X X
advertisement

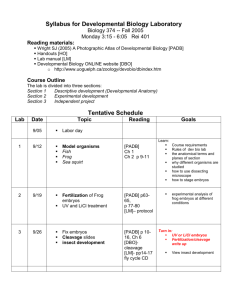
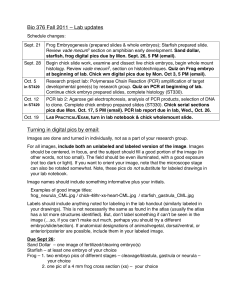
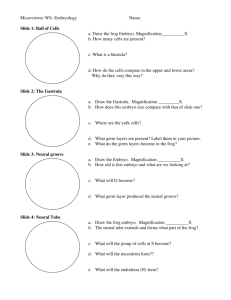
Template No. (12) Course Specification University/Academy: Suez Canal University Faculty/Institute: Science Department: Zoology 1-Course data Course Title: Embryology of Code: ZL 315 Vertebrates Credit/ Taught Hours: 3 2- Course aim Theoretical: 2 Academic year/ Level: 3rd level Zoology Student Department/program: Practical: 2 Zoology / Zoology 1.1. Acquire the theoretical background and experience in the field of embryology that will prepare them for future career. 1.2. Be familiar with applications and principles of experimental design, laboratory safety, data collection and interpretation in embryology. 3- Intended Learning Outcomes (ILOs): A1- Illustrate basic scientific facts, concepts, principles, and applications related to embryology. 3.A- Knowledge and understandings: 3.B- Intellectual Skills: 3.C- Professional Skills: 3.D- General Skills: 4- Course content: (theoretical and then practical) A3. Represent examples for types of interrelationships between different organisms and their embryonic development. A4. List theories and methods applied for interpreting and analyzing data related to embryology. A5. Illustrate developmental progress of the embryology -related knowledge. B2. Assess interrelationships between the major developmental stages and processes with an emphasis on vertebrate embryos B4. Interpret experimental data and relevant literature for enhancing the ability of students to deal with different developmental processes of major body systems of chordates. C1. Implement appropriate biological techniques in embryology following ethical and safety considerations. C3. Utilize different scientific approaches and recent technology for understanding the differences in embryonic events of different chordates. D1- Employ recent communication and information technologies, models and tools effectively in different tasks related to Embryology. D2- Lead team work effectively for appreciating the values of independent thinking, continuous learning and ethics in the field of Embryology. Theoretical part content Topic No. of No. of Lecture hours week(s) (s) 1- General introduction to the science of embryology. . 2- Common scientific terms used for studying direction, orientation and development of 2 week (1) 1 embryos. 3- Origin of primordial germ cells and gametogenesis. 2 week (2) 1 A- Spermatogenesis - Sperm types, structure and viability. B- Oogenosis - Egg types, structure and viability. Fertilization - Types and mechanisms of fertilization Parthenogenesis - Natural and artificial parthenogenesis. Cleavage and blastulation - Mechanics, planes, patterns, and results of cleavage - Peculiarities of cell division involved in cleavage. Gastrulation - General processes involved in gastrulation (morphogenetic movements) - Significance of gastrulation. - Fate of germinal layers (ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm). Development of Amphioxus 1- Gonads and gametes 2- Cleavage, blastulation, and gastrulation. 3- Differentiation of the primary germ layers. 4- Formation of the neural tube, notochord, mesoderm, mesodermal somites and coelom.. Quiz 5-Development of the anterior gut diverticula and gut. 6- Development of the club-shaped gland, endostyle, the mouth, the first gill slit, the anus, and the liver diverticulum. 7- Hatching, larval development, formation of the atrium and metamorphosis. 8- A comparison between the embryonic and the larval periods of amphioxus. Quiz (Computer Lab.). Development of frog 1- Maturation division of frog ovum and fertilization. 2- Cleavage and blastulation of frog embryo. 3- Fate maps of frog blastula. 4- Gastrulation, neurulation and early organogenesis. 5-Formation of the neural tube and the central nervous system. 6- Formation of the notochord. 7- Development of mesoderm and its derivatives. 8- Development of the eye. 9- Formation of the primitive tubular heart. 10- 2.5 mm frog embryo (tail bud stage 17, Rugh, 1948). 11- 4 mm frog embryo, stage 19 (Rugh, 1948). 12- 10 mm frog embryo, stage 23 (Rugh, 1948). Development of the Chick 1- Egg Membranes, fertilization and cleavage, blastulation, gastrulation and cellular movement during gastrulation 2 week (3) 1 2 week (4) 1 2 week (5) 1 2 week (6) 1 2 week (7) 2 week (8) 2 week (9) 2 week (10) 1 2 week (11) 1 2 week (12) 1 1 2- Formation and function of the primitive streak 3- Regression of the Primitive Streak and Formation of the Organ Rudiments. 4- Formation of the neural tube, foregut, mesodermal somites 5- Development of the Heart 6- 24-hour embryo - Divisions of the brain and their neuromeric structure - Formation of extra-embryonic blood vessels - Formation of intra-embryonic blood vessels. 7- Structure of chick embryo between thirty-three and thirty–eight hours of incubation 8- Structure of chick embryo between thirty– eight and fifty hours of 9- 72 hours chick embryo. 2 10- 96 hours chick embryo. Development of Mammals - Extraembryonic Membranes. - The placenta. Practical Exam 2 Practical part content No. of No. of Topic hours week(s) 1- Slides of 11- day old chick embryo to show the primordial germ cells and their migration to the primordia of gametes. 2 week (1) 2- Dissection of male and females gonads of mature rat or mice 3- T.s in the ovary and testis of toad, mice and cats. A- Spermatogenesis Ts. of the trunk regions of amphioxus, petromyzon and dog fish to show gonads structure. Dissection of male rat testis to 2 week (2) show the sperm types, structure and viability. B- Oogenosis - Egg types, structure of Chicken egg. Development of Amphioxus - Cleavage, blastulation, and gastrulation. -Differentiation of the primary germ layers. 2 week(3) - Formation of the neural tube, notochord, mesoderm, mesodermal somites and coelom. - Development of the anterior gut diverticula and gut. - Development of the club2 week (4) shaped gland, endostyle, the mouth, the first gill slit, the week (13) 1 week (14) Practical (s) Tutorial 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 anus, and the liver diverticulum. Larval development, formation of the atrium and metamorphosis 14 somite stage. - The larval periods of Amphioxus 16 somite stage. Development of frog 1- Cleavage and blastulation of frog embryo. 2- Fate maps of frog blastula. 3- Gastrulation, neurulation and early organogenesis. 5-Formation of the neural tube and the central nervous system. 6-Formation of the notochord. 7-Development of mesoderm and its derivatives. 8- Development of the eye. 9- 2.5 mm frog embryo (tail bud stage 17, Rugh,1948). 10- 4 mm frog embryo, stage 19(Rugh, 1948). 11- 10 mm frog embryo, stage 23 (Rugh, 1948). Development of the Chick - Egg structure and cleavage, blastulation, gastrulation - Formation of the primitive streak 2 week (5) 1 1 2 week (6) 1 1 2 week (7) 1 1 2 week (8) 1 1 2 week (9) 1 1 2 week (10) 1 1 2 week (11) 1 1 2 week (12) 1 1 2 2 week (13) week (14) 1 1 1 1 18 hr chick embryo 24 hrs chick embryo Early embryonic development of Chick 28 hrs chick embryo 33 hrs chick embryo 48 hrs chick embryo - Structure of chick embryo between fifty hours and fifty six hours of incubation. - 72 hours chick embryo. - 96 hours chick embryo. Development of Mammals -Extraembryonic Membranes of mice or rat. - The placenta of mice or rat. *Revision Term Exam 1- Board 2-Photographs 5- Teaching and 3- Data show 4-Vidio movies learning methods: 5- CD & Internet 7- Students assessment: 7.A- Assessment Methods: 7.B- Assessment schedule 7.1- Oral examination to assess Knowledge and understandings 7.2- Practical examination to assess Professional Skills 7.3- Midterm examination to assess the overall skills 7.4- Final examination to assess the overall skills Assessment 1 Mid-term examination Week 7 Assessment 2 Oral examination according to faculty's exam schedule Assessment 3 Practical examination week 14 Assessment 4 Final-term examination Week according to faculty's exam schedule Mid-term examination % Final-term examination % Oral examination % Practical examination % 100% Total 10% 60% 10% 20% 7.C- Assessments Weights 8- List of Books and references 8.A- Notes: 8.B- Essential books: 8.CRecommended books: Handout 1. Peter, H. Raven; George B. Johnson; Jonathan B. Losos; Susan R. Singer (2005). "Biology" seventh edition. McGraw-Hill companies, New York USA. 2. Khanna, D.R. (2005). "Text book of embryology". Discovery Publishing House. New Delhi, India. 1. Peter, H. Raven; George B. Johnson; Jonathan B. Losos; Susan R. Singer (2005). "Biology" seventh edition. McGraw-Hill companies, New York USA. 2. Carlson, Bruce M. (1996). Foundations of Embryology, 6th Edition, McGraw Hill Publishing Company. New York USA. - 4. Balinsky, B.I. (1996): "An introduction to embryology" seventh edition. CBS Collegue Publishing. The Dryden press. Japan. 8.D- Scientific periodicals, websites ….etc http://www.eulc.edu.eg/eulc/libraries/index.aspx http://www.eul.edu.eg/eulc/libraries/index.aspx Course coordinator: Yomn Mobarak Head of Department Prof. Yomn Mohamed Shahat Mobarak Prof. Maha Soliman Suez Canal University: Faculty of Science: Course code: ZL315 Course title: Embryology of Vertebrates Matrix of intended knowledge and skills of the course 1- Intended Learning Outcomes (ILOs): A- Knowledge and understandings: A1- Illustrate basic scientific facts, concepts, principles, and applications related to embryology. A3. Represent examples for types of interrelationships between different organisms and their embryonic development. A4. List theories and methods applied for interpreting and analyzing data related to embryology. A5. Illustrate developmental progress of the embryology -related knowledge. B- Intellectual Skills: B2. Assess interrelationships between the major developmental stages and processes with an emphasis on vertebrate embryos B4. Interpret experimental data and relevant literature for enhancing the ability of students to deal with different developmental processes of major body systems of chordates. C- Professional Skills: C1. Implement appropriate biological techniques in embryology following ethical and safety considerations. C3. Utilize different scientific approaches and recent technology for understanding the differences in embryonic events of different chordates. D- General Skills: D1- Employ recent communication and information technologies, models and tools effectively in different tasks related to Embryology. D2- Lead team work effectively for appreciating the values of independent thinking, continuous learning and ethics in the field of Embryology. Suez Canal University: Faculty of Science: Course content of the Theoretical part Course code: ZL315 Course title: Embryology of Vertebrates Week (s) No. A knowledge and Understanding Skills A1 1- General introduction to the science of embryology. . 2- Common scientific terms used for studying direction, orientation and development of embryos. 3- Origin of primordial germ cells and gametogenesis. A- Spermatogenesis - Sperm types, structure and viability. B- Oogenosis - Egg types, structure and viability. Fertilization - Types and mechanisms of fertilization Parthenogenesis - Natural and artificial parthenogenesis. Cleavage and blastulation - Mechanics, planes, patterns, and results of cleavage - Peculiarities of cell division involved in cleavage Gastrulation - General processes involved in gastrulation (morphogenetic movements) - Significance of gastrulation. Fate of germinal layers (ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm). A2 A3 A4 A5 Professional and Practical Skills Intellectual Skills B1 B2 B3 B4 B5 C1 C2 C3 General skills D1 D2 1,2 X X X X X X X X 3,4 X X X X X X X X 5,6 X X X X X X X X Development of Amphioxus 1- Gonads and gametes 2- Cleavage, blastulation, and gastrulation. 3- Differentiation of the primary germ layers.4Formation of the neural tube, notochord, mesoderm, mesodermal somites and coelom.. 5-Development of the anterior gut diverticula and gut. 6- Development of the club-shaped gland, endostyle, the mouth, the first gill slit, the anus, and the liver diverticulum. 7- Hatching, larval development, formation of the atrium and metamorphosis. 8- A comparison between the embryonic and the larval periods of amphioxus. Development of frog 1- Maturation division of frog ovum and fertilization. 2- Cleavage and blastulation of frog embryo. 3- Fate maps of frog blastula. 4- Gastrulation, neurulation and early organogenesis. 5-Formation of the neural tube and the central nervous system. 6- Formation of the notochord. 7- Development of mesoderm and its derivatives. 8- Development of the eye. 9- Formation of the primitive tubular heart. 10- 2.5 mm frog embryo (tail bud stage 17, Rugh, 1948). 11- 4 mm frog embryo, stage 19 (Rugh, 1948). 12- 10 mm frog embryo, stage 23 (Rugh, 1948). Development of the Chick Development of Mammals - Extraembryonic Membranes. - The placenta 8,9 X X X X X X X X 10,11 X X X X X X X X 12,13 X X X X X X X X Course content of the Practical part Week (s) No. A knowledge and Understanding Skills A1 - Slides of 11- day old chick embryo to show the primordial germ cells and their migration to the primordia of gametes. 2- Dissection of male and females gonads of mature rat or mice 3- T.s in the ovary and testis of toad, mice and cats. A- Spermatogenesis Ts. of the trunk regions of amphioxus, petromyzon and dog fish to show gonads structure. Dissection of male rat testis to show the sperm types, structure and viability. B- Oogenosis - Egg types, structure of Chicken egg. Development of Amphioxus - Cleavage, blastulation, and gastrulation. -Differentiation of the primary germ layers. - Formation of the neural tube, notochord, mesoderm, mesodermal somites and coelom. - Development of the anterior gut diverticula and gut. - Development of the club-shaped gland, endostyle, the mouth, the first gill slit, the anus, and the liver diverticulum. - larval development, formation of the atrium and metamorphosis 14 somite stage. - the larval periods of Amphioxus 16 somite stage. Development of frog 1- Cleavage and blastulation of frog embryo. 2- Fate maps of frog blastula. 3- Gastrulation, neurulation and early organogenesis. A2 A3 A4 Professional and Practical Skills Intellectual Skills A5 B1 B2 B3 B4 B5 C1 C2 C3 1 X X 2 X X 3 X X 4 X X 5,6 X X General skills D1 D2 4-Formation of the neural tube and the central nervous system. 5-Formation of the notochord. 6-Development of mesoderm and its derivatives. 7- Development of the eye. 9- Formation of the primitive tubular heart. 10- 2.5 mm frog embryo (tail bud stage 17, Rugh,1948). 11- 4 mm frog embryo, stage 19(Rugh, 1948). 12- 10 mm frog embryo, stage 23 (Rugh, 1948). 7 X X 8 X X 9,10 X X 11 X X 12 X X Development of Chick Egg structure and cleavage, blastulation, gastrulation Formation of primitive streak 18 hr chick embryo 24 hrs chick embryo Early embryonic development of Chick 28 hrs chick embryo 33 hrs chick embryo 48 hrs chick embryo Early embryonic development of Chick 50 hrs chick embryo 56 hrs chick embryo 72 hrs chick embryo 96 hrs chick embryo. Development of Mammals -Extraembryonic Membranes of mice or rat. - The placenta of mice or rat. Course coordinator: Yomn Mobarak Head of Department Prof. Yomn Mohamed Shahat Mobarak Prof. Maha Soliman