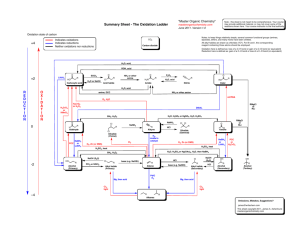
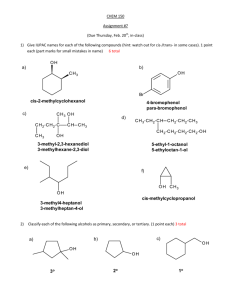
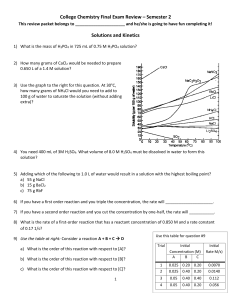
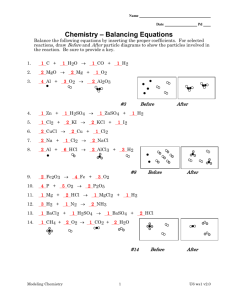
E:\My Documents\sch4u\chapter 1 test answers.wpd
advertisement

SCH4U Chapter 1 Test Part A Answer each question without the use of the flow chart on the back of the test sheet. Do not give detailed reactions for part A, only the steps needed. 1 3 1) a) How does the reactivity of benzene with halogens compare to that of cyclohexene and cyclohexane with halogens? Benzene and cyclohexane react slowly with halogens while cyclohexene reacts rapidly. b) Explain the three reactivities in terms of orbitals. Cyclohexene has localized pi bonding orbitals, the other two do not. 1 2) Arrange the following in order of increasing solubility in water. a) 1-chloropropene, b) 1-propanol (most), c) propane (least) 1 3) Arrange the following in order of increasing solubility in water. a) 2-methyl-2-butanol (most), b) 3-pentanol, c) 1-pentanol (least) 1 4) What is the major product of the reaction between HBr and 1-propene? a) 2-bromopropane* b) 2-bromopropene c) 1-bromopropane d) 1-bromopropene 1 5) Which of the following is a tertiary alcohol? a) 3-pentanol b) 1-butanol 9 3 c) 2-methyl-2-propanol* 6) Complete the following reactions, if they will occur. Give the most likely product(s) in each case. a) CH3-CH=CH2 + HBr —> CH3-CBrH-CH3 b) C3H8 + Cl2 —> CH3-CClH-CH3 + HCl c) BrCH2-CH2-CH3 + NaOH —> CH2=CH-CH3 + NaCl + H2O d) CH3-CH=CH2 + H2O —> CH3-C(OH)H-CH3 f) CH3CCH + Br2 —> CH3-CBr=CBrH g) CH3CH2NH2 + CH3COOH —> CH3CH2NH2COCH3 (ethyl ethanamide) h) 3-methyl-3-pentanol + MnO4 —> NR (tertiary alcohol) i) CH3CH(OH)CH3 + MnO4 —> CH3COCH3 (propanone) j) CH3CH2OH + CH3CH2OH —> CH3CH2OCH2CH3 (diethyl ether) d) 2-propanol (room temperature) (UV light) (room temperature) (with dilute H2SO4) (room temperature) (conc. H2SO4) (room temperature) (room temperature) (with conc. H2SO4) 7) Match the reactions in column A with the correct label from column B. _C_ _A_ _B_ Column A CH3CH2OH —> CH2CH2 + H2O C2H6 + Br2 —> C2H5Br + HBr C2H4 + HBr —> H3CCH2Br Column B a) Substitution b) Addition c) Elimination 1 8) Into what type of organic molecule could controlled oxidation transform a primary alcohol? An aldehyde 2 9) Outline the two steps needed to change an alkene to an amine. Alkene + hydrogen halide —> alkyl halide Alkyl halide + ammonia —> amine + hydrogen halide 3 10) a) What two types of compounds are needed to make an ester? An alcohol and a carboxylic acid. b) What catalyzing agent is needed? Conc. H2SO4 1 11) Are propanal and propanone isomers of each other? Yes 1 12) Arrange the following in order from lowest to highest boiling point: a) propanol b) propanal (lowest) c) propanoic acid (highest) Part B You may use the flow chart on the back side of the test sheet to answer the questions in this part. 3 1) a) What chloroalkene could be transformed into 2-oxopentanoic acid? b) Outline the steps needed for this transformation. i) 1-chloro-1-pentene reacts with water to make 1,2-dihydroxypentane (adds H2O to the double bond puts OH on carbon #2) (and substitutes OH for the Cl on carbon #1) ii) 1,2-dihydroxypentane (1,2-pentanediol) reacts with oxidizing agent to make 2-oxopentanal iii) 2-oxopentanal reacts with oxidizing agent to make 2-oxopentanoic acid (ii and iii can be combined into one step) 4 2) What two compounds would be produced by the hydrolysis of: a) N-ethylbutyl butanamide b) ethyl propanoate a) N-ethyl-1-aminobutane and butanoic acid. (more complex amine than on an exam) b) ethanol and propanoic acid. 5 3) Write the reactions needed to form ethyl propanoate from an alkene and an alkyl halide. A) 1-chloropropane + H2O —> 1-propanol + HCl 1-propanol + O* —> propanal propanal + O* —> propanoic acid B) ethene + H2O —> ethanol C) ethanol + propanoic acid + conc. H2SO4 —> ethyl propanoate + conc. H2SO4 + H2O