Ch. 2 Sec. 2 Review Questions
advertisement

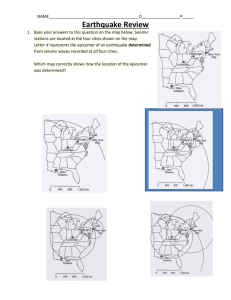
Ch. 2 Sec. 2 Review Questions 1. Why does the greatest shaking of the ground occur near an earthquake's epicenter? Seismic waves lose more energy the further they travel. 2. What information do you need to completely describe where an earthquake started? It's epicenter and depth (focus) 3. What types of information can a scientist get by studying seismographs? Where earthquakes start and how strong they are. Ch. 2 Sec. 2 Review Questions 4. How are the primary and secondary waves similar? How are they different? PRIMARY SECONDARY -Second waves -Fastest seismic to arrive at a -both travel out location after an waves from the focus of earthquake. -First to reach an earthquake any location -Travel @ about -both can travel after an half the speed of through Earth's earthquake primary waves. interior -Primary means -They can NOT "first" travel through liquids or solids. Ch. 2 Sec. 2 Review Questions 5. What information could you get about an earthquake's location from only two seismic stations' data? Explain. Circles showing distances from two stations to the epicenter will usually intersect in two places, only one of which can be the actual epicenter. 6. Why might an earthquake's primary waves, but not its secondary waves, reach a location on the other side of the world from the epicenter? Secondary waves can not pass through Earth's outer core, but primary waves can. Hmm...who REALLY completed the reading?? 1. How do scientists often name their earthquakes? Usually after the city that is closest to its epicenter. 2. In what year did an earthquake stop baseball's World Series at Candlestick Park in San Francisco? 1989 3. How many types of seismic waves exist? Three--primary, secondary, and surface. 4. What is the average speed of a primary wave? 5 kilometers per second (3 miles per second) 5. What type of waves leave at the same time as primary waves? Secondary 6. How did scientists learn that the Earth's outer core was a liquid? B/c the secondary waves could not pass through Earth's outer core. Hmm...who REALLY completed the reading?? 7. Which type of waves cause the largest ground movements and most damage? Surface waves 8. What do we call the place where ground movements are measured? Seismic Stations 9. What is the recording called that a seismograph produces? Seismograms 10. What is the FIRST step in locating the epicenter of an earthquake? 1. Find the difference in the arrival times of the primary and secondary waves @ each of the three locations. earthquakes vibrations seismic waves first movement along fault underground X the house on the right will shake first b/c it is closer to the focus. primary waves are the fastest seismic waves. they can travel through solids, liquids, gases. Secondary waves travel through the interior @ about 1/2 the speed and can not travel through liquids or gases. Surface waves cause the most damage and travel the slowest. They occur along Earth's surface. Earthquake instrument Ground movements lines The seismograph contains suspended weight. When the ground moves, the weights stay in place. Pens attached to weights record movement. 3 seismograms are needed to locate Seismograms are used to locate a focus an epicenter They record how much the ground moved.