Z Scores and the Normal Curve
advertisement

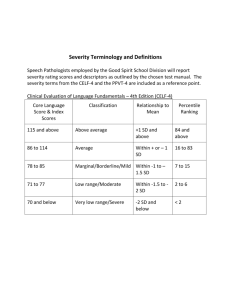
Z Scores and the Normal Curve Vartanian, SW 134 The z score used in these examples gives the area between the value (x) and the mean ( x ). Example 1. Mean=10 SD=4 What proportion of cases are between 10 and 12 z= x − x 12 − 10 = = .5 s 4 Z==>Deviation from the mean in standard deviation units. From this Z score, we can look at a z table ==> and see that the value for .50 is 19.15. If we had gotten a value of 0.51, the area under the curve would have been 19.50. Example 2: If we had wanted to know the area between 8 and 12, we would have simply doubled the # that we got. 2*19.15=38.30 The table gives us half the area of the curve. But since the curve is symmetrical, we can determine the entire area by doubling what is in the table. Example 3: The area below 8. z= x − x 8 − 10 = = −.5 s 4 at Z=.50, the Percentage of the area under the curve between 8 and the mean is 19.15. To determine the area to the left of 8, we would subtract 19.15 from 50.00 (half the area under the curve). Thus our total area = 50.00 19.15 = 30.85 Example 4: X = 50 SD =6 We want to find the area to the left of 42. What percentage of people had scores below 42? x − x 42 − 50 z= = = −1.33 s 6 The table in the back of the book tells us that a score of -1.33 = 40.83. Thus, between the mean and 42 there is an area of 40.83. To determine the area below 42, we subtract 40.83 from 50.00 = 9.17. 1 H:\Word 2010\Lect2.mss\Z Scores\Z_Scores_and_the_Normal_Curve.docx Calculating Z scores. z= x−x Z values indicate how many standard deviation units the x value is from the mean. s Example 1: In a class of 22 students, the mean score is 80%. You get a 90%. The standard deviation is 10. At what percentile are you located? z= 90 − 80 10 = =1 10 10 . Thus, you are 1 standard deviation above the mean. This corresponds to 34.13% above the mean. If you add this to 50% (because you are 34.13% above the mean, and the mean is located at the 50th percentile), then you are at the 84.13 percentile. Example 2: Given the same characteristics as above, but you received a 70% on the exam, at what percentile would you be located? For this problem, you would subtract 34.13 from 50. 50-34.13=15.87 percentile. The 34.13 is indicating how far below the mean you are located so you subtract it from 50. z= 70 − 80 10 = − = −1 10 10 . Thus, you are 1 standard deviation below the mean. This again corresponds to 34.14%. Example 3: In a class of 36 students, the mean test score is 80%. You get a 70%. The standard deviation is 11. Where are you on the distribution? z= 70 − 80 10 = − = −.91 , or you are .91 standard deviations below the mean. This corresponds to 31.86% of the 11 11 distribution. If you subtract this from 50, you get 18.14, or you’re at the 18.14 percentile. Example 4: Given the same characteristics as example #3 (where the SD =11 and the mean=10), where would you be in the distribution if you got a score of 90? z= 90 − 80 10 = = .91 11 11 . This corresponds to 31.86%. You would add this on to the 50th percentile, and you would be located at the 81.86 percentile. Example 5: Assume that the mean is 400 and the SD is 50. At what percentile is a score of 475? z= 475 − 400 75 = = 1.5 50 50 . This corresponds to a value of 43.32. We would add this to 50 because we are above the mean. So, 50+43.32=93.32. A score of 475 is at the 93.32nd percentile. Example 6: Assume that the mean is 400 and the SD is 50. At what percentile is a score of 300? z= 300 − 400 100 =− = −2.0 50 50 . This corresponds to 47.72 in the z table. We would subtract this from 50 to get a value of 2.28 percentile. 2 H:\Word 2010\Lect2.mss\Z Scores\Z_Scores_and_the_Normal_Curve.docx