Click
advertisement
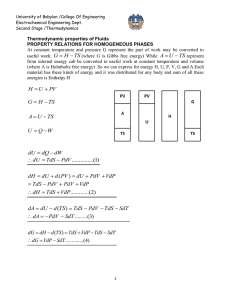
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 5.60 Thermodynamics & Kinetics Spring 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 5.60 Spring 2008 Lecture #13 page 1 The Gibbs Free Energy • With the free energies Helmholtz free energy Gibbs free energy A = U - TS G = H - TS we’ve introduced all our state functions. For closed systems, U (S ,V From and ) ⇒ dU =TdS − pdV H (S , p ) ⇒ dH =TdS +Vdp A (T ,V ) ⇒ dA = −SdT − pdV G (T , p ) ⇒ dG = −SdT +Vdp Fundamental equations ∂A ⎞ ⎛ ∂A ⎞ dV ⎟ dT + ⎜ ⎟ ⎝ ∂T ⎠V ⎝ ∂V ⎠T ⎛ ∂G ⎞ ⎛ ∂G ⎞ dG = ⎜ ⎟ dp ⎟ dT + ⎜ ⎝ ∂T ⎠ p ⎝ ∂p ⎠T dA = ⎛⎜ ⎛ ∂A ⎞ = −S ⎜ ⎟ ⎝ ∂T ⎠V ⎛ ∂A ⎞ = − p ⎜ ⎟ ⎝ ∂V ⎠T ⎛ ∂G ⎞ ⎜ ⎟ = −S ⎝ ∂T ⎠ p ⎛ ∂G ⎞ ⎜ ⎟ =V ⎝ ∂p ⎠T The Maxwell relations: ∂ 2A ∂2A = ∂V ∂T ∂T ∂V and ∂ 2G ∂2G = ∂p ∂T ∂T ∂p now allow us to find how S depends on V and p. ⇒ ⎛ ∂S ⎞ = ⎛ ∂p ⎞ ⎜ ⎟ ⎜ ⎟ ⎝ ∂V ⎠T ⎝ ∂T ⎠V ⎛ ∂S ⎞ ⎛ ∂V ⎞ ⎜ ⎟ = −⎜ ⎟ ⎝ ∂T ⎠ p ⎝ ∂p ⎠T These can be obtained from an equation of state. 5.60 Spring 2008 Lecture #13 page 2 We can now also relate T and H to p-V-T data. ⎛ ∂p ⎞ ⎜ ⎟ −p ⎝ ∂T ⎠V ⎛ ∂U ⎞ ⎜ ⎟ =T ⎝ ∂V ⎠T ⎛ ∂S ⎞ ⎜ ⎟ − p =T ⎝ ∂V ⎠T ⎛ ∂H ⎞ ⎜ ⎟ =T ∂ p ⎝ ⎠T ⎛ ∂S ⎞ ⎛ ∂V ⎞ ⎜ ⎟ +V = V −T ⎜ ⎟ ⎝ ∂T ⎠ p ⎝ ∂p ⎠T • For an ideal gas → U and H from equations of state! pV = nRT nR p ⎛ ∂p ⎞ = ⎜ ⎟ = T ⎝ ∂T ⎠V V ⇒ ⎛ ∂U ⎞ ⎜ ⎟ =0 ⎝ ∂V ⎠T nR V ⎛ ∂V ⎞ = ⎜ ⎟ = p T ⎝ ∂T ⎠ p ⇒ ⎛ ∂H ⎞ ⎜ ⎟ =0 ⎝ ∂p ⎠T This proves that for an ideal gas U(T) and H(T), functions of T only. We had assumed this was true from Joule and Joule-Thomson expansion experiments. Now we know it is rigorously true. • For a van der Waals gas ⎛ p + a ⎞ V − b = RT ⎜ ⎟ V 2⎠ ⎝ ( p= RT a ⎛ ∂U ⎞ −p = 2 ≠0 ⎜ ⎟ = V ⎝ ∂V ⎠T V − b ) RT a − 2 V −b V ⇒ U( T, V ) 5.60 Spring 2008 • Lecture #13 The special role of G(T,p): ⎛ ∂G ⎞ ⎟ , ⎝ ∂T ⎠ p V =⎜ ⎛ ∂G ⎞ ⎟ ⎝ ∂T ⎠ p H = G +TS ⇒ H = G −T ⎜ U = H − pV ⇒ U = G −T ⎜ A =U −TS ⇒ A =G − p⎜ ∂S ⎞ ⎟ ⎝ ∂T ⎠ p If you know G(T,p), you know everything! ⎛ ∂G ⎞ ⎟ ⎝ ∂p ⎠T S = −⎜ C p =T ⎛⎜ page 3 ⇒ ⎛ ∂G ⎞ ⎛ ∂G ⎞ ⎟ ⎟ − p⎜ ⎝ ∂T ⎠ p ⎝ ∂p ⎠T ⎛ ∂G ⎞ ⎟ ⎝ ∂p ⎠T ⎛ ∂2G ⎞ 2 ⎟ ⎝ ∂T ⎠ p C p = −T ⎜ Can get all the thermodynamic functions from G(T,p)! • G ( T, p ) for liquids, solids, and gases (ideal) From V =⎜ ⎛ ∂G ⎞ ⎟ ⎝ ∂p ⎠T p2 ⇒ G (T , p2 ) = G (T , p1 ) + ∫ Vdp • Liquids and solids p1 ⇒ V is small G (T , p2 ) = G (T , p1 ) +V ( p2 − p1 ) ≈ G (T , p1 ) ⇒ G (T ) 5.60 Spring 2008 • Lecture #13 page 4 Ideal gases G (T , p2 ) = G (T , p1 ) + ∫ p2 p1 p RT dp = G (T , p1 ) + RT ln 2 p p1 Take p1 = p o = 1 bar G (T , p ) = G o (T ) + RT ln From p p0 ⎛ ∂G ⎞ S = −⎜ ⎟ ⎝ ∂T ⎠ p or G (T , p ) = G o (T ) + RT ln p (p in bar) ⇒ S (T , p ) = S o (T ) − R ln p