CHEM 213 Exp 2 Directing Bromination S08
advertisement

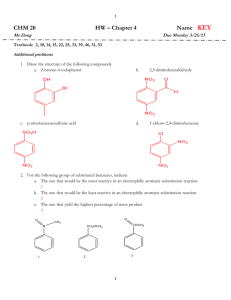
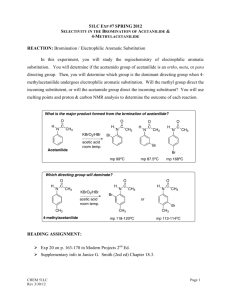
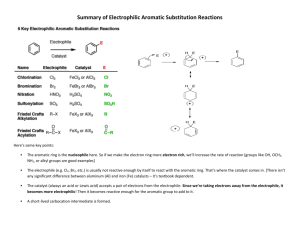
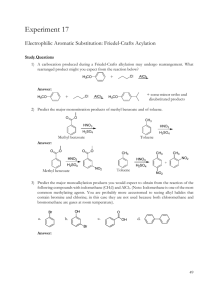
Experiment 2 CHEM 213 Directing Effects in Electrophilic Aromatic Bromination Bromination of acetanilides: R O KBrO 3, HBr N H R O N H Br R = H; acetanilide R = CH 3 ; 4-methylacetanilide R = OEt; 4-ethoxyacetanilide Introduction The presence of a group on an aromatic ring has a profound effect on any subsequent electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions. Depending on this groups electron withdrawing or donating effects, the addition of an electrophile will either occur ortho-para or meta. Furthermore, if more than one group is present on the ring, the directing effects will either combine or compete for the observed directing effect. In this experiment you will perform two bromination reactions, each an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. In each case you will develop an initial hypothesis, based on the directing effects of the groups already on the ring, as to which position on the aromatic ring the bromine will add. After purification of each respective product, melting points and IR spectra will be obtained to elucidate the structure of the product. Electrophilic aromatic substitution with elemental bromine is often inconvenient and hazardous. You will generate bromine within the reaction mixture (called in situ) by the following reaction: 6H+ + 5Br- + BrO3 → 3Br2 + 3H2O In the first week of the experiment you will brominate acetanilide, 4-methylacetanilide and 4-ethoxyacetanilide and recrystallize each product. During the second week you will determine melting points and obtain IR spectra to compare to known standards. Objectives: 1. Synthesize the brominated acetanilide derivatives. 2. Develop a hypothesis as to which product should form in each case, based on your knowledge. 3. Identify the particular regioisomer formed in each case by comparison of melting point, IR and 1H NMR Procedure: Melting point data: Will be obtained from your instructor upon inspection of your three products General Bromination Procedure: You will need to calculate weights of each starting material based on the molar values given. CAUTION: HBr and Br2 (even when generated in small amounts) are severe lachrymators. Goggles must be worn! Brominated aromatics are also lachrymators, gloves are recommended. • • • • • • Report Topics : • Discuss the chemistry of electrophilic aromatic substitution as it pertains to the substrates from this experiment. Which directing groups are present? Classify them. Based on your knowledge, which regioisomer is expected in each case? Using the mechanism to illustrate your answer would be helpful. • Which regioisomer is obtained in each case? this match your original hypothesis? • Address yield—what are the points where most product is lost? • Discuss the IR—does it support the general structure of the products? • Discuss 1H NMR—does it support the general structure of each product? Which isomer did you synthesize? Place 5 mmol (calculate!) of acetanilide (or 4-methyl or 4ethoxyacetanilide) and glacial acetic acid (8 mL) into a 25 mL round bottomed flask. Do not use aqueous acetic acid! Add 1.7 mmol of potassium bromate (KBrO3). Stir the mixture rapidly with a magnetic stirrer. Add 1 mL of 48% HBr to the stirring mixture dropwise and observe. Stir the mixture 30 minutes after addition is complete. Pour the reaction mixture into 50 mL of ice-cold water and add about 20 drops of dilute sodium bisulfite solution (this should remove any red/orange color due to excess Br2). Stir for 5 minutes. Collect the solid that forms by vacuum filtration. Wash the solid with a few mL of water. The product can be recrystallized from a small amount of 95% ethanol. IF the product does not recrystallize from solution, the addition of a few drops of water can induce crystal formation. References: Mc Gowans, S.I.; Siversmith, E.F. J. Chem. Ed. 1998, 75, 1293 Schatz, P. F. J. Chem. Ed. 1996, 73, 267. • Allow the crystals to dry in your drawer until the next laboratory session. Obtain a melting point and IR spectrum (Nujol®). Clean up: • Aqueous filtrate can go down the sink with plenty of water. • Dispose of product in halogenated waste after first dissolving it in a small amount of acetone. • Make sure all salt plates are clean and put away in the tin provided. • Return all items to the designated locations. Does