Tissues - classification, general structure and function. Connective
advertisement

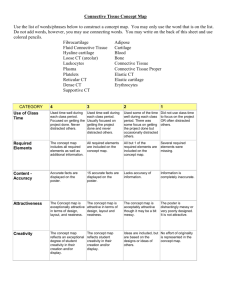
Charles University in Prague, First Faculty of Medicine Tissues - classification, general structure and function. Connective tissue - general characterization. Extracellular matrix - its synthesis and composition. Cartilage - structure and function. Doc. MUDr. Marie Jirkovská,CSc Institute of Histology and Embryology Subject: GHGE Code: B82241 Tissue – organized aggregation of cells that function in a collective manner. Cells in the tissue have common origin, morphological characteristics and organization. Tissues are responsible for maintaining body functions. All organs are made up from only four basic tissue types: •epithelial tissue (epithelium), •connective tissue, •muscle tissue, •nerve tissue Each type may be further subdivided. Epithelium (epithelial tissue) – covers body surface, lines body cavities and forms glands. Originates directly from germ layer. Epithelium of the urinary bladder Secretory epithelium of pancreas Connective tissue – structurally and functionally underlies and supports the orther three basic tissues. Originates from mesenchyme. Cells are separated from one another by their product extracellular matrix (ECM). Dense connective tissue (tendon) Hyalinne cartilage Muscle tissue - responsible for movement. Originates from mesoderm or mesenchyme. Smooth muscle tissue Skeletal muscle Nervous tissue - receives, transmits and integrates information from outside and inside the body to control the activities of the body. It originates from neuroectoderm. Spinal cord Peripheral nerve Connective tissue developed from mesenchyme, cells are separated from one another by their product - extracellular matrix (ECM). Classification of connective tissue: •Connective tissue proper •Cartilage •Bone •Dentin •Cementum Connective tissue proper Classification: Dental pulp, umbilical cord Jelly-like (mucous) connective tissue Mesenchyme Spleen, lymph nodes, bone marrow Reticular connective tissue Interstitial, e.g. stroma of epithelial organs Adipose tissue Loose connective tissue Dense connective tissue Tendons, ligaments, aponeuroses White (unilocular Storage of energy adipocytes) Brown (multilocular adipocytes) Newborns Regular (arrangement of ECM fibrillar component) Sclera, dermis Irregular (arrangement of ECM fibrillar component) Jelly-like c.t. Dense regular c.t. Loose c.t. Reticular t. Dense irregular c.t. White adipose t. Connective tissue cells: resident: • fibroblast • fibrocyte • myofibroblast • adipocyte – unilocular multilocular • melanocyte (pigment cell) (originating from the neural crest) • adult stem cells free (wandering): • histocyte – macrophage • granulocyte – neutrophilic eosinophilic basophilic • lymphocyte • monocyte – precursor of macrophage • plasma cell – effector of immune response • mast cell – heparin and histamin – Resident cells adipocytes fibroblasts in the lamina propria mucosae of gallbladder mikrograph: Wheater´s Funct. Histology, 2000 pigment cells fibrocytes (melanocytes) in uvea Wandering cells eosinophils in lamina propria of the intestinal villus macrophages in a lymphnode heparinocytes (mast cells) plasma cell Extracellular matrix (EMC) produced by cells (fibroblasts, chondroblasts, osteoblasts,…) consists of fibrillar component (collagen fibres - type I collagen, reticular fibres - type III collagen, elastic fibers (elastin, fibrillin) and ground (amorphous) substance (GAGs, proteoglycans, adhesive glycoproteins) Connective tissue fibres produced by fibroblasts, composed of proteins consisting of long peptide chains Collagen fibres = bundles of collagen fibrils (the fibril is 20-300 nm in diameter; 68 nm banding pattern reflects the size, shape and arrangement of collagen molecules) micrograph by atomic force microscopy Intracellular events Synthesis of collagen fibres Extracellular events Kierszenbaum: Histology and Cell Biology 2007 Structure and synthesis of elastic fibres Kierszenbaum: Histology and Cell Biology 2007 Ground (amorphous) substance a viscous clear substance with high water content composed of • hyaluronan (a carbohydrate chain of thousands of sugar molecules - glucuronic acid and N-acetylglucosamin, it forms dense hyaluronan network) abundant in ECM • proteoglycans (= core proteins and GAGs (glycosaminoglycans) •glycosaminoglycans = long unbranched chains composed of repeating disacharide units (e.g. chondroitinsulfates, heparansulfate,…), negatively charged (sulfate and carboxyl groups) • multiadhesive glycoproteins - stabilizing the EMC and linking it to cell surface (fibronectin, laminin, tenascin, osteopontin) GAGs Proteoglycan aggregate Proteoglycans Ross, Pawlina: Histology, 2005 Interrelationship of cell and EMC Co = collagen fibril, F = fibronectin, HA = hyaluronan, MF = actin filament, PG = proteoglycan, R = integrine Organization of loose connective tissue Ross, Pawlina: Histology, 2005 Interrelationship of epithelial cell and EMC Ross, Pawlina: Histology, 2005 Cartilage is an avascular tissue formed by Cells: chondroblasts, chondrocytes (product and maintain ECM = carry out matrix turnover) chondroclasts (originate from fused mononuclear macrophages precursors, function: removal of cartilage during endochondral bone formation) ECM: solid and firm, but pliable fibrillar component - collagen fibrils (collagen type I and II) and elastic fibrils (elastin & fibrillin) amorphous component - hyaluronan, proteoglycans, glycosaminoglycans (aggrecans), minor collagens (VI, IX, X, XI) Hyaline cartilagearticular cartilage, airways, larynx, trachea, bronchi, rib cartilage isogenous group capsular matrix perichondrium teritorial matrix interteritorial matrix Growth of cartilage: interstitial and appositional Hyaline cartilage - matrix type II collagen fibrils, hyaluronan, proteoglycans (aggrecan), fibronectin, tenascin Elastic cartilageexternal ear, auditory (Eustachian) tube, epiglottis, larynx perichondrium elastic fibers haematoxylin - eosin orcein Fibrocartilage - no surrounding perichondrium, resilient and resistent, (intervertebral discs, symphysis ossis pubis, menisci in joints) Chondrocytes- singular, in rows or in small isogenous groups ECM – abundant collagen fibres (type I collagen) and fibrils (type II collagen), considerably less amorphous matrix (proteoglycan versican) azan staining