Integration of 1H NMR Signal Areas
advertisement

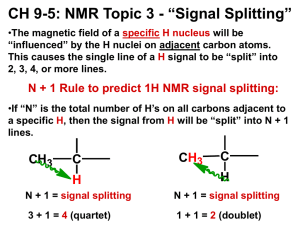
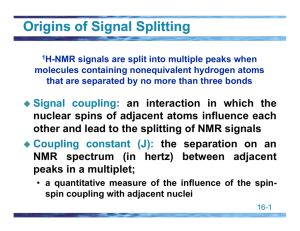
Integration of 1H NMR Information about the total number of hydrogen atoms Signal Areas Relative areas of signals are proportional to the number of hydrogens giving rise to each signal. All modern NMR spectrometers electronically integrate and record the area of each signal. 1 2 Peak splitting in 1H NMR Information about the number of nearby hydrogen atoms Typical 1H splitting ethylbenzene 3 Origins of Signal Splitting Spin-½ nucleii are influenced by neighboring spin-½ nucleii. This is a magnetic effect. When the chemical shift of one nucleus is influenced by the spin of another, the two are said to be coupled. Consider nonequivalent hydrogens Ha and Hb on adjacent carbons: Ha Hb C C Origins of Signal Splitting B0 Hb Hb reduces the field felt by Ha; Ha signal is shifted upfield. upfield Hb Hb increases the field felt by Ha; Ha signal is shifted downfield. downfield Ha 4 Origins of Signal Splitting Origins of Signal Splitting Observed signal splitting patterns for an H with 0, 1, 2, and 3 equivalent neighboring hydrogens Structure Spin States of H b Signal of H a Ha C C Ha Hb C 1 1 C 5 Origins of Signal Splitting Ha Hb C C 1 2 1 Hb Ha Hb C C Hb 1 3 3 1 Hb The (n+1) rule Peak: the units into which an NMR signal is split; doublet, triplet, quartet, etc. (n + 1) rule: the NMR signal of a set of equivalent spin-½ nucleii is split into (n + 1) peaks by a nonequivalent set of n equivalent neighboring spin½ nucleii 6 The (n+1) rule ethylbenzene The (n+1) rule 3-pentanone 7 The (n+1) rule 1,1-dichloroethane Signal Splitting (n + 1) n = 1. Their signal is split into (1 + 1) or 2 peaks ; a doublet Cl CH 3 -CH-Cl n = 3. Its signal is split into (3 + 1) or 4 peaks; a quartet predict the number of 1H-NMR signals and the splitting pattern of each Problem: O (a) CH 3 CCH 2 CH 3 O (b) CH 3 CH 2 CCH 2 CH 3 O (c) CH 3 CCH(CH 3 ) 2 8 Coupling Constants Coupling constant (J): the distance between peaks in an NMR multiplet, expressed in hertz J is a quantitative measure of the magnetic interaction of nuclei whose spins are coupled Ha Ha HaHb Hb -C-CHb 6-8 Hz 8-14 Hz Ha Ha C C Ha Hb C C Hb 11-18 Hz 0-5 Hz 5-10 Hz C C Hb 0-5 Hz Splitting in vinyl acetate 9 300-MHz 1H-NMR spectrum of vinyl acetate 60-MHz 1H-NMR spectrum of vinyl acetate 10