blood
advertisement

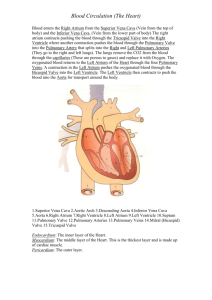
Cardiovascular System By Meghan Hillis, Gretchen Stolte, Kathleen Burks Period 5 FUNctions Heart: Pumps and delivers blood through the body Blood: ● ● ● Delivers nutrients and oxygen to the body Carries waste and hormones Maintains homeostasis http://www.cea1.com/anatomy-sistems/human-heart-diagram/ FUNctions Vessels: ● Arteries and Arterioles - Carries oxygenated blood away from the heart and distributes it throughout the body http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/3/35/Artery.svg/275px-Artery.svg.png FUNctions Vessels: ● Veins and VenulesCarries deoxygenated blood back to the heart. It also carries waste away from the cells. http://m.everythingscience.co.za/lifesciences/grade-10/07-transport-systems-inanimals/images/89578f5caf2769cfce331380b14ad96f.jpg Major Parts of the System https://www.smm.org/heart/ lessons/gifs/heartDiagram.gif Atria and Ventricles Atria: ● Upper Chambers of Heart ● Thin Walls ● Receive blood returning to the heart ● Have auricles - ear like projections extending anteriorly from the atria Ventricles: ● Lower Chambers of the Heart ● Receive blood from atria ● Contract to push blood out of the heart into the arteries *Right side has thinner walls Septum ● Solid and wall-like ● Separates the left atria and ventricle from the right ● Because of septum, deoxygenated blood and oxygen rich blood will never mix http://dellchildrens.kramesonline.com/HealthSheets/104527.img Atrioventricular Valve (A-V Valve) ● Tricuspid Valve: -has 3 cusps - lies between right atrium and right ventricle - Prevents backflow into atrium -Has Chordae Tendineaeoriginate from papillary muscles and prevents valve from swinging into atrium ● Mitral Valve: - lies between the left atrium and left ventricle - Shaped like a miter - Also called Bicuspid Valve - Prevents backflow into atrium - Also contains Chordae Tendineae Semilunar Valves ● Pulmonary Valve: ● Aortic Valve: - lies between right ventricle and pulmonary trunk leading to lungs - At the base of the aorta, an artery leading to the rest of the body - Has 3 cusps - Has 3 cusps - Prevents backflow into ventricle - Pulmonary trunk divides into pulmonary veins which lead to lungs - Allows blood into aorta and not back into the left ventricle *Both named for their half-moon shapes of their cusps Coverings of the Heart https://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072539623/information_center_view0/feature_summary.html Wall of the Heart ● Myocardium: - Cardiac Muscle Tissue that pumps blood out of the heart chamber - Muscle fibers are separated into planes, separated by connective tissue - Connective tissue is supplied with amply blood and lymph capillaries, and nerve fibers ● Endocardium: - Epithelium and Connective tissue that has many elastic and collagenous fibers - Contains blood vessels and Purkinje Fibers - Continuous with the inner linings of blood vessels attached to the heart Wall of the Heart http://faculty.stcc.edu/AandP/ AP/imagesAP2/heart/heartwall.gif http://www.tooloop.com/picture-of-diagram-of-the-human-body-withveins-and-arteries/ Arteries ● Carries oxygenated blood to body cells ● Has thick walls ● A smaller branch of the artery is an arteriole which leads to a capillary http://www.stiffarteries.com/resources/artery-vein-diagram_edited.JPG? timestamp=1319089146432 Coronary Arteries ● First two branches of the aorta ● Supplies blood to the tissues of the heart ● Openings lie just beyond the aortic valve ● Myocardial cells needs oxygenated blood to keep the heart pumping ● Coronary Arteries supply blood to the capillaries of the Myocardium http://www.edoctoronline.com/media/19/photos_245A975B-66AD-4F7E-86D8-82D3CA7D0120. jpg Capillaries https://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072539623/information_center_view0/feature_summary.html Venules ● Are the microscopic vessels that continue from capillaries and form veins http://customers.hbci.com/~wenonah/riddick/ridd176.jpg Veins ● Carries deoxygenated blood back to the heart ● Has thin walls ● Valves prevent backflow of blood http://annablogia.files.wordpress.com/2013/02/vein-diagram.jpg Cardiac Veins and Coronary Sinus ● Branches of the veins parallel the coronary arteries ● Drains the blood that has passed from the myocardial capillaries ● Veins join an enlarged vein on the heart’s posterior surface, the Coronary Sinus ● Coronary Sinus empties into the right atrium http://o.quizlet.com/U4T4-PYz0XZuJF5uKXCWCw_m.png https://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072539623/information_center_view0/feature_summary.html Pathway of Blood in the Heart 1. Superior/Inferior Vena Cava 9. Left Atrium 2. Right Atrium 10. Bicuspid/Mitral Valve 3. Tricuspid Valve 11. Left Ventricle 12. Aortic Valve 4. Right Ventricle 5. Pulmonary Valve 6. Pulmonary Arteries 15. Goes to Veins 7. Lungs 16. Back to Vena Cava 8. Pulmonary Veins 13. Aorta 14. Distributed through Arteries Pulmonary vs Systemic Circulations http://fce-studymode.netdna-ssl.com/images/upload-flashcards/883783/524576_m.jpg Heart Sounds ● ● ● ● ● Sounds come from the closing of the valves of the heart First Sound = Lubb The Lubb sounds during ventricular contraction when the A-V Valves close Second Sound = Dupp The Dupp sounds during ventricular relaxation when the Semilunar Valves close http://heart-symptoms.org/wp-content/uploads/2011/08/Normalheart-sounds.jpg Components of Blood Fun Facts: - Slightly heavier than water - 3 or 4 times more viscous than water Components: -Red Blood Cells -White Blood Cells -Blood Platelets -Blood Plasma -Gases and Nutrients http://www.fi.edu/learn/heart/blood/images/red-blood-cells.jpg Components of Blood http://images.wisegeek.com/diagram-of-blood-composition.jpg Red Blood Cells ● Also called erythrocytes ● Biconcave discs - this shape allows the cell membrane to be closer to the oxygen-carrying Hemoglobin ● Transports Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide http://www.biosbcc.net/doohan/sample/images/blood% 20cells/RBC.jpg White Blood Cells ● Also called Leukocytes ● Protect against disease - destroys pathogenic microorganisms and parasites ● Removes worn cells ● 5 types: Granulocytes, Agranulocytes, Neutrophils, Eosinophils, Basophils http://image.wistatutor.com/content/feed/u1330/leukocytes%20.gif Blood Platelets ● Also known as thrombocytes ● Helps control blood loss from broken vessels by closing breaks in damaged blood cells and initiating the formation of blood clots ● Arise from large cells in red bone marrow called megakaryocytes http://upload.wikimedia. org/wikipedia/commons/2/24/Red_White_Blood_cells.jpg Blood Plasma ● Clear straw Colored liquid protein of the blood in which the cells and platelets are suspended ● 92% water ● Functions: Transporting nutrients, gases and vitamins; Helps regulate fluid and electrolytes; Maintaining a favorable pH Gases and Nutrients Gases: ● ● Most important gases are Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide Blood also contains dissolved Nitrogen Nutrients: ● ● Include amino acids, simple sugars, nucleotides, and lipids Plasma Lipids include fats, phospholipids, and cholesterol Lipoproteins ● ● Plasma lipids combine with proteins to make lipoprotein complexes 4 types of Lipoproteins: -Chylomicron: transports dietary fats to muscle and adipose cells -Very low-density Lipoproteins (VLDL): transports triglycerides from the liver to adipose cells -Low-density Lipoproteins (LDL): Delivers cholesterol to various cells including liver cells -High-density Lipoproteins (HDL): Transports to the liver remnants of Chylomicrons that has given up their triglycerides http://people.csail.mit.edu/seneff/IDL_LDL_HDL.gif Blood Types ABO Blood Group: ● ● ● Antigens: Red blood cell surface molecules (also called agglutinogens) and react with protein antibodies (agglutinins) Antibody: a protein that B cells of the immune system produce in response to the presence of a nonself antigen Blood is grouped according to the presence or absence of antigens A and B https://highered.mcgraw-hill. com/sites/0072539623/information_center_view0/feature_summary.html Blood Transfusions ● The major concern in blood transfusion procedures is that the cells in the donated blood do not clump due to antibodies in the recipients plasma ● An antibody of one type will react with an antigen of the same type and clump red blood cells therefore such combinations must be avoided https://highered.mcgraw-hill. com/sites/0072539623/information_center_view0/feature_summary.html The Rh Factor ● ● ● ● ● The Rh Factor are antigens, the most important of these is antigen D If any of the Rh antigens are present on red blood cell membranes = Rh Positive If there are not any Rh antigens = Rh Negative Rh antibodies only appear due to a special stimulation Rh is what determines the negative or positive aspect of blood : AB- or AB+ http://waynesword. palomar. edu/images/blood1.gif http://waynesword.palomar.edu/images/blood1. gif The Rh Factor https://highered.mcgraw-hill. com/sites/0072539623/information_center_view0/feature_summary.html Diseases Heart Diseases: ● ● ● Atherosclerosis: arterial disease; deposits of fatty materials (cholesterol) form within and on the walls of the heart Pericarditis: inflammation of the pericardium because of a bacterial infection MVP (Mitral Valve Prolapse): cusps of mitral valve stretch and bulge in left atrium during ventricular contraction http://www.omnimedicalsearch.com/conditionsdiseases/images/atherosclerosis-plaque1.jpg Diseases Blood Diseases: ● Sickle Cell Disease: a single DNA base change causes an incorrect amino acid to be incorporated into globin, causing hemoglobin to crystallize in a low oxygen environment and blends red blood cells with hemoglobin in a sickle shape which blocks circulation in a small blood vessels http://www.sicklecellanaemia.org/wpcontent/uploads/2011/03/adenosine.gif Diseases Blood Diseases: ● Leukemia: cancer of the white blood cells; too few red blood cells and platelets and too many white blood cells ● Hemophilia: clotting disorder causing uncontrollable bleeding http://www.sciencekids.co.nz/images/pictures/health/leukemiasymptoms.jpg