a count of 19 bubbles was recorded. Conclusion: Part 2 The control recorded outside in the sun offered a count of 28 bubbles. The bubble count indicated the rate of photosynthesis; if there was a higher count that meant that there was a higher rate of photosynthesis. As the results showed, when the light source was the closest the count was the highest. That proved the hypothesis correct. In the experiment, there were some procedural errors that may have affected the data. One of those errors was the possibility of recounting the same bubble. In the 3rd run of the first trial, the lamp was crooked and may have not focused the full beam intensity. If the lamp had not been crooked, the results may have changed. The largest error was the fact that not all of the trials were finished. Only trial 1 was recorded due to the fact that there wasn’t enough time to do a total of 15 minutes of counting for 3 trials. Conclusion: Part 3 This lab may change if the light source is more natural, like the sun at different times of day. It would most likely extend to only 1 trial a day, as you would have to count at sunrise, noon and sunset. But the results may be more reliable. This lab would affect the real world for plant growers and harvesters. If farmers put their plants closer to the light, photosynthesis would increase, as the experiment results show. Bibliography Aquatic Biologists (2014) Weed Info-Elodea (Canadian Water Weed) Rader, Andrew (2014) Photosynthesis Retrieved from http://www.biology4kids.com/files/plants_photosynthesis.html Pearson (2014) An Overview of Photosynthesis Retrieved from https://www.aquaticbiologists.com/algae--weed-id-guide/submergedweeds/elodea-(canadian-water-weed) Retrieved from http://www.phschool.com/science/biology_place/biocoach/photosynth/overview.html Swistock, Bryan (2014) Elodea (Common Waterweed) Retrieved from http://extension.psu.edu/natural-resources/water/ponds/pondmanagement/aquatic-plants/elodea-common-waterweed ELODEA SCIENCE FAIR PROJECT By Ryan Roulette QUESTION Does the distance from the light effect the rate of photosynthesis. VARIABLES The independent variable is the distance from the light source, the dependent variable is the rate of photosynthesis and the constant is the time the elodea is exposed to the light. HYPOTHESIS If the elodea is closer to the light, then the rate of photosynthesis will be faster because plants need light to photosynthesize. MATERIALS Material Amount (SI Units) Test tube 3 Water 90 millilers elodea 30 centimeters Heat lamp 1 Lamp stand 1 PROCEDURES 1. Gather DATA Science Fair BY: SAM STRINGER Question Does the distance of the light source affect the rate of photosynthesis in the elodea plant? Variables The Independent Variable in this experiment is the distance the light source is from the elodea plant. The Dependent Variable is the rate that the photosynthesis occurs. Purpose The purpose of the lab was to find out if the distance that light travels affects the rate of photosynthesis. Hypothesis If the light source is further away from the elodea plant then the affect will be less powerful and will cause less photosynthesis to occur in the plant, because the further the light is the more distance the light has to travel and that will cause the light to be less effective. Materials Material Lamp Elodea 125ml Flask Test Tube Ruler Distilled Water Stop Watch Goggles Apron Amount 1 45cm 1 1 1 900ml 1 1 1 Procedures Wear safety goggles and apron at all times when around any glass objects or chemicals. Gather all materials. (Refer to materials list) Go to a dark area in the testing place. Put 400ml of water into your testing flask. Use scissors and a ruler to cut a piece of elodea plant to be 5cm long. Place that piece of elodea into the water filled flask. Put test tube with open end into the flask on top of the elodea. Prepare your lamp for the testing. Place flask 10cm away from the lamp then turn it on and start stopwatch and stop in 3.5 minutes. Count bubbles and record. Repeat steps 3 -10 two more times for trial 1. Each trial move the flask 5cm further away from the lamp. Record and graph all results. Logging Sep. 17 - Wrote the question / Started lab report Sep. 20 - Formulated hypothesis Sep. 25 - Made materials list Oct. 4 - Started procedures Oct. 6 - Wrote research paper on photosynthesis Oct. 7 - Started testing Oct. 10 - Graphed all data Oct. 12 - Wrote conclusion Oct. 17 – Wrote abstract Data Results 6 Bubbles Counted 5 4 3 2 1 0 Trial 1 Trial 2 10cm 15cm Trial 3 20cm Research Essay on Photosynthesis Photosynthesis is a process that a plant goes through to turn light energy into sugars that give the plant the nutrients it needs. “It occurs whenever plants are exposed to the sun”. The light energy that it takes in is normally sun light. This process is vital for a plant to be able to live. All of a plant’s activities throughout the day take a lot of energy, which is given to it by photosynthesis. Photosynthesis was discovered by Jan Van Helmont in the 1600s. “Later Theodor Engelmann figured out that this occurred in chloroplast.” Chloroplast is an organ in a plant cell that contains chlorophyll. He found this when he experimented by weighing a tree with the soil and then he planted the tree. After 5 years he weighed the tree again and the tree weighed more and grew taller, but the soil’s weight was about the same. This meant that the tree was not taking any of the soil as energy and it had an alternate source of energy. Then he realized that he had been giving the tree water, so it must have been getting the energy from that. He was partially right. The tree needs water, light and carbon dioxide to live and get nutrients. Photosynthesis mostly takes place in the leaves of a plant. The sun light enters through the pores of the leaf called stomata. The chlorophyll inside of the chloroplast is what absorbs the sunlight. Then the chlorophyll forms antenna complexes, which are a complex of protein molecules. This transfers light into different photo chemicals, which then turn into energy. This process is what keeps plants alive today. When a plant lives inside of a house someone needs to water it and it has to have sunlight for these reasons. If you put a plant in the back of a closet and didn’t give it water at any time it would die. There are many ways to measure if an elodea plant is photosynthesizing. ”Elodea is sometimes confused with Hydrilla and Egeria”. One example is to get a twig with elodea on it and remove all leaves from around the twig. Place the elodea into a test tube with the stem facing upward and fill the tube with water then place the test tube on the test tube rack. Place a 40 watt light bulb 5 cm under the plant. After one minute has passed count the number of bubbles in the test tube and record your results. In conclusion, photosynthesis is a vital part of the plants life. Photosynthesis provides the plant with nutrients and energy that it needs to live. Photosynthesis is a short and productive process the plant does without any hesitation. This is somewhat like the human body breathing. We never have to think about doing this. Works Cited Gregory, M. (n.d.). Photosynthesis. Retrieved from http://faculty.clintoncc.suny.edu/faculty/michael.gregory/files/bio 101/bio 101 laboratory/photosynthesis/photosynthesis.htm Elodea. (n.d.). Retrieved from http://aquaplant.tamu.edu/plantidentification/alphabetical-index/elodea/ Photosynthesis History. (n.d.). Retrieved from http://www.shmoop.com/photosynthesis/history.html Conclusion The purpose of the lab was to find out if distance affects how fast photosynthesis occurs. The independent variable was the distance away the lamp was from the elodea. The dependent variable was the rate of the photosynthesis. The relationship between them was that the distance of the light will affect the rate of the photosynthesis. The hypothesis is that the further away the light got the less photosynthesis would occur in the flask. This was supported by the results that we got during the lab. They show that the further away the light got the less powerful the light became. This means the further the light traveled the energy became weaker. The procedural error that ended up being fixed was that the trials weren’t totally finished. The investigations that could be based off of this project could be instead of changing the distance of the light you could change the light bulb wattage. This project could help the people who work with agriculture. Abstract The purpose of the lab was to find out if the distance of the light source would affect the rate of the photosynthesis. The bubbles that rise would show use how much photosynthesis was occurring at the specific distance. The hypothesis was the father away the light got the less photosynthesis would occur. First the Elodea would be cut to be 5cm long. The Elodea was then placed in the glass flask. The flask was 100ml full of water. The lights where then turned on and we saw the bubbles raise to the top of the water. Then the steps were repeated the steps over and over until we got enough to record the data. In conclusion the results showed that the father away the light got the less photosynthesis occurred. This shows that the light energy is less affective when it is further away. It also shows that the distance makes the energy slowly deteriorate over time. The hypothesis that was stated at the beginning of the project was proven and the reasons for this prediction were also proven correct. Photosynthesis lab Purpose • Does the distance of the light source affect the rate of photosynthesis. Hypothesis • If the distance of the light source increases then the rate of photosynthesis will decrease because the light source is farther away. variables • Independent variable the distance of the light source • Dependent variable rate of photosynthesis Materials • • • • • • 4 6 cm live elodea samples 1 heat lamp 500 ml of distilled water Safety goggles (1 or more) 3-4 125 ml flasks Journal (1 or more) procedures • • • • • • • • • • • 1. Put on safety goggles and gather materials (see materials list.) 2. label and fill each 125 ml flask with distilled water. 3. Place each live elodea sample in each 125 ml flask of distilled water make sure completely submerged. 4. Take the first elodea sample and put it 10 cm away from heat lamp (turn on high.) 5. Count how many bubbles appear on the plant count for 3 min. 6. record results. 7. Remove sample 1 away from the heat lamp and put sample 2 20 cm away from the heat lamp. 8. repeat 5-6. 9. remove sample 2 away from heat lamp and place sample 3 30 cm away from the heat lamp. 10. repeat 5-6. 11. calculate results in journal. Data table • Trial 1: 1, 0, 13 • Trial 2: 2, 2, 19 • Trial 3: 3, 14, 29 Graph Rate of photosynthesis 30 25 20 trial 1 15 trial 2 trial 3 10 5 0 trail 1 trial 2 trial 3 conclusion • • • • • Relationship between variables- when the distance of the light source (independent variable) increased the rate of photosynthesis (dependent variable) increased. Hypothesis- the hypothesis stated “If the distance of the light source increases then the rate of photosynthesis will decrease” this was incorrect the data proves that when the distance of the light source increased the rate of photosynthesis also increased. Explanation of results- trial 1 the light source was 10 cm away from the elodea the average bubbles that appeared was 2. trial 2 the light source was 20 cm away from the elodea with an average of 5 bubbles. Trial 3 the light source was 30 cm away from the elodea with an average of 3 bubbles. Procedural errors- while counting the bubbles the flask containing the elodea was turned and some bubbles might have been counted twice. This resulted inconclusive data. If the elodea was not turned then it would have led to more precise data. Further investigation- the independent variable could have been changed by instead of the distance of the light source it could be measured by the length of the elodea plant. Elodea Lab Shy’La and Kaliyah 7th Period Purpose The purpose of the lab was to figure out if the distance of light source changed, would if affect the rate photosynthesis occurs at. Hypothesis If the distance of light source is further away, then the rate of photosynthesis will decrease, because then it will be less light and less light in the chloroplasts means less photosynthesis. Procedures • • • • 1. 2. 3. 4. • 5. • 6. • 7. Safety is priority. Put on apron and safety goggles. Gather materials. Place 10 cm elodea plant in 30 mL of distilled water. Arrange light sources at points 10cm, 20cm, and 30cm pointing towards the elodea plants with y being the control. Throughout 2 minutes time of testing, record how many bubbles appear in each test tube. Record results in notebook. Repeat steps 1-6 2 times Abstract The purpose of the project was to figure out if the distance of light source had an affect on the rate of photosynthesis of an Elodea Plant. The hypothesis stated that if the source of light is further away, then the rate of photosynthesis will decrease because there will be less light and less light in the chloroplasts means less photosynthesis. Before starting the lab, safety is top priority. We put on goggles and aprons. After that, we gather our materials. Then, place 10 cm elodea plant in 30 mL of distilled water. Then, Arrange light sources at points 10cm, 20cm, and 30cm pointing towards the elodea plants with y being the control. After that, Throughout 2 minutes time of testing, record how many bubbles appear in each test tube. Finally, record results in notebook and repeat steps 1-6 for trials 2 and 3. In this lab, we witnessed photosynthesis occur in an Elodea plant. To see this process happening, we noticed that as the light distance changed, in some trials, our hypothesis was supported. Meaning that it decreased in some trials, but in some other trials, the bubbles increased. This showed that plants need light in order for photosynthesis to occur. Data Trials 10cm 20cm 30cm Control 1 14 16 9 10 2 12 13 10 11 3 14 11 13 15 Graph Y Photosynthesis and Elodea Lab 10cm Amt. Of Bubbles 18 16 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 Trial 1 Trial 2 Trials Trial 3 20cm 30cm Control X Conclusion The hypothesis stated that if the source of light is further away, then the rate of photosynthesis will decrease, because there will be less light and less light in the chloroplasts means less photosynthesis. The hypothesis was supported, although in some trials the bubbles increased. To get more precise data, all the leave should’ve been removed. One of the Elodea plants had no leaves at all, which could’ve been resulted in counting more bubbles. If all the leaves would’ve been removed, more bubbles would’ve been shown, and the data would have shown more increase rather than more decrease. In trial 1, the bubbles increased by 14, then by 2, and decreased suddenly by 7. Afterwards, trial 2 showed that 12 bubbles were recorded, then 13, and ended with 10. Finally, in trial 3 the experiment concluded with 14 bubbles, decreasing by 3, and then by 2 more. Depending on the distance and how frequent oxygen circulates, does the process of photosynthesis change? Science fair 2014-2015 Question • Depending on the distance and how frequent oxygen circulates, does the process of photosynthesis change? Hypothesis • If the light source is closer to plant, then the rate of photosynthesis would increase, because the light source is closer to the plant. Variables • The dependent variable was the rate of photosynthesis, which was measured by counting oxygen bubbles that came from the Endola plants. • The independent variable was the distance of the light source. • The control group in this experiment was the plants with no light. • One constant in this experiment was the light source. Although the distance was raised each time, the light source itself remained the same. Materials List • One Lamp, it should be at least 15 cm tall and make sure you can adjust the bulb’s height. • One lamp clamp, this is to adjust the height of the bulb. • One lamp holder, this is to hold your lamp in place. • Goggles, you should have goggles for each person working on the experiment. • One test tube holder. The holder should hold at least nine test tubes. • Test tubes, the test tubes need to be big enough to hold 20 mL of spring water and a 5 cm plant. Depending on how many trials, more test tubes will be needed. As with any scientific experiment, be sure to label the test tubes. • One 250 mL beaker. This will hold the spring water until it is needed. • One graduated cylinder. Just in case the beaker isn’t enough, you can also use this to hold water. A 300 milliliter-graduated cylinder should do the trick. • One plastic funnel. Use this to pour water into the test tubes. This also prevents accidental spilling. • One pair of scissors, use the scissors to cut stocks to their proper sizes. • Endola plant samples, the samples should be cut down to 5 cm stalks without leaves. Depending on how many trials planned, three for each trial is standard. For three trials, nine samples will be needed. • For each sample, use 20 mL of spring water. Procedures 1) Above all, always use safe practices. When using the electrical equipment in this experiment, be careful. 2) Collect all the materials needed, see previous slide for details. 3) Using the lamp clamp, raise or lower the lamp to 5 cm. 4) Place the Endola plant sample in the test tube. The samples should be 5 cm long and also have the leaves taken off. Pour 10 milliliters of spring water in the test tube, then place the test tube in the test tube holder. 5) Place the test tube holder under the lamp for 3 min. 6) Record how many bubbles are in the test tube. 7) Repeat this two more times with a different sample and a different test tube. Don’t change the height of the lamp. 8) Raise the lamp to 10 cm. Get three different samples. 9) Follow steps four through seven, changing the test tubes and the samples as needed. Change the samples for each trial. 10) Raise the lamp to 15 cm. 11) Follow steps four through seven, changing test tubes and samples as needed. 12) Be sure to record all of the data. Data table (in number of bubbles) Height of Lamp (in centimeters) 5 cm 10 cm 15 cm 1st Trial 5 7 8 2nd Trial 12 8 9 3rd Trial 11 8 8 Control – No Light 6 N.D. N.D. 2nd Time 3rd Time Control 8 1st Time 8 8 8 9 THE EFFECT THAT DISTANCE OF THE LIGHT SOURCE HAS ON PHOTOSYNTHESIS 7 BUBBLES COUNTED (RATE OF PHOTOSYNTHESIS Graph 10 CM 15 CM DISTANCE OF THE LIGHT IN CM Purpose of the Lab • The purpose of this lab was to find out more about photosynthesis. • Another purpose was to figure out which distance, 5 cm, 10 cm or 15 cm the Endola oxidizes best in. Hypothesis Restated • If the light source is closer to the plant, then the rate of photosynthesis would increase, because the light source is closer to the plant. This was supported by the fact that in the second and third trial when the lamp was at 5 cm, 11 and 12 bubbles were counted, respectively. Relationship between Variables • The dependent variable was the number of bubbles counted. The independent variable was the height of the lamp in centimeters. At 15 cm, the lamp was furthest from the plant. The farther the lamp was the less, on average, number of bubbles were counted. At 5 cm, the lamp was closest to the plant. Thus, the most bubbles, on average, were counted. This means that the closer the lamp was, the more bubbles were counted. The distance of the lamp affected the number of bubbles counted. Explanation of results • As mentioned previously, the lamp at 5 cm had the fastest rate of photosynthesis. Surprisingly, the lamp at 15 cm had the second fastest rate of photosynthesis. The lamp at 10 cm had the slowest rate Recall that the rate of photosynthesis was determined by how many bubbles were counted. The first trial at 5 cm had five bubbles counted, at 10 cm, seven bubbles were counted. At 15 cm for the first trial eight bubbles were counted. For the second trial, at 5 cm, 12 bubbles were counted, at 10 cm, eight bubbles were counted, at 15 cm, nine bubbles were counted. The third and final trial had 11 bubbles counted at 5 cm, at 10 cm, eight bubble were counted, this is the same for 15 cm as well. The control with no light had six bubbles counted. Procedural errors • Since a time limit to do this experiment was in place, more time to record as the lamp was being raised would have been favored. Further investigations • Changing the type of plant would be a nice way to extend the life of this experiment. Different plants might have different rates and it would be fun to compare the different rates. Real-world Application • If a person goes off in a spaceship, they might need extra oxygen. One might use this experiment to do so. Elodea Undergoing Photosynthesis Underwater? BY: LEAH HENRY AND ADRIELLE LANGSTON PURPOSE Is the Rate of Photosynthesis affected by the light source? HYPOTHESIS If the light source is closer then the rate of photosynthesis will increase because plants use green pigments called chlorophylls that trap light energy to produce glucose, called photosynthesis, so, if the light source is closer the plant will be able to trap more light energy an make more photosynthesis. VARIABLES • Independent Variable- The Distance of Light • Dependent Variable- The Rate of Photosynthesis MATERIALS Elodea Goggles Distilled Water Timer/Watch Small Metal Lamp Test Tubes Scissors Measuring cup Test Tube Stand 1(10cm) 4 Pairs 125ml 1 1 3 1 1 1 PROCEDURES 1. Safety; wear goggles for eye protection, and be careful with/of hot objects. 2. Label test tubes Trial 1,2, and 3. 3. Cut elodea to 10cm. 4. Take leaves off of elodea carefully with scissors. 5. Fill beaker to 125ml with distilled water and pour gently in test tube(Trial 1). 6. Gently place elodea in the test tube (Trial 1) filled with the distilled water. 7. Make ring stand and gently place lamp in/on it. 8. Mark points on lamp at 10cm, 20cm, and 30cm. 9. Place test tube in the test tube(Trial 1) stand carefully. 10. Repeat steps 3-9 but with Trial 2 and 3. 11. Place lamp at 10cm. 12. Turn the lamp on. 13. After 3 minutes turn light off. 14. Record how many bubbles were on each plant. 15. Repeat steps 9-13 but put the lamp at 10cm and 20cm. 30cm 10cm ABSTRACT The purpose of this lab was to decide if the rate of photosynthesis is effected by the light source. We wanted to find this out because plants do grow underwater but, do they go through photosynthesis while there in the water? If the light source is closer then, the rate of photosynthesis will increase because plants use green pigment’s called chlorophylls to trap energy to produce glucose, so, if the light source is closer the plant can trap more energy and make more photosynthesis. This will make sure that if you have this plant and its growing to fast and you think it will die then you know to just move it farther away. To analyze this purpose we labeled three test tubes trial one, two, and three. After we labeled you ten cut the elodeas to 10cm then, take the leaves of them carefully with scissors, and once you have done that to all three fill the beakers to 125ml with distilled water and pour into test tube and then, gently place elodea in the test tube. After all that is set up now it’s time to set up the rest and then get started. Make the ring stand and gently place lamp in/on it then mark points on lamp at 10cm, 20cm, and at 30cm. Then, place test tube 1, 2, and 3 under the lamp and put the lamp at 10cm then, turn the light on. After 3 minutes turn the light off and record how many bubbles came up. Now repeat steps 9-13 but put the lamp at 20cm and 30cm and record the results of how many bubbles there were. The purpose of this lab was to determine if the distance of light will affect the rate of photosynthesis which it did. The hypothesis stated that “If the light source is closer than the rate of photosynthesis will increase because plants use green pigment’s called chlorophylls to trap light energy to produce glucose, called photosynthesis, so if the light source is closer it will be able to trap more energy and make more photosynthesis” This hypothesis was not supported because the results had shown that when the light was closer there were less bubble which means not as much photosynthesis going on. In this observation the objective was met because we did get our question answered. DATA # of Bubbles at 10cm # of Bubbles at 20cm # of Bubbles at 30cm Trial 1 0 7 15 Trial 2 2 2 3 Trial 3 11 20 13 Control 0 0 0 GRAPH ELODEA RESULTS AMOUNT OF BUBBLES/RATE OF PHOTOSYNTHESIS y 25 20 20 15 15 13 # of Bubbles at 10cm 11 # of Bubbles at 20cm 10 #of Bubbles at 30cm 7 5 2 0 2 3 0 0 Tral 1 Trial 2 Trial 3 TRIALS 0 Control 0 x CONCLUSION The light source (independent variable) causes the rate of photosynthesis to vary for each trial. As the distance increased, so did the rate of photosynthesis, so when the light source was lower, so was the rate of photosynthesis. The purpose of the lab is to determine if the distance of the light will effect the rate of photosynthesis. The hypothesis stated ‘ The light source is closer, then the rate of photosynthesis will increase because plants use green pigments called chlorophylls that trap light energy to produce glucose, called photosynthesis so if the light source is closer, it will be able to trap more energy and make more glucose. This hypothesis was not supported because when it was closer, the rate of photosynthesis was lower. The results were found by counting bubbles. The results were inconsistent because trial 1 had 0 bubbles at 10 centimeters, 7 bubbles at 20 cm, and 15 bubbles at 30 cm. Trial 2 had 2 bubbles at 10 cm, 2 bubbles, at 20 cm, and 3 bubbles at 30 cm. Trial 3 had 11 bubbles at 10 cm, 20 bubbles at 20 cm, and 13 bubbles at 30 cm. A procedural error that occurred was that the leaves on the elodea were not cut for trial 2 and trial 3. By going back and doing it again there may have been more accurate results. Another procedural error was miscounting bubbles. Maybe by having more people counting, the results might have been different. Instead of using regular lights, use LED lights like red, blue, green, and purple to determine which grows faster. This could be used for plant companies for making their plant thicker or thinner for water glasses/pots, so the plants can grow bigger and better.