The Seven Dimensions of Islam
advertisement

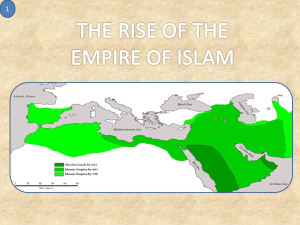
The Seven Dimensions of Islam Ritual: Holidays o Ramadan Month in which the Qur’an was revealed Fasting throughout whole month Emphasis on developing self-control o Eid ul-Fitr End of Ramadan Celebration Thanking God for self-control throughout previous month o Eid ul-Adha Commemoration of Abraham’s willingness to sacrifice his son Sacrifice a cow Hajj o Pilgrimage once in a lifetime to Mecca Prayer Mosque attendance o Fridays o Prayer toward the o Separation of men and women Narrative and Mythic: The Story of Islam o In 570, Mohammad was born in Mecca. As a young boy, he was orphaned and was raised by his uncle. Managing caravans for merchants, Muhammad was exposed to Christians, Jews, and Pagans. In 610, while in isolation for contemplation, the Angel Gabriel came to Mohammad and told him to spread the word of Allah. Mohammad agreed and was persecuted for trying to spread Islam. He escaped to the city of Medina which means “the city of the prophet.” Non- Muslims from Mecca and Muslims in Medina fought a series of wars; eventually, the Muslims won. The Muslims from Medina reclaimed Mecca and most non-Muslims there converted. The Ka’ba (in Mecca), the holiest shrine in Islam, where all Muslims face during prayer, was rededicated to Allah, and Islam spread throughout the Arab peninsula in a short period of time. Interfaith in Qur’an o Surely those who believe, and those who are Jews, and the Christians, and the Sabians -- whoever believes in God and the Last Day and does good, they shall have their reward from their Lord. And there will be no fear for them, nor shall they grieve (2:62, 5:69, and many other verses). Experiential and emotional: Ask a friend! Social and Institutional: Sufism o Mystical approach to Islam o Direct, personal experience of God o Belief in teachers, not just book learning o Grew out of an early ascetic movement within Islam to counteract worldliness that came with rapid Muslim expansion (661-749) o Change from asceticism to mysticism with emphasis on love (pure love of God) o Orthodox Islam (though some are monism/pantheism) o Absolute trust in God (tawakkul) and the truth that there is no deity but God (tawhid) o Purify the self from selfishness o Ritual prayer--rosary with 33 beads o Whirling, teachings of Rumi, form of meditation in which they seek to abandon the self and contemplate God, sometimes achieving an ecstatic state Shi’a/ Sunni o Difference in who would follow the Prophet Muhammad (peace be upon him) as leader of Muslim community o Abu Bakr, companion of Prophet as political not spiritual leader (appointed Caliph, the ruler of the Islamic Community)—they were called Sunni Muslims o Others wanted son-in-law Ali as Caliph, and both political and spiritual leader—called Shi’a Muslims o Now: Shi’a is hierarchical, and only 10-15% of Muslims (mostly found in Iran) o Sunni doesn’t have hierarchy, and 85-90% of Muslims o The two sects are different historically, ethnically, politically and socially. o Shi’a has fixed ecclesiastical body; Sunnis do not. o Shi’a Muslims believe in “Imams,” figures that appeared historically that were leaders of the Shi’as (the number of historical Imams differs among Shiism); these figures were not prophets in the sense that Muhammad (peace be upon him) is--they did not have revelation from God; however, they had the authority, a God-granted protection from error, that allowed them to give binding rulings. o Current conflicts are not theologically based, they are politically based under guises of religion Ethical and legal: All people should try to follow in the ways of Muhammad (peace be upon him) because he was the most perfect of human beings Five Pillars o Belief or Faith in One God and Muhammad (peace be upon him) as a messenger of God o Prayer occurs five times a day o Concern for charity, obligatory (2.5% of your savings) o Fasting during the month of Ramadan o Pilgrimage to Mecca Day of Judgment: A time when God will assess every human and whether he/she will go to heaven or hell Jihad o Translation- struggle or effort o struggle to be a good Muslim o struggle to defend Islam Halal o Similar to Kosher diet o Animal must be ritually slaughtered prior to being eaten o No pork Doctrinal and philosophical: Qur’an o Translation: “the recitation;” traditionally, a literal recitation of the text o The holy book that was revealed to Muhammad (peace be upon him) by Allah (God) by the Angel Gabriel over 23 years o The Old and New Testament are to be respected, but are incorrect Sunna: o The normative practices of the Prophet Muhammad’s (peace be upon him) life, meant for transmission to the community o Translation: a well-trodden path o Words, habits and practices for living a life in accordance with God’s will Hadith o Individual reports of the life of the Prophet (peace be upon him) by those who were in his life, or those who knew people in his life People of the Book o Believe in the Tawrat (Torah from Moses), Zaboor (Psalms of David), and Injil (Gospels of Jesus) Material: Hijab o Head scarf, used by many Muslim women (esp. in Muslim countries) o Contested requirement Ka’ba o Muslims face this in prayer, because it is the holiest shrine in Islam (house of God) o Central place of pilgrimage Prophet’s Mosque in Medina o In respect to the Prophet Dome of the Rock o In Jerusalem, place from which the Prophet ascended to Heaven to meet God Islamic Art o Calligraphy o Geometrical shapes o Lack of human forms, spiritual representation of objects and beings o Begins with and centers on Allah Islamic Architecture o Minaret Tower used by the criers of the call to prayer Today, mostly decorative o Minbar Pulpit from which the Friday sermon is given