Cycle of Renewal Drawings 4-4
advertisement

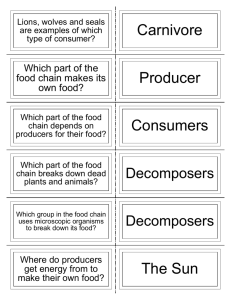
Quick & Easy Habitat Education Activities Cycle of Renewal Drawings ©Starflower Foundation Developed by Heidi Bohan/ Starflower Foundation Description: Students learn that the habitat area is a complex system, through drawing, imaginative role playing and exploration. They gain an appreciation for tiny organisms and soil, as well as for larger plants and animals. Students develop appreciation for the habitat components which will be important as they conduct other activities in the habitat area. Objectives: • Students gain understanding that all components of an ecosystem are important • Students recognize natural processes and components in a natural habitat area. • Students gain appreciation for non-living components of the habitat area (such as soil, and decaying matter). Print Materials: • ‘How-to-do Activity: Terminology & Definitions’ • Image: ‘Cycle of Renewal’ poster • Master: ‘Cycle of Renewal Drawing’ (for overhead and student worksheets), ‘Cycle of Renewal Diagram’ graphic organizer Teacher supplied: • Copies of ‘Cycle of Renewal Drawing’, and ‘Cycle of Renewal Diagram’ graphic organizer: 1 per student Fourth Grade 20-30 Minutes Outdoors/Indoors 4-4 Vocabulary Cycle: an interval of time in which a repeated sequence of events is completed Habitat area: a natural area that provides habitat for plants and animals Washington State EALRs Science 1.1 Categorize plants and animals into groups according to how they accomplish life processes. 1.2 Describe the life cycles of plants and animals; Know that energy can be transferred between various forms. 1.3 Recognize that living things need constant energy supplied from food or light and that, in ecosystems, substances such as air, water, nutrients, and the chemicals in food are continually recycled. Describe how an organism’s behavior and ability to survive is influenced by its environment, other life forms, and availability of food and/or other resources. Know that humans and other living things depend on the natural environment, and can cause changes in the environment that affect their ability to survive. Science Kits: Ecosystems Activity: • In class, show image (or overhead) of ‘Cycle of Renewal’ poster. Tell students that the poster represents the natural cycle of life in the habitat area. Share what students know and recognize in this poster about life cycles of plants and animals. Use words, such as deciduous, scat, photosynthesis, sprout/germinate, decompose, humus, and nutrients which should be familiar to students. • Pass out ‘Cycle of Renewal Drawings’ and have students color in the components as you discuss them (see ‘How-to-do Activity’). Point out and discuss the following boldface terms, adapted to student’s knowledge: o Sun: Provides energy (warmth, photosynthesis) o Producers: Plants (which ‘produce’ their own food). Producers provide food for all animals, either directly or indirectly. o Consumers: Animals that eat plants for food/energy’ (herbivores), Animals that eat animals for food/energy’ (carnivores and omnivores) o Animal and Plant Waste: Leaves, animal excretions (poop, scat) and remains (carcasses, body, fallen tree). Point out and discuss Decomposers; small animals and plants that get their food/energy from plant and animal waste. What does it turn into? (soil). Share examples of decomposers (slugs, termites) “Has anyone seen a…? Point out and discuss Soil and Nutrients for New Growth. New plants get their food from the soil (nutrients), air (carbon dioxide) and sun (energy to make food). • Go to habitat area. Show students image: ‘Cycle of Renewal’ poster. Ask students to locate examples of each major component. • How is each of these components important? Are dead or non-living things important? (yes, they provide nutrients and minerals necessary for plant growth, the primary producers). • Discuss “What is the most important component in the cycle of renewal? Conjecture, “What if there was no sun? What if there were no decomposers? Plants? Animals? Soil? Are they all important? (yes). • Pass out ‘Cycle of Renewal Diagram’ graphic organizer: Ask students to draw an example of a component of the cycle of renewal in each oval, making sure they use an example from the habitat area (not a zebra, lion, etc.) • Summarize: “All components in the cycle of renewal are important, and should be treated with respect and care while visiting the habitat areas”. Terminology & Definitions Teacher background information, suggested terms and definitions for elementary grades (K-5). Review this prior to presenting ‘Cycle of Renewal’ activity to the class. Determine the terminology and discussions appropriate for your class maturity and knowledge level. Present in a clockwise manner starting with the Producers. Producers: “Makers” An organism that makes its own Sun er gy to pr od uc er s food from the energy of the sun, and nutrients in soil, air and water. All green plants are producers, as are algae. En Fact: 90% of plants in Pacific Northwest forests grow on decomposing forest debris. 4-4a How-to-do Activity: Cycle of Renewal How-to-do activity- Cycle of Renewal Feeds Consumers Remains of plants Feeds decomposers Consumers:“Eaters” An organism (from tiny to large) that consumes producers or other consumers for food. Consumers are made up of two groups: First consumers (herbivores), and Second consumers (carnivores). Omnivores, organisms that feed on both plants and animals, sometimes act as first consumers, sometimes as second. First Consumers Herbivores: “Animals that eat plants” Omnivores: “When they eat plants” Soil and Nutrients for New Growth. New plant growth comes from food (nutrients) in the soil and water, air (carbon dioxide) and sun (energy). Nutrients in the soil, water, and air are available to plants through the process of decomposition. Many minerals (from rocks) in the soil are only available to plants through soil organisms. dec om pos ers Dead Matter The “remains of plants and animals” and “animal waste” Fee ds Decomposers “Breakers” Decomposers are tiny organisms (from insects to bacteria to fungi) that are involved in the process of breaking down dead plants and animals into tiny matter, which is eventually converted into nutrients and gases that become food for producers. Remains and waste of animals Second Consumers Carnivores: “Animals that eat animals” also called predators. Drawing by Heidi Bohan Omnivores: “When they eat animals”. Forest Floor Decomposers and Consumers Scavengers: Organisms such as earthworms, slugs, larvae of beetles, termites and flies, that break down larger dead matter (woody debris, animal remains, dung, etc) into smaller matter (usually known as humus). Microscopic decomposers: Usually microscopic bacteria and fungi that break down the smaller matter created by the scavengers into minerals and gases (nutrients). Predators: Tiny animals that eat decomposers. These include ants, centipedes, sow bugs, and some bacteria. in the westside lowland forest Producers Solar energy Pla nt gro wth Primary Consumers Nutrients Secondary Consumers Anim al w aste & de ad a nim als Plant waste & dead plants From soil, air and water nic ga Or ma r tte Decomposers Illustration by Heidi Bohan Producers (Organisms that store the suns energy) Green Plants Algae, moss, ferns, horsetail, conifers, flowering plants. Primary Consumers Secondary Consumers (Animals that eat producers) (Animals that eat other animals) Herbivores, Plant Parasites & Omnivores (when they feed on plants) Vertebrate Grazers and Seed Eaters: Deer, elk; mice, beaver, moles, rabbits, squirrels; seed– and fruit-eating birds. Invertebrate Grazers and Seed Eaters: Herbivorous insects such as bees, butterflies, aphids. Parasites on Plants: Fungi, bacteria, parasitic flowering plants; insect galls, nematode worms, some protozoa. Carnivores, Animal Parasites, Scavengers & Omnivores (when they feed on animals) Vertebrate Carnivores: Coyotes, bats, bobcats, weasels, mole shrews; many birds (owls, flickers, hawks, warblers), etc. Invertebrate Carnivores: Many insects such as beetles and wasps. Vertebrate Omnivores: Black bears, raccoons, crows, etc. Animal Parasites: Worms, bacteria, etc. Scavengers: Crows, many invertebrates Decomposers (Organisms that feed by breaking down dead organic matter) Bacteria, Fungi, Invertebrates Bacteria: numerous Fungi: Bracket, cup, spore fungi; lichens, chantrelles, gilled mushrooms, etc; Slime molds, water molds, etc. Invertebrates: Banana slugs, snails, millipedes, termites, grubs, pill bugs, etc. 4-4b Cycle of Renewal Poster Cycle of Renewal in the westside lowland forest Producers Solar energy Pla nt gro wth Primary Consumers nim ad a & de Secondary Consumers nic ga Or Anim al w aste From soil, air and water als Plant waste & dead plants Nutrients r tte ma Decomposers Illustration by Heidi Bohan Producers Primary Consumers (Organisms that store the (Animals that eat producers) sun’s energy) Herbivores & Plant Parasites Green Plants Vertebrate Grazers and Seed Eaters: Algae, moss, ferns, horsetail, Deer, elk; mice, beavers, moles, rabbits, conifers, all flowering plants. squirrels; seed and fruit-eating birds. Invertebrate Grazers and Seed Eaters: Herbivorous insects such as bees, butterflies, aphids. Parasites on Plants: Fungi, bacteria, parasitic flowering plants, insect galls, nematode worms, some protozoa. Secondary Consumers Decomposers (Animals that eat other animals) Carnivores, Animal Parasites & Omnivores (which feed on plants and animals) (Organisms that feed by breaking down dead organic matter) Bacteria, Fungi, Invertebrates Vertebrate Carnivores: Coyotes, bats, bobcats, weasels, mole shrews; many birds (owls, flickers, hawks, warblers), etc. Invertebrate Carnivores: Many insects such as beetles and wasps. Vertebrate Omnivores: Black bears, raccoons, crows, etc. Animal Parasites: Worms, bacteria, etc. Bacteria: numerous Fungi: Bracket, cup, spore fungi, lichens, chanterelles, gilled mushrooms, slime molds, water molds, etc. Invertebrates: Banana slugs, snails, millipedes, termites, grubs, pill bugs, etc. 4-4c Master: Cycle of Renewal Drawing Cycle of Renewal Draw and label an example of the habitat component listed in the oval. Producer New growth Consumer Decomposer 4-4d Master: Cycle of Renewal Diagram Cycle of Renewal Diagram