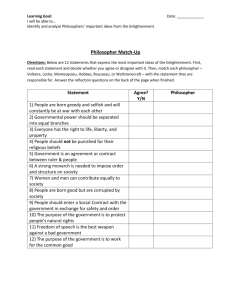
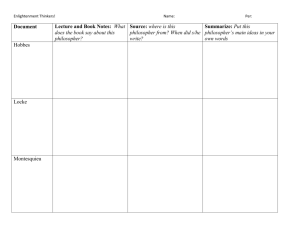
Social Studies Glossary - Inter
advertisement

Social Studies Glossary Economic Terms acquisition - something gained asset - something of value owned by a firm, household or individual; what a company owns after the debts are paid balance of trade - the difference between the export and import of merchandise barter - a moneyless exchange of goods and services borrow - receive with the intention of returning, often with interest budget - a financial plan which summarizes income and expenditures over a period of time capital - any object used to produce a good or service; the tools of production capitalism - another term for market economy or free enterprise system, when private individuals own the productive resources CEO - Chief Executive Officer CFO - Chief Financial Officer choice - the power to select or decide freely for oneself circular flow - a representation that shows the flow of goods and services and of resources and the flow of money through the product and factor markets command economy - a system in which the basic economic questions of what to produce, how to produce, and who should receive what is produced are answered by the government competition - a situation in which many producers offer the same good or service for sale to many consumers consume - use goods or services corporation - a business or company that is owned by many people but is considered a single legal entity cost/benefit analysis - judgments made from a comparison of price and benefit CPI - consumer price index currency - paper money and coins provided by the government debt - something owed, typically money deficit - when expenditures exceed income demand - the quantity of a product that consumers will purchase at each possible price DJIA - Down Jones Industrial Average earnings - profits economics - the study of people producing and exchanging to get the goods and services that they want EU - European Union exchange rate - the price of one currency in terms of another export - good or service sold to a buyer in another country free enterprise - another term for market economy or capitalism, a system in which people are free to start businesses and decide how resources will be used to produce goods and services of their choice flux - a continuing state of change goods - a tangible object that is capable of satisfying human wants import - a good or service purchased from a seller in another country IMF - International Monetary Fund incentives - a reason to do something; in market economies profit, interest, wages, and rents are incentives that provide economic incentives inflation - a sustained increase in the average price level interest rate - rate of payment for borrowing someone else’s money or income for allowing someone to use one’s capital invest - to commit resources (usually money) in order to earn a financial return IPO - Initial Public Offering law of demand - all else being equal, more items will be sold at a lower price than at a higher price law of supply - all else being equal, more items will be offered for sale at a higher price than at a lower price liability - any claim or debt of an individual or business; what a business owes market economy - using markets (voluntary exchange) as the primary means of organizing and coordinating production, also called capitalism or free enterprise market price - price at which goods or services and money will actually be exchanged; price at which the supply equals the demand market system - system where buyers and sellers exchange goods, services and money merger - absorption by a corporation of one or more others, a method of combining businesses mixed economy - an economic system in which the basic economic questions are answered by a mixture of market, command and traditional approaches monopoly - market in which there is only one seller Nasdaq - National Association of Securities Automated Quotation System; 500 businesses with an emphasis on technology securities NAFTA - North American Free Trade Organization needs - what is essential oligopoly - a market condition in which a few firms dominate production of a particular type of good or service and have a substantial degree of independence OPEC - Oil Producing Exporting Countries or Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries partnership - a business organization that is owned by two or more individuals under a contractual agreement price - the money value of a good or service privitization - when a business previously owned and operated by the government is sold to private individuals or businesses produce - create goods or services profit - the difference between a firm’s total revenues and its total costs progressive tax - one that takes a larger percentage of higher income and a smaller percentage of lower income proportional tax - one that takes the same percentage of all incomes quota - a restriction on the number of goods that can enter a country from abroad regressive tax - one that takes a higher percentage of a low income and a lower percentage of a high income resources - the basic elements used to create goods and services, such as minerals, timber, and fresh air salary - the earnings of workers paid on a weekly or monthly basis scarcity - the result of an inability to satisfy all of everyone’s wants services - products you can’t touch, intangible items of value specialization - production of a limited variety of products by a business, region, or country socialism - an economic system in which the principal means of production are owned by the state and usually the government allocates resources according to an economic plan sole proprietorship - a business owned by one person subsidy - financial aid, usually to a business supply - the quantity of a good or service that firms will offer for sale at a possible price tariff - a tax or duty on import TINSTAAFL - There is no such thing as a free lunch. traditional economy - a system in which the basic economic questions of what to produce, how to produce it, and who should get what is produced are generally answered by traditions and customs value-added tax- tax levied on the value added to goods at every stage of production wants - what is desired but not necessary world marketplace - arena of global trade WTO - World Trade Organization Geographic Terms absolute location - location using coordinates (latitude, longitude) relative location - location in relation to other places - eg. New Hampshire is west of Maine, east of Vermont, and north of Massachusetts. demographic - relating to the statistical study of human population geopolitical divisions - a particular state, region, or other place defined by geographic and demographic factors human geographic features - communication, transportation, technology, culture, etc. physical geographic features - landforms, vegetation, climate, wildlife, soil, etc. landforms - a feature of the earth’s surface attributed to nature non-renewable resource - resources that are not replaced by natural ecological cycles renewable resource - resources that can be replaced by natural ecological cycles Civics/Government Terms checks and balances - a political system in which different branches of the government limit (or check) the power of the other branches civilian control of the military - civilian authority should control the military in order to preserve constitutional government (implied in the Constitution that the President is Commander and Chief of the armed forces & that Congress has the power to declare war) common good - welfare of all people compromise - a settling of differences by arbitration or by consent reached by mutual concessions equal opportunity - opportunities for all, non-discrimination equal protection - protection for all, non-discrimination minority rights - rights of under-represented (smaller) populations norms - a principle of right action which guides, controls and regulates proper and acceptable behavior popular sovereignty - government created by the people and subject to the will of the people rule of law - the principle that both government and the governed are subject to the law; government decisions and actions are made according to established laws rather than by arbitrary action or decree sanctions - the detriment, loss of reward or coercive intervention designed to help enforce a law separation of church and state - church and state should be separated in order to preserve liberty of conscience and belief tolerance - a sympathy or indulgence for beliefs or practices differing from one’s own authoritarian - a government favoring a concentration of power in a leader who is not constitutionally responsible to the people constitutional democracy - government according to constitutional principles where the power is vested in the people democracy - government in which the supreme power is vested in the people and exercised by them directly or indirectly through a system of representation usually involving periodically held free elections democratic republic - a country governed by representatives elected by the people, representative democracy direct democracy - form of government where all people meet together to make laws and decide issues monarchy - a government having a hereditary chief of state with life tenure and powers varying from nominal to absolute oligarchy - government by the few representative democracy - form of government where people choose representatives to govern, democratic republic theocracy - government of a state by immediate divine guidance or by officials who are regarded as divinely guided totalitarian - government controlled by an autocratic leader or a political regime, based in subordination of the individual to the state and strict control of all aspects of life and productive capacity of the nation, often by coercive measures Historical Terms artifact - a product of civilization; a simple object showing human workmanship or modification chronology - an arrangement in order of occurrence (time) institution - a significant practice, relationship or organization in a culture or society interdependence - mutual dependence the Great Wars - World War I and World War II Introduction Social Studies Topic Outline Social Studies education is the study of history, the humanities and the social sciences, including economics, political science, sociology, anthropology, psychology, archaeology, geography and philosophy. The social studies provide students with opportunities to understand and appreciate their place in the past and present history of our communities, our state, our country and the world. It helps them to understand the ideals and principles of our democratic government and the foundations of responsible citizenship. When students learn the processes and skills of inquiry and social studies research, they are able to apply the concepts, principles and knowledge they have learned to make informed and reasoned judgments and decisions. Social Studies education provides students with the knowledge, skills and appreciation that enable them to be contributing members of society. This Social Studies curriculum is delineated by grade levels. The curriculum and proficiency standards in this topic outline spiral as concepts and skills are applied in different contexts at an increasingly higher level of understanding each year. An appendix includes a list of vital themes from the study of the Social Studies, a list of famous people in history and their cross curricular connections, a timeline of some important events and developments in world history and a glossary of Social Studies terms. Teachers in all disciplines are encouraged to use these resources as they integrate the study of civics, geography, economics and history into their planning and instruction. The Social Studies topic outline is a guide book for all who teach Social Studies in our school district. It is based on the New Hampshire State Frameworks and the National Social Studies Teachers Association standards. Clear, consistent, rigorous expectations for student learning are articulated throughout the K-12 experience in the Inter-Lakes School District. The goal is to prepare our students for a life time of learning. Inter-Lakes School District Social Studies Topic Outline This document is the result of the dedication and collaborative thinking of the Social Studies Topic Outline committee: Juli Dennett Anne Galligan Laurie Johnson Steve Kelley Alesia Parks Nancy Watt Some Famous People in History and their Cross-Curricular Connections Note: This list is not exhaustive but lists many of the famous people who have been influential. Please feel free to add others to the list. Kindergarten Martin Luther King - American clergyman who was assassinated Abraham Lincoln - 16th President of the U.S. George Washington - 1st President of the U.S. Grade 1 Martin Luther King - American clergyman who was assassinated Abraham Lincoln - 16th President of the U.S. George Washington - 1st President of the U.S. Grade 2 Martin Luther King - American clergyman who was assassinated Abraham Lincoln - 16th President of the U.S. George Washington - 1st President of the U.S. Grade 3 famous people from cultures studied Grade 4 famous NH people Grade 5 Alexander Graham Bell - inventor of the telephone George Washington Carver - researcher on industrial uses of the peanut Thomas Edison - inventor with over a thousand patents including the incandescent light bulb, the mimeograph, the phonograph and the microphone Henry Ford - American automobile manufacturer Benjamin Franklin - statesman, scientist, philosopher - famous diplomat, experiments with electricity and publisher of Pennsylvania Gazette and Poor Richard’s Almanac Thomas Jefferson - third President of the US, wrote Declaration of Independence Abraham Lincoln - 16th President of the US during the Civil War - assassinated while in office Guglielmo Marconi - Italian inventor known for the telegraph Harriet Tubman - spy for the Union during the Civil War, known for her work with the Underground Railroad Eli Whitney - inventor of the cotton gin Orville and Wilbur Wright - pioneers in aviation Grade 6 Alexander the Great - famous Greek leader and conqueror Aristotle - Greek philosopher Augustus Caesar - first Roman emperor Julius Caesar - Roman general and statesman, head of the oligarchic party, known for reform of the calendar as well Charlemagne - King of the Franks and emperor of the West, founded schools, patron of literature, science and art Cheops - or Khufu - first king of the 4th dynasty of Egypt, erected largest of pyramids of Giza Jesus Christ - man whose teachings, personal example and sacrificial death are the foundations of the Christian religion Christopher Columbus - explorer who believed the earth was round, and discovered America on behalf of Spain Nicholaus Copernicus - Polish scientist who is regarded as the founder of modern astronomy in establishing a theory that earth rotates on its axis and that the planets revolve around the sun Hernando Cortez - Spanish conqueror of Mexico Rene Descartes - French mathematician, scientist and philosopher who developed the Cartesian system Euclid - Greek geometer (also a Greek philosopher by the same name who was a follower of Socrates) Galileo Galilei - Italian astronomer and physicist who first conceived the laws of motion later formulated by Newton Vasco de Gama - Portuguese explorer who first sailed from around Africa to the East Johan Gutenberg - German inventor of printing from moveable type Homer - traditional ancient Greek poet to whom the Iliad and the Odyssey are attributed Queen Isabella I - joint sovereign with her husband Ferdinand in Spain, gave money to Columbus Justinian I - emperor of the Eastern Empire who preserved Roman law for future generations Ferdinand Magellan - Portuguese explorer whose expedition completed circumnavigation of the globe; he died enroute Mani - Persian sage who began a new religious movement combining Zoroastrianism and Christianity who was crucified for preaching Michelangelo - Italian sculptor, painter, architect and poet of the high renaissance Moses - Hebrew prophet and lawgiver Francisco Pizzaro - Spanish conqueror of Peru Plato - Greek philosopher who was a disciple of Socrates and teacher of Aristotle Pope Urban II - powerful Benedictine pope during the middle ages Edward de Vere (Shakespeare) - English dramatist and poet Leonardo da Vinci - Italian painter, sculptor, architect, engineer and scientist Grade 7 Buddha - Indian philosopher, founder of Buddhism Confucius - Chines philosopher whose writing deals with morals and whose maxims are still taught as a guide for daily life for people Gandhi - Hindu nationalist & spiritual leader who advocated for social reforms Genghis Khan - Mongol conqueror Mohammed - Arabian prophet and founder of the Islam religion Shih Huang Ti - Chinese emperor, fourth monarch of the Ch’in Dynasty, known for ordering the burning of the books Ts’ai Lun - Chinese man who invented paper from tree bark, hemp, rages and fish nets Lao Tzu - Chinese philosopher and founder of Taoism Grade 8 Benjamin Franklin - statesman, scientist, philosopher - famous diplomat, experiments with electricity and publisher of Pennsylvania Gazette and Poor Richard’s Almanac Thomas Jefferson - 3rd President of the U.S. George Washington - 1st President of the U.S. U.S. and N.H. Government state and national legislators who represent our towns/state governor President and his Cabinet Economics Adam Smith - Scottish economist Karl Marx - German political philosopher who developed the theory of socialism Thomas Malthus - English economist Ricardo - known for the idea of comparative advantage John Maynard Keynes - Keynesian theory U.S. History I Simon Bolivar - South American soldier, statesman and revolutionary leader Napolean Bonaparte - emperor of France with exceptional military genius Benjamin Franklin - statesman, scientist, philosopher - famous diplomat, experiments with electricity and publisher of Pennsylvania Gazette and Poor Richard’s Almanac Alexander Hamilton - American lawyer and statesman who was the first Secretary of the Treasury John Hancock - American Revolutionary statesman, first governor of Massachusetts, first signer of Declaration of Independence Patrick Henry - American Revolutionary leader attributed to the statement “Give me liberty or give me death!” Thomas Jefferson - third President of the U.S. John Locke - English philosopher U.S. History I (continued) James Madison - fourth President of the U.S. James Monroe - fifth President of the U.S. Montesquieu - French lawyer, writer and political philosopher Thomas Paine - political philosopher and author, wrote Common Sense Voltaire - French writer known for satire James Watt - Scottish mechanical engineer and inventor, known for steam engine U.S. History II Albert Einstein - theoretical physicist known for the theory of relativity and many other physics theories, who immigrated to US from Germany and became a naturalized citizen Adolf Hitler - German chancellor and Fuhrer who instituted violent anti-Semitic policy John F. Kennedy - 35th President of the U.S. John Locke - English philosopher Franklin D. Roosevelt - 32nd President of the U.S. Theodore Roosevelt - 26th President of the U.S. Adam Smith - Scottish economist Mao Zedong - Chinese Communist leader Ancient and Medieval History Aristotle - Greek philosopher Julius Caesar - Roman general and statesman, head of the oligarchic party, known for reform of the calendar as well Simon Bolivar - South American soldier, statesman and revolutionary leader Charlemagne - King of the Franks and emperor of the West, founded schools, patron of literature, science and art Cheops - or Khufu - first king of the 4th dynasty of Egypt, erected largest of pyramids of Giza Jesus Christ - man whose teachings, personal example and sacrificial death are the foundations of the Christian religion Constantine the Great - Roman emperor Copernicus - Polish scientist who is regarded as the founder of modern astronomy in establishing a theory that earth rotates on its axis and that the planets revolve around the sun Cyrus the Great - King of Persia and founder of the Persian empire Euclid - Greek geometer (also a Greek philosopher by the same name who was a follower of Socrates) Galileo Galilei - Italian astronomer and physicist who first conceived the laws of motion later formulated by Newton Johan Gutenberg - German inventor of printing from moveable type Homer - traditional ancient Greek poet to whom the Iliad and the Odyssey are attributed Justinian I - emperor of the Eastern Empire who preserved Roman law for future generations Ancient and Medieval History (continued) Mani - Persian sage who began a new religious movement combining Zoroastrianism and Christianity who was crucified for preaching Menes - First King of the Thinite dynasty in Egypt, united the north & south kingdoms Michelangelo - Italian sculptor, painter, architect and poet of the high renaissance Mohammed - Arabian prophet and founder of the Islam religion Moses - Hebrew prophet and lawgiver Saint Paul - apostle of Jesus whose conversion to Christianity was preceded by a vision Plato - Greek philosopher who was a disciple of Socrates and teacher of Aristotle Pope Urban II - powerful Benedictine pope during the middle ages William the Conqueror - King of England who strengthened the power of the crown by building castles and giving land to his followers, established the feudal system Zoroaster - founder of the religion Zoroastrianism of the ancient Persians Modern European History St. Thomas Aquinas - Italian scholastic philosopher Francis Bacon - English philosopher and author John Calvin - French theologian and reformer Nicholaus Copernicus - Polish scientist who is regarded as the founder of modern astronomy in establishing a theory that earth rotates on its axis and that the planets revolve around the sun Winston Churchill - British statesman and author Oliver Cromwell - Lord Protector of England Madame Curie - physical chemist who discovered radium with her husband, Pierre Albert Einstein - theoretical physicist known for the theory of relativity and many other physics theories, who immigrated to US from Germany and became a naturalized citizen Queen Elizabeth II - current Queen of Great Britain and Northern Ireland Mikhail Gorbachev - Russian President Adolf Hitler - German chancellor and Fuhrer who instituted violent anti-Semitic policy Queen Isabella I - joint sovereign with her husband Ferdinand in Spain, gave money to Columbus Lenin - Russian Communist leader John Locke - English philosopher Martin Luther - German religious reformer Niccolo Machiavelli - Italian statesman and political philosopher Thomas Malthus - English economist Karl Marx - German political philosopher who developed the theory of socialism Isaac Newton - English natural philosopher and mathematician Louis Pasteur - French chemist Peter the Great - Russian ruler who ruled with brother Ivan & founded Saint Petersburg John Jacques Rousseau - French author and philosopher Adam Smith - Scottish economist Joseph Stalin - Russian political leader, Socialist Voltaire - French author known for satire Sociology Comte - French philosopher and mathematician, founder of positivism Charles Darwin - British naturalist and physician, known for theory of evolution Durkheim - French sociologist Sigmund Freud - Austrian neurologist, founder of psychoanalysis Karl Marx - German political philosopher who developed the theory of socialism Spencer - English philosopher advocating individualism Max Weber - sociologist known for views on social organization and bureaucracy Contemporary World Issues famous people in the news Mathematics Archimedes - Greek mathematician and inventor, known for work in mechanics and hydrostatics Rene Descartes - French mathematician, scientist and philosopher who developed the Cartesian system Euclid - Greek geometer (also a Greek philosopher by the same name who was a follower of Socrates) Leonard Euler - Swiss mathematician and physicist known as one of the founders of pure mathematics Science Nicholaus Copernicus - Polish scientist who is regarded as the founder of modern astronomy in establishing a theory that earth rotates on its axis and that the planets revolve around the sun Madame Curie - physical chemist who discovered radium with her husband, Pierre John Dalton - English chemist and physicist, known for table of atomic weights Charles Darwin - British naturalist and physician, know for theory of evolution Thomas Edison - inventor with over a thousand patents including the incandescent light bulb, the mimeograph, the phonograph and the microphone Albert Einstein - theoretical physicist know for the theory of relativity and many other physics theories, who immigrated to US from Germany and became a naturalized citizen Enrico Fermi - Italian physicist known for work in quantum theory and atomic structure and behavior Michael Faraday - English chemist and physicist known for his study of electricity Alexander Fleming - British bacteriologist who discovered penicillin Galileo Galilei - Italian astronomer and physicist who first conceived the laws of motion later formulated by Newton William Harvey - English physician and anatomist, discoverer of the circulation of blood Werner Heisenberg - German Byzantine scholar and physicist Johannes Kepler - German astronomer who discovered three laws of planetary motion Anthony van Leeuwenhoek - Dutch naturalist who studied microorganisms Joseph Lister - English optician, connected with the microscope George Mendel - Austrian botanist known for breeding experiments William T.G. Morton - American dentist who experimented with ether Isaac Newton - English natural philosopher and mathematician who conceived the idea of universal gravitation Nikolaus August Otto - German technician who conceived the early internal combustion engine Louis Pasteur - French chemist Gregory Pincus (Health) - known for birth control pill Ernest Rutherford - British physicist who studied radioactivity James Watt - Scottish engineer and inventor, known for the steam engine Leonardo da Vinci - Italian painter, sculptor, architect, engineer and scientist English/Language Arts Francis Bacon - English philosopher and author Homer - traditional ancient Greek poet to whom the Iliad and the Odyssey are attributed Jean Jacques Rousseau - French author and philosopher Voltaire - French author known for satire Edward de Vere (Shakespeare) - English dramatist and poet The Arts Johann Sebastian Bach - German musician and composer Ludwig van Beethoven - German composer Louis Daguerre - French painter, inventor of the daguerreotype (early photography) Michelangelo - Italian sculptor, painter, architect and poet of the high Renaissance Mozart - Austrian composer of the Viennese or classical school William Conrad Rontgen - German cabinet maker known for development of ornamental furniture in Germany and France Social Studies Topic Outline Appendix 1. 2. 3. 4. Vital Themes Glossary Some Famous People Historical Chart/Timeline