Data Analysis
advertisement

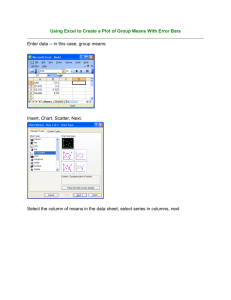
Click the Office button, and then click Options (near the bottom) ◦ Click Add-ins (on the left, near the bottom), and then in the Manage box (on the main panel, at the bottom), select Excel Add-ins and click Go ◦ In the Add-Ins Available box, select the Analysis ToolPak check box, and then click OK. ◦ If you are prompted that the Analysis ToolPak is not currently installed on your computer, click Yes to install it When you load the Analysis ToolPak, the Data Analysis command is added to the Data tab Mac (Excel 2011 / 2008) Excel 2011 / 2008 does not include the Analysis ToolPak (but Excel 2004 does have it) Download and install for free StatPlus:mac LE http://www.analystsoft.com/en/products/sta tplusmacle Open the Excel workbook that contains the data that you want to analyze Open StatPlus:mac LE, where the functions are located in the StatPlus:mac LE menus Average ◦ Is the average score for two groups/conditions different? ◦ In excel type: = average(highlight column of numbers) Standard Deviation ◦ How much do the scores for each group/condition vary? -in excel type: = stdev(highlight column of numbers) Under Data Analysis, select t-Test: TwoSample Assuming Equal Variances Type in the cell range for Group 1 in Variable 1 and for Group 2 in Variable 2 Type in 0 (zero) for Hypothesized Mean difference (the null hypothesis of no difference) Type in 0.05 for Alpha Click ok t(df) = t-value, p = p-value, two-tailed E.g., An independent samples t-test level was conducted to test for a difference in the average RT for the two age groups. The young group (M = 129.63, SD = 8.07) had significantly Faster RTs compared to the old group (M = 150.25, SD = 11.04) [t(14) = 4.01, p = .001, two-tailed]. Under Data Analysis, select t-Test: Paired Two-Sample for Means Type in the cell range for Measure 1 in Variable 1 and for Measure 2 in Variable 2 Type in 0 for Hypothesized Mean Difference Type in 0.05 for Alpha Click OK t(df) = (insert t-value), p = (insert p-value), two-tailed E.g., A paired-samples t-test level was conducted to test for a difference in the average RT for the sad and happy conditions . The sad condition RT (M = 129.63, SD = 8.07) was significantly faster than the happy condition RT (M = 150.25, SD = 11.04) [t(14) = 4.01, p = .001, two-tailed]. Under Data Analysis, select ANOVA: Single Factor Type in the cell range first cell of first column:last cell of last column in Input Range Select Columns in the Grouped By option Type in 0.05 for Alpha Click OK F(df between groups, df within groups) = xx.xx, p = .xx E.g., A one-way between-groups ANOVA was conducted to test for the effect of mood on exam grade. The grades differed significantly across the three mood groups [F(2, 15) = 9.55, p = .002]… Enter each data set into a column in Excel Under Data Analysis, select ANOVA: TwoFactor Without Replication Type in the cell range first cell of first column:last cell of last column in Input Range Type in 0.05 for Alpha Click OK F(df columns, df error) = xx.xx, p = .xx E.g., A one-way repeated measures ANOVA was conducted to test for the effect of mood on exam grade. The grades differed significantly across the three mood conditions [F(2, 15) = 9.55, p = .002]… If and only if the ANOVA is significant, then run t-tests on each pair of groups/conditions ◦ Follow instructions for between subjects or within subjects t-test, depending on your design Plot the group/condition averages Add standard error bars ◦ =stdev(first cell of column:last cell of column)/sqrt(count(first cell:last cell)) ◦ E.g., =stdev(b2:b17)/sqrt(count(b2:b17)) Insert Chart Tools Layout Analysis Error Bars ◦ Charts : Column ◦ Right-click on blank chart Select Data ◦ Chart Data Range: Select all the group means ◦ More Error Bars ◦ (Do NOT use default Excel error bars. See highlighted text below for CUSTOM error bars.) ◦ Display Direction Both ◦ Error Amount Custom Specify Value ◦ Positive Error Value: Select all standard errors (SEM) ◦ Negative Error Value: Select all standard errors again ◦ Make sure to select in the same order as the means